The Impact of Lymphedema on Mental Health: Living with a Compromised Lymphatic System
Definition of Lymphedema and its Causes
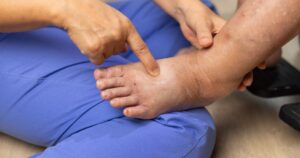
Lymphedema is a condition marked by the abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, typically causing swelling, discomfort, and sometimes infections. It occurs when the lymphatic system, responsible for draining excess fluids, becomes damaged or impaired. This can result from a variety of causes, including cancer treatments like surgery or radiation, trauma, or congenital factors such as primary lymphedema. The condition is commonly associated with secondary lymphedema, where another disease or injury disrupts the lymphatic system’s function.
Lymphedema’s physical effects—such as swelling, heavy limbs, and fibrosis—can have profound implications for quality of life. While much attention has been given to managing these physical symptoms, an often overlooked aspect is the mental health challenges that individuals living with lymphedema face daily.
Overview of the Lymphatic System’s Role in the Body
The lymphatic system is a critical part of the body’s immune system, helping to maintain fluid balance and defend against infections. Lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, circulates throughout the body via lymph nodes and vessels. When the lymphatic system is compromised through surgery, injury, or disease, it can build lymph fluid, contributing to swelling and discomfort in affected areas. While the physical effects are visible, the internal disruption to bodily functions can lead to significant emotional and mental health challenges, complicating the overall well-being of individuals with lymphedema.
Importance of Addressing Mental Health in Chronic Conditions
Mental health is a fundamental component of overall health, yet it is often sidelined when discussing chronic physical conditions like lymphedema. The physical toll of lymphedema, coupled with its ongoing management, can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Chronic conditions can also trigger body image issues, significantly when visible symptoms like swelling alter one’s appearance. Addressing mental health alongside physical health is essential for a holistic approach to managing lymphedema.
Purpose of the Blog Post: To Explore the Mental Health Implications of Living with Lymphedema
This article explores how lymphedema impacts mental health, focusing on the emotional and psychological struggles individuals face while living with this chronic condition. By delving into these challenges, we aim to raise awareness, encourage open dialogue, and provide strategies to support better those living with lymphedema.
Understanding Lymphedema
Description of Lymphedema Symptoms and Physical Challenges
Lymphedema primarily manifests through persistent swelling, commonly in the limbs, but it can also affect other body parts. Symptoms can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild swelling, while others face more severe cases that impair movement and cause discomfort. Over time, the swelling may become more pronounced, leading to skin thickening and fibrosis, making the condition more difficult to treat.
In addition to physical symptoms, patients with lymphedema may face various complications, such as recurrent infections (cellulitis), decreased mobility, and a higher risk of developing further health issues. These complications can further exacerbate the emotional strain individuals experience, creating a cycle of physical discomfort and mental distress.
Discussion of the Chronic Nature of the Condition
Lymphedema is typically a lifelong, chronic condition with no known cure. While it can be managed with manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, the condition persists over time. The chronic nature of lymphedema means that individuals are constantly dealing with its symptoms, often leading to frustration and feelings of helplessness. Over time, the emotional burden of this continuous condition can significantly affect mental health.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
It is estimated that nearly 140 million people worldwide suffer from lymphedema, with a significant number being breast cancer survivors with lymphedema. In the U.S., it’s estimated that more than 2 million individuals are living with the condition, many of whom experience secondary lymphedema as a result of cancer treatments. The condition is not limited to any specific demographic but affects both men and women, with certain groups—such as women with lymphedema related to breast cancer treatment—facing unique challenges.
The Relationship Between Physical Health and Mental Well-Being
Physical health and mental well-being are inextricably linked, especially when dealing with chronic health challenges like lymphedema. The physical limitations imposed by lymphedema—whether it’s difficulty moving, managing pain, or facing visible changes in appearance—can have a significant psychological impact. This connection between the physical and mental toll is essential to recognize as part of comprehensive lymphedema care.
Mental Health Challenges Associated with Lymphedema
Emotional Impact: Anxiety, Depression, and Body Image Issues
Living with lymphedema can bring about a range of emotional challenges. Anxiety is one of the most common mental health struggles, as individuals often worry about the progression of their condition, possible flare-ups, or complications like infections. Depression is also common, especially for individuals who feel overwhelmed by the demands of managing lymphedema on top of their daily responsibilities.
Moreover, body image issues are a significant concern for individuals with visible swelling or changes in their appearance. The visible effects of lymphedema, particularly in the limbs, can contribute to self-consciousness and a decline in self-esteem. These feelings of inadequacy can further compound anxiety and depression, making it even harder for individuals to seek help.
Social Isolation and Its Effects on Mental Health
Another mental health challenge associated with lymphedema is social isolation. The visible effects of the condition may make some individuals feel embarrassed or ashamed, leading them to withdraw from social situations or activities they once enjoyed. This isolation can have serious consequences for mental health, contributing to feelings of loneliness and deepening the emotional burden of living with lymphedema.
The Role of Stigma and Misunderstanding in Mental Health Struggles
Lymphedema is often misunderstood by the public, leading to stigma that compounds the mental health struggles of those affected. Many people are unaware of the condition, and as a result, those living with it may feel like they are judged or treated differently. This lack of understanding can make it harder for individuals to openly discuss their condition, which may contribute to feelings of isolation and alienation.
Coping Mechanisms and Their Effectiveness
For many individuals with lymphedema, coping mechanisms play a significant role in managing mental health. Some may approach support groups, mindfulness practices, or therapy to address their emotional challenges. While these strategies can be effective for some, it’s important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Coping mechanisms need to be personalized, focusing on physical and mental well-being.
Strategies for Managing Mental Health
Importance of Seeking Professional Help and Therapy
Mental health struggles related to lymphedema should not be ignored. Seeking professional help from therapists, psychologists, or counsellors can provide individuals with tools to manage anxiety, depression, and body image concerns. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most commonly recommended therapies, as it helps individuals reframe negative thought patterns and develop healthier coping strategies.
Support Groups and Community Resources
Support groups are invaluable resources for individuals with lymphedema. Connecting with others experiencing similar struggles can help reduce feelings of isolation. These groups offer a safe space to share experiences, learn from others, and find emotional support. Many community resources, including online forums and local organizations, focus on providing education and emotional assistance for those affected by lymphedema.
Mindfulness and Stress-Reduction Techniques
Mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga, have been proven to reduce stress and improve mental health. These practices can help individuals cope with the emotional strain of living with a chronic condition. In addition, regular exercise, when appropriate, can help reduce swelling and improve mood by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.
Encouraging Open Conversations About Mental Health in the Context of Lymphedema
One of the most powerful strategies for improving mental health in individuals with lymphedema is fostering open dialogue. By creating spaces where patients can talk about their emotional experiences and mental health struggles, we can reduce stigma and offer support. These conversations can happen between patients and healthcare providers, in support groups, or even through online communities.
Call to Action for Increased Awareness and Support
There is a critical need for increased awareness of the mental health challenges associated with lymphedema. Healthcare providers, support groups, and the general public must be better informed about how lymphedema affects the psychological well-being of those living with it. Improving understanding and providing support can help individuals with lymphedema lead fuller, more satisfying lives.
Emphasis on the Importance of Holistic Care for Individuals with Lymphedema
Lymphedema requires a holistic care approach, addressing physical and mental health needs. Effective management of lymphedema should include treatment for emotional well-being, physical therapy, and symptom management. By integrating mental health support into lymphedema care, we can improve quality of life and help patients navigate the challenges of this chronic condition.
Final Thoughts on Fostering Resilience and Hope in the Face of Chronic Illness
While living with a chronic condition like lymphedema can be daunting, it is possible to foster resilience and hope. By recognizing the mental health challenges and implementing support strategies, individuals with lymphedema can build strength and find a sense of empowerment. A compassionate and comprehensive approach to care—encompassing both physical and mental health—is essential to helping individuals live well with lymphedema.
FAQs
Q: How do lymphedema and mental health relate to each other?
A: Lymphedema can significantly affect mental health by contributing to feelings of anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. The psychological impact of lymphedema often stems from the physical limitations and changes in body image that patients experience.
Q: What are the common psychological impacts of lymphedema?
A: The psychological impact of lymphedema may include low self-esteem, anxiety about body image, and feelings of isolation. These issues can adversely affect the quality of life for individuals dealing with lymphedema.
Q: How can lymphedema management affect mental health?
A: Effective lymphedema management can improve mental health by reducing physical symptoms and enhancing the overall quality of life. Patients who actively engage in lymphedema treatment often report better psychological well-being.
Q: Do breast cancer survivors with and without lymphedema experience different mental health outcomes?
A: Yes, studies have shown that breast cancer survivors with lymphedema often report lower health scores and higher levels of psychological distress compared to breast cancer survivors without lymphedema.
Q: What tools can help assess the mental health of lymphedema patients?
A: The short-form health survey is commonly used to evaluate the quality of life and mental health status of lymphedema patients, providing insights into their psychological well-being.
Q: Can lymphedema lead to long-term mental health issues?
A: Yes, lymphedema can lead to long-term mental health issues if not addressed. The ongoing physical challenges and social stigma associated with lymphedema may contribute to chronic stress and mental health disorders.
Q: How does lower limb lymphedema impact mental health differently than upper limb lymphedema?
A: Lower limb lymphedema may lead to more significant mobility issues, which can exacerbate feelings of helplessness and depression compared to upper limb lymphedema, where daily activities may be less hindered.
Q: Are individuals with primary lymphedema more affected mentally than those with secondary lymphedema?
A: Individuals with primary lymphedema may face unique psychological challenges, including feelings of confusion and frustration about their condition, which can differ from the experiences of those with secondary lymphedema, who may have a clearer cause related to another health condition.
Q: How can support groups help individuals with lymphedema?
A: Support groups can provide emotional support and a sense of community for individuals with lymphedema, helping to alleviate feelings of isolation and providing a platform to share experiences related to the psychological impact of lymphedema.