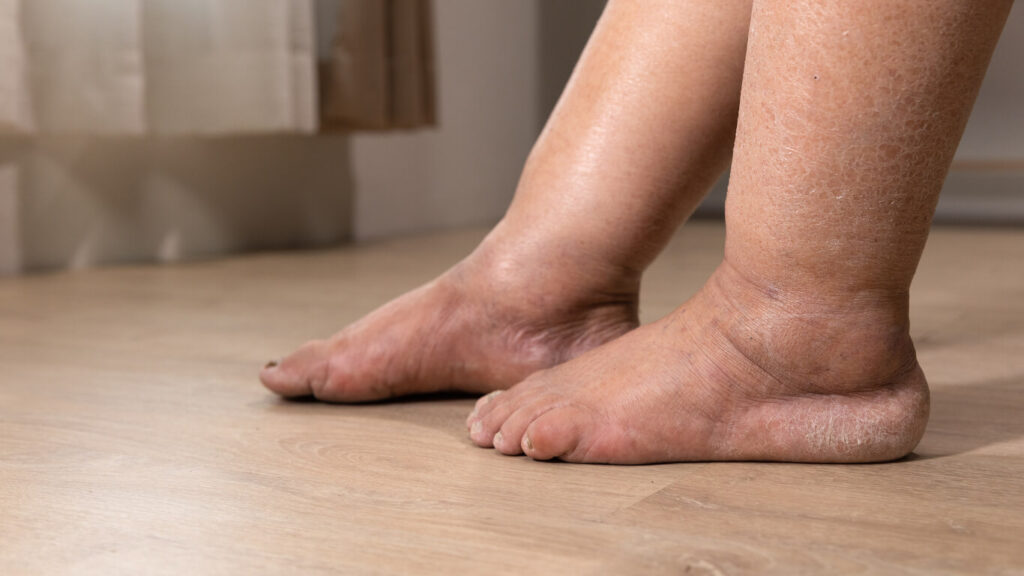
lymphedema in legs: Understanding Symptoms, Stages, and Prevention
lymphedema in legs can be a challenging condition, but with the right knowledge, you can take steps to manage it effectively. Whether you’ve recently noticed swelling in your legs or have been diagnosed with lymphedema, understanding the symptoms, stages, and prevention strategies is essential. In this blog, I’ll guide you through what you need to know, including treatment options, daily management tips, and ways to lower your risk of developing leg lymphedema.
Key Takeaways
- Lymphedema is swelling caused by a buildup of lymph fluid in the tissues, often affecting the legs or arms.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to managing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Adopting a lymphedema self-care routine and working with a certified therapist can significantly improve quality of life.
- Prevention strategies like maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding injuries, and wearing compression garments can help reduce your risk of developing lymphedema in your legs.
What Are the Early Signs and Symptoms of lymphedema in legs?
Recognizing Swelling in Your Legs
The first sign of lymphedema is often swelling in one or both legs. This swelling may start mild and worsen, particularly if left untreated. You might notice that your shoes feel tighter or your legs feel heavy by the end of the day. This swelling occurs because the lymphatic system isn’t properly draining lymph fluid, leading to an accumulation in the tissues.
If you experience persistent swollen legs, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a lymphedema diagnosis. Catching these signs of lymphedema early can significantly improve management.
Understanding How Lymphedema Affects Mobility
Lymphedema doesn’t just cause swelling—it can also make it harder to move around. The affected leg may feel stiff or uncomfortable as fluid builds up, making walking or exercising difficult. Over time, untreated lymphedema symptoms can decrease strength and flexibility, further impacting your ability to stay active.
Staying mobile is crucial for improving circulation and reducing the risk of severe lymphedema. Regular physical activity, even simple exercises, can help move lymph fluid and alleviate discomfort.
Identifying Skin Changes Associated with Lymphedema
One less obvious symptom of lymphedema is changes to your skin. You might notice it becoming thickened, tight, or even developing a texture similar to orange peel. These skin changes indicate that the condition has progressed and can increase your risk of infections like cellulitis.
Protecting your skin and keeping it moisturized can prevent irritation and complications. If you notice redness, warmth, or pain, these may be signs of an infection that needs immediate medical attention.
What Causes lymphedema in legs?
Primary Lymphedema: Genetic Factors
Primary lymphedema is a rare genetic condition affecting the lymphatic system’s development. It may appear at birth, during puberty, or later in life. While this type of lymphedema is less common, understanding your family history can help identify whether you may be at risk.
Secondary Lymphedema: Cancer Treatment and Surgery
More commonly, secondary lymphedema develops due to an external factor, such as cancer treatment. Procedures like cancer surgery, radiation, or lymph node removal can damage the lymphatic system, making it difficult for the body to drain fluid properly. For instance, radiation treatment for cancer or breast cancer treatment may increase your risk for lymphedema, sometimes even years after the treatment.
Other Risk Factors for Developing Leg Lymphedema
Beyond cancer-related causes, other factors can cause lymphedema in legs. Obesity, infections, and certain chronic conditions can also contribute to developing this condition. Staying aware of these risk factors for lymphedema can help you take proactive steps to prevent it.
How Is Lymphedema Diagnosed, and What Are the Stages?
Diagnostic Methods for Lymphedema
Diagnosing lymphedema often involves a physical exam and imaging tests to assess the extent of lymph fluid buildup. Your doctor might use an MRI, CT scan, or lymphoscintigraphy to get a clearer picture of your lymphatic system.
Understanding the Stages of Lymphedema
Lymphedema occurs in stages, from mild swelling to irreversible tissue damage. In the early stages, symptoms may be subtle and reversible, while later stages can lead to more permanent changes. Knowing the stages of lymphedema helps tailor the appropriate treatment.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications from lymphedema, such as infections and fibrosis. If you notice signs of lymphedema, seek treatment immediately to manage the condition effectively.
What Are the Treatment Options for lymphedema in legs?
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
One of the most effective treatments is complete decongestive therapy. This comprehensive approach combines lymphatic drainage, skincare, and compression garments to reduce swelling and improve mobility. It’s often the first line of treatment.
Compression Garments and Their Role in Management
Compression garments are essential for managing lymphedema. These specially designed stockings apply pressure to help reduce swelling and prevent fluid buildup. Wearing these garments consistently can make a noticeable difference in your symptoms.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage and Massage Techniques
Manual lymphatic drainage is a gentle massage technique performed by a lymphedema therapist. This therapy helps stimulate the flow of lymph fluid, reducing swelling and improving overall comfort. Adding this to your lymphedema therapy routine can enhance results.
How Can I Prevent Lymphedema or Reduce My Risk?
Lifestyle Modifications to Lower Your Risk
Small changes, like exercising regularly and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, can lower your risk of lymphedema. Staying active helps improve circulation and supports the lymphatic system.
Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a major risk factor for developing lymphedema, so maintaining a healthy weight is critical. A balanced diet and regular exercise can also help prevent the condition.
Protective Measures During Activities
Simple precautions, like wearing gloves while gardening or avoiding injuries, can prevent lymphedema. Protecting your skin minimizes the risk of infection and keeps your lymphedema self-care routine on track.
What Complications Can Arise From Untreated Lymphedema?
Increased Risk of Infections
Untreated lymphedema may lead to frequent infections, as the lymphatic system plays a key role in immune defense. Conditions like cellulitis are common in people with severe lymphedema.
Long-Term Effects on Skin and Tissue
Chronic swelling can cause thickened skin and fibrosis over time. These long-term changes highlight the importance of seeking lymphedema treatment early.
Impact on Quality of Life
Lymphedema can affect daily activities and emotional well-being. Managing the condition can help maintain quality of life.
Living With Lymphedema: Tips for Daily Management
Self-Care Techniques for Lymphedema Patients
Incorporating daily habits, like wearing compression garments and performing light exercises, can help you manage lymphedema symptoms. Regular skin care is also crucial to prevent irritation and infection.
Working With a Certified Lymphedema Therapist
A certified lymphedema therapist can tailor a management plan to your needs, including techniques like lymphatic drainage and massage. Their expertise can make a big difference in your progress.
Emotional Support and Coping Strategies
Living with lymphedema can be emotionally challenging, but connecting with support groups or counselors can help. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
FAQs About Lymphedema in Legs
- Can lymphedema be cured? Unfortunately, lymphedema has no cure, but early treatment can effectively manage symptoms.
- What is the best way to prevent lymphedema? Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding injuries, and using compression garments during high-risk activities are key strategies.
- How does cancer treatment increase the risk of lymphedema? Treatments like radiation therapy and cancer surgery can damage the lymphatic system, increasing the risk of developing lymphedema.
- What are the symptoms of severe lymphedema? Severe cases of lymphedema may include significant swelling, hardened skin, and frequent infections.
- Who should I see for lymphedema diagnosis and treatment? A certified lymphedema therapist or a specialist trained in lymphedema therapy can help you navigate diagnosis and management.