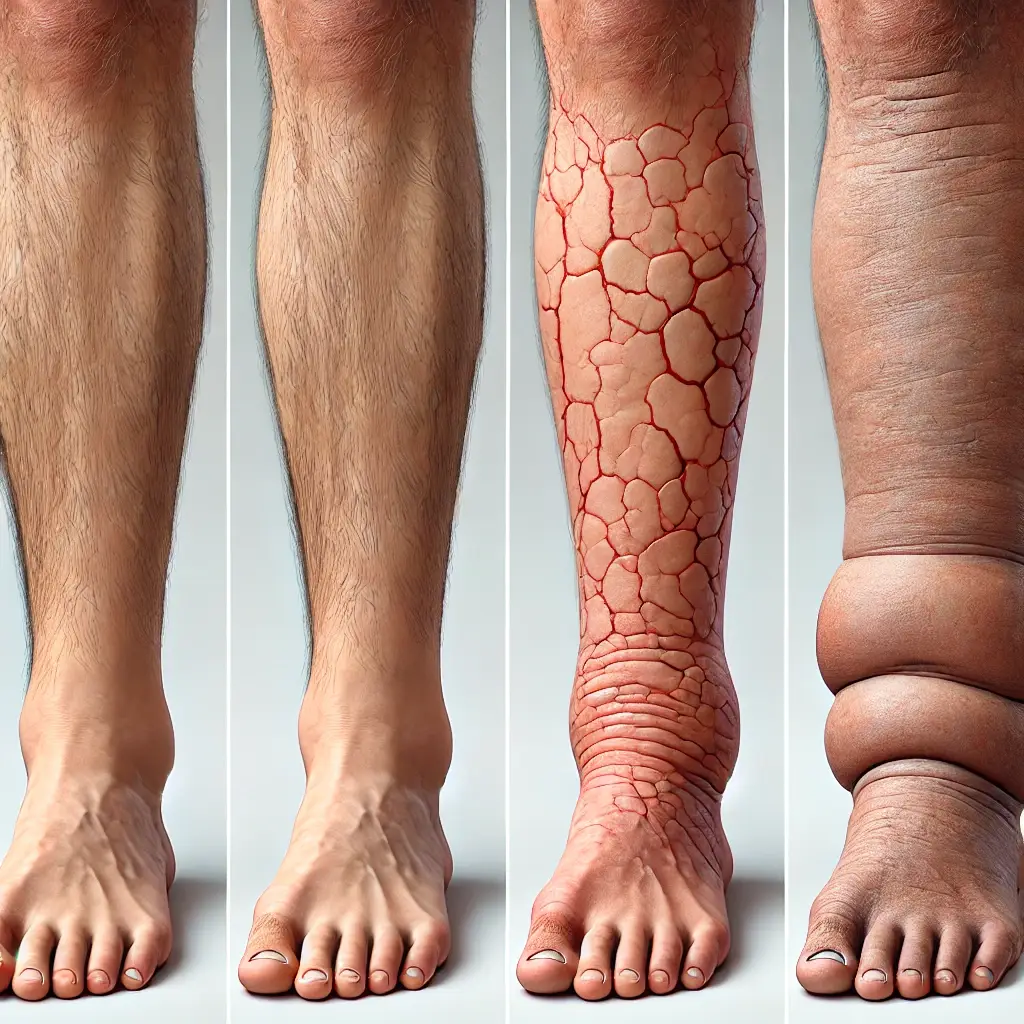
Understanding the Four Stages of Lymphedema: Reversible vs. Irreversible
Lymphedema is a chronic condition where excess lymph fluid builds up in tissues, causing swelling, discomfort, and other complications. It often affects the limbs but can occur in other parts of the body as well. While lymphedema is a lifelong condition, understanding the stages and differences between reversible and irreversible lymphedema can significantly improve outcomes. This article breaks down the four stages of lymphedema, identifies symptoms, and discusses how early intervention can make a difference in managing and potentially reversing the condition.
What are the Stages of Lymphedema?
Lymphedema progresses through four stages, each with its own symptoms and potential for improvement. Understanding the stages of lymphedema is key to early detection and effective treatment. The stages are typically categorized as Stage 0 (latent stage), Stage 1 (early-stage lymphedema), Stage 2 (progression of lymphedema), and Stage 3 (irreversible lymphedema and elephantiasis). Let’s take a closer look at each stage.
Stage 0: Latent Stage of Lymphedema
Stage 0 of lymphedema, also known as the latent stage, is characterized by the absence of noticeable symptoms, but the lymphatic system begins to function abnormally. During this stage, the lymphatic vessels may be compromised, but fluid retention has not yet caused visible swelling. This is a crucial time for intervention, as the risk of progression can be managed more effectively at this point.
Patients in Stage 0 might feel a sensation of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb, but swelling is not yet present. Because of the subtle nature of this stage, early detection can be difficult. A lymphedema specialist may be able to diagnose it through tests like lymphoscintigraphy or by tracking the patient’s symptoms over time. Early-stage lymphedema treatment at this stage can prevent the condition from advancing further.
Stage 1: Early-Stage Lymphedema Symptoms
In Stage 1, also known as early-stage lymphedema, visible swelling begins to appear in the affected limb. This swelling tends to subside with rest or elevation and is often soft to the touch. The affected limb may feel tight or heavy, and patients might notice that their skin feels more stretched or uncomfortable.
At this stage, the lymphatic fluid is still able to move around to some extent, so the condition remains reversible with proper management. Treatment for early-stage lymphedema typically includes compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), and lifestyle modifications to manage the swelling. Identifying this stage early is essential, as Stage 1 is the most responsive to non-invasive treatments, and patients can achieve a significant reduction in swelling.
Stage 2: Progression of Lymphedema
Stage 2 marks the progression of lymphedema, where swelling becomes more persistent and is less likely to go down with rest. The tissue in the affected area begins to thicken, and the fluid buildup increases, making the limb feel firmer and harder. The skin may also begin to show visible changes, including a more fibrotic texture due to the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis).
At this stage, lymphedema is more challenging to manage, but it is still reversible with early and aggressive treatment. The focus shifts to more intensive therapies, including the continuation of compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and the potential use of skin care techniques to prevent infection and skin breakdown. While the swelling may not be as easily reduced, the right treatment can still help manage symptoms effectively.
Stage 3: Irreversible Lymphedema and Elephantiasis
Stage 3, the final and most severe stage of lymphedema, is characterized by irreversible swelling and tissue changes. The swelling becomes extremely pronounced and persistent, with the affected limb often taking on an elephant-like appearance (elephantiasis). Skin changes such as thickening, hardened tissue, and deep folds or wrinkles are common, and the limb may experience a significant reduction in mobility.
At this stage, the lymphatic system has suffered significant damage, and the condition is generally considered irreversible. Lymphedema at this point may also lead to complications such as cellulitis (skin infection), severe pain, and ulcers. However, treatment options can still help manage symptoms and prevent further complications. Surgical treatments, such as lymph node transfer or liposuction, may be considered to improve the appearance of the limb and alleviate discomfort.
How to Identify Reversible vs. Irreversible Lymphedema?
Understanding the differences between reversible and irreversible lymphedema is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. While Stage 0 and Stage 1 are typically reversible with appropriate care, Stage 2 and Stage 3 require more complex approaches.
Signs of Spontaneously Reversible Lymphedema
Lymphedema that is spontaneously reversible is often seen in the earlier stages of the condition (Stage 1). In these stages, the swelling is softer, more fluctuating, and can be reduced with rest, elevation, or compression therapy. Symptoms like a feeling of tightness, mild swelling, and changes in the skin texture can often improve or disappear with treatment.
Effective treatment at this stage can lead to a significant reduction in swelling, and in some cases, the condition may be completely managed. However, early intervention is key to reversing the condition and avoiding progression to more severe stages.
Characteristics of Spontaneously Irreversible Lymphedema
In contrast, spontaneously irreversible lymphedema often occurs in later stages, where tissue changes such as fibrosis and hardening of the skin are present. At this stage, the fluid buildup in the lymphatic system becomes harder to manage, and the condition may no longer respond well to conservative treatments. The skin becomes thickened, and the affected limb may experience more severe complications, including reduced mobility and risk of infection.
Stage 3 lymphedema is usually considered irreversible, and while it is still possible to manage symptoms, full recovery may not be achievable. Surgery or more advanced medical treatments may be required to address the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Understanding the Role of Fibrosis
Fibrosis plays a major role in the progression from reversible to irreversible lymphedema. As the lymphatic fluid builds up over time, the tissue in the affected area undergoes changes, thickening and hardening as it forms scar tissue. This process is known as fibrosis, and it makes the condition more difficult to treat.
The presence of fibrosis typically signifies that the lymphedema has progressed beyond the point of being easily reversible. In these cases, more intensive treatment options, such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and skin care practices, can still help manage symptoms, but the underlying fibrosis may make the condition harder to fully reverse.
What are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
The symptoms of lymphedema can vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. However, certain common signs are typically present across all stages.
Visible Swelling in Affected Limbs
The most common symptom of lymphedema is visible swelling, which often occurs in the arms or legs but can affect other body parts. Early-stage swelling may come and go, but as the condition progresses, the swelling becomes more constant and harder to reduce.
Feeling of Heaviness or Tightness
A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb is another common symptom, especially during early stages. This sensation can be worsened after physical activity or prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Skin Changes and Fibrotic Tissue Development
As the condition progresses, changes in the skin and underlying tissue may occur. The skin may thicken and become firmer, especially in later stages, leading to fibrosis. These changes can result in a hardened texture and sometimes deep folds or wrinkles in the skin.
What Treatments are Available for Lymphedema?
While there is no cure for lymphedema, effective treatments can help manage the symptoms and reduce swelling. Here are some common treatment options:
Compression Therapy for Swelling Reduction
Compression therapy is a primary treatment for reducing swelling in lymphedema. It involves wearing compression garments, such as stockings or sleeves, that apply consistent pressure to the affected limb to help reduce fluid buildup and improve lymphatic drainage.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage Techniques
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique performed by a trained therapist to encourage the movement of lymph fluid out of the swollen area. This technique can help reduce swelling and improve the overall function of the lymphatic system.
Skin Care Practices for Lymphedema Management
Proper skin care is essential for patients with lymphedema, as swollen limbs are more susceptible to infection. Keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding cuts and scrapes, and using gentle cleansers can help prevent complications like cellulitis.
How to Live with Lymphedema?
Living with lymphedema requires ongoing management and a proactive approach to symptom control.
Daily Management Strategies for Affected Areas
Daily management includes wearing compression garments, performing self-care techniques like MLD, and engaging in gentle exercises to promote lymphatic drainage.
Working with a Lymphedema Specialist
A lymphedema specialist can provide personalized treatment plans and guide patients through the best management practices to keep swelling under control.
Support and Resources for Patients
Patients with lymphedema can benefit from joining support groups, accessing educational resources, and connecting with professionals who specialize in lymphatic care.
What is the Importance of Early Detection of Lymphedema?
Recognizing Early Symptoms for Better Outcomes
Early detection of lymphedema is crucial for preventing progression and improving outcomes. Identifying subtle changes like a feeling of tightness, early swelling, or skin changes can make a significant difference in managing the condition before it becomes irreversible.
Long-Term Effects of Delayed Diagnosis
Delayed diagnosis can result in the condition progressing to Stage 2 or Stage 3, where treatment becomes more complex and less effective. Early intervention helps avoid severe complications and reduces the impact of lymphedema on daily life.
Preventive Measures for At-Risk Individuals
At-risk individuals, such as those who have had surgery or radiation therapy affecting the lymph nodes, should be monitored regularly for early signs of lymphedema. Preventive care, including compression garments and lymphatic drainage techniques, can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Conclusion
Understanding the four stages of lymphedema—ranging from the latent, reversible Stage 0 to the irreversible Stage 3—is essential for effective management and treatment. Early intervention can prevent the condition from progressing, while more advanced stages may require surgical options and ongoing care. By recognizing the symptoms early, working with a lymphedema specialist, and adopting treatment strategies like compression therapy and manual lymphatic drainage, patients can significantly improve their quality of life.
FAQs
Q: What is lymphedema and how does it relate to the lymphatic system?
A: Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system is compromised, leading to swelling in the body region due to the accumulation of lymph fluid. Understanding lymphedema involves recognizing its causes, symptoms, and how it can be managed effectively.
Q: What are the four lymphedema stages?
A: The four lymphedema stages are stage 0 (latent stage), stage 1 (reversible lymphedema), stage 2 (spontaneously irreversible lymphedema), and stage 3 (lymphostatic elephantiasis). Each stage has distinct characteristics related to swelling and tissue changes.
Q: What is stage 0 lymphedema, and how can it be identified?
A: Stage 0 lymphedema is characterized by no visible swelling but may involve a feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the arm or leg. Early detection and diagnosis are crucial for managing lymphedema before noticeable symptoms develop.
Q: Can stage 1 lymphedema be reversed?
A: Yes, stage 1 lymphedema is reversible. It involves noticeable swelling that can be reduced with appropriate lymphedema treatment. Seeking treatment during this stage can prevent progression to more severe forms.
Q: What are the signs of swelling associated with lymphedema?
A: Signs of swelling include noticeable swelling, a feeling of fullness, and sometimes a pit that forms when pressure is applied to the swollen area. These symptoms can vary based on the stage of lymphedema.
Q: What role does a lymphedema therapist play in treatment?
A: A lymphedema therapist specializes in managing lymphedema through various treatment methods, including manual lymph drainage, compression therapy, and education on self-care techniques to manage lymphedema effectively.
Q: What complications can arise if lymphedema is left untreated?
A: If left untreated, lymphedema can lead to complications such as cellulitis, skin infections, and lymphostatic elephantiasis. Managing symptoms and preventing complications is essential to maintaining quality of life.
Q: How does the thicken and harden of the skin relate to lymphedema?
A: As lymphedema progresses, the affected tissue may undergo changes, leading to thickening of the skin and hardening of the underlying tissue. These tissue consistency changes are caused by prolonged swelling and inflammation.
Q: What is the risk of lymphedema after surgery or injury?
A: The risk of lymphedema increases after surgeries, particularly those involving lymph node removal or radiation therapy. Secondary lymphedema may develop as a complication, making early detection and management vital post-surgery.