Understanding Lymphedema in Arms: Essential Guide for Breast Cancer Survivors
As a breast cancer survivor, you’ve already been through so much. Surgery, chemotherapy, and the emotional toll of dealing with such a life-altering diagnosis. But beyond the primary treatments and their immediate aftermath, other long-term challenges can emerge along the way. One of the most common complications that many breast cancer survivors face is lymphedema. This condition, which involves the swelling of the arms, can be both physically and emotionally taxing. In this guide, I’ll help you understand what lymphedema is, its connection to breast cancer, how to spot its symptoms early, and the steps to manage it. Let’s dive in.
What is Lymphedema and How Does It Affect the Arms?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system is blocked, causing fluid to build up in the body. This buildup leads to swelling, typically in the arms or legs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. In the case of breast cancer survivors, the arms are the most commonly affected area, particularly on the side where surgery or radiation treatment occurred.
Defining Lymphedema and Its Connection to the Lymphatic System
To better understand lymphedema, let’s first take a closer look at the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is a key part of your immune system. It consists of a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that help clear waste, toxins, and excess fluids from the body. When your lymphatic system works properly, it transports lymph—a clear fluid containing white blood cells—throughout your body, helping fight infections and removing waste.
However, if the lymphatic system becomes damaged or blocked, the fluid it carries can’t flow properly. As a result, fluid accumulates, causing swelling in the affected areas. For breast cancer patients, this often occurs in the arm, particularly on the side where the cancer treatment was administered. Whether it was surgery to remove lymph nodes, radiation therapy, or a combination of both, these treatments can interfere with the normal flow of lymph fluid, resulting in lymphedema.
Common Causes of Arm Lymphedema, Including Breast Cancer Treatment
The most common cause of arm lymphedema in breast cancer survivors is the removal or damage to the lymph nodes during surgery. This often happens during a procedure called axillary lymph node dissection (ALND), where lymph nodes under the arm are removed to check for cancer spread. In some cases, radiation therapy can also damage the lymphatic vessels, leading to blockages that prevent proper drainage.
Lymphedema can also develop after chemotherapy, though this is less common. Chemotherapy can affect the lymphatic system by weakening the immune system or causing inflammation. Some women are more prone to developing lymphedema due to a combination of factors such as the extent of surgery, radiation treatments, and even infections that damage the lymphatic system.
Primary vs. Secondary Lymphedema: Understanding the Differences
Lymphedema can be classified into two types: primary and secondary. Understanding the difference between the two is crucial, especially for breast cancer survivors.
Primary lymphedema is a rare condition that occurs at birth or during adolescence or adulthood. It occurs when the lymphatic system is underdeveloped or dysfunctional. In primary lymphedema, the swelling is usually seen in the legs, though it can also affect the arms.
Secondary lymphedema, on the other hand, is much more common in breast cancer survivors. It occurs due to damage or blockage to the lymphatic system due to external factors, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or infection. For breast cancer survivors, secondary lymphedema typically affects the arm on the same side as the cancer treatment, though it can sometimes affect both arms.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Lymphedema in the Arms?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of lymphedema early on can make all the difference in preventing it from becoming a more serious issue. The earlier you detect it, the sooner you can begin treatment to reduce swelling and prevent further complications.
Early Warning Signs and Common Symptoms of Arm Lymphedema
The symptoms of lymphedema can be subtle at first. In the early stages, you might notice a feeling of heaviness or tightness in your arm, particularly on the side where you had surgery or radiation. Your arm may also feel full or uncomfortable, and you might notice changes in the skin, such as a feeling of tightness or a slight puffiness.
Other common early warning signs include:
- Swelling that starts in the hand, wrist, or fingers and spreads up the arm
- A feeling of fullness or heaviness in the arm or hand
- A tight or stretched feeling in the skin
- Decreased range of motion in the arm, making it harder to perform everyday tasks
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early intervention is key to managing lymphedema effectively.
Stages of Lymphedema: From Mild Swelling to Severe Complications
Lymphedema develops in stages, and it’s crucial to understand these stages to help manage the condition effectively.
- Stage 0 (Latency stage): There are no visible symptoms at this stage, but the lymphatic system is compromised. You may feel a sense of heaviness or tightness, but swelling is not yet apparent.
- Stage 1 (Mild swelling): Swelling is noticeable but may be soft and can be reduced by elevation or gentle massage. The skin may feel tight, and there could be some discomfort.
- Stage 2 (Moderate swelling): Swelling becomes more pronounced and harder to reduce. The arm may feel heavy, and the skin could develop a thicker texture. Infections are more likely to occur at this stage.
- Stage 3 (Severe swelling): The swelling is permanent and cannot be reduced. The arm may be extremely large and stiff, and the skin may become bumpy, leading to more serious complications like infections or ulcers.
Recognizing lymphedema early and starting treatment at Stage 1 can help prevent it from progressing to Stage 2 or 3, where the effects are more difficult to reverse.
How to Recognize Lymphedema Symptoms After Breast Cancer Surgery
After breast cancer surgery, lymphedema can develop at any time, even years after treatment. This means that it’s essential to be aware of the risk and to watch for any swelling or changes in your arm, especially on the side where you had surgery or radiation.
Some signs to watch for include:
- Swelling in the arm, hand, or fingers
- A feeling of tightness or fullness in the arm
- Changes in skin texture, such as thickening or hardening
- Difficulty moving the arm or hand
- A feeling of heaviness or weakness in the arm
Be sure to seek medical advice if you notice any of these symptoms. The sooner you catch lymphedema, the better you can manage it and prevent further issues.
Can Lymphedema Be Prevented or Treated?
While lymphedema can’t always be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and manage the condition if it does occur. Early detection and intervention are key.
Prevention Tips for Lymphedema
Although there’s no guaranteed way to prevent lymphedema, several lifestyle changes and habits may reduce your risk. These include:
- Taking care of your skin: Keep the skin on your arm moisturized and clean to prevent infections, which can trigger lymphedema.
- Avoiding injury: Avoid cuts, scrapes, or burns on the affected arm, as these can lead to infections.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can strain your lymphatic system, increasing the risk of lymphedema.
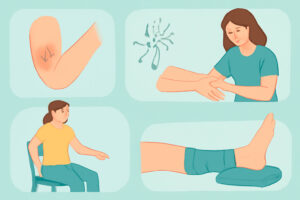
- Regular exercise: Gentle exercises, especially those that promote arm movement and fluid drainage, can help reduce your risk.
Treatment Options for Lymphedema
If you develop lymphedema, treatment options are available to manage the condition and improve quality of life. Some common treatment methods include:
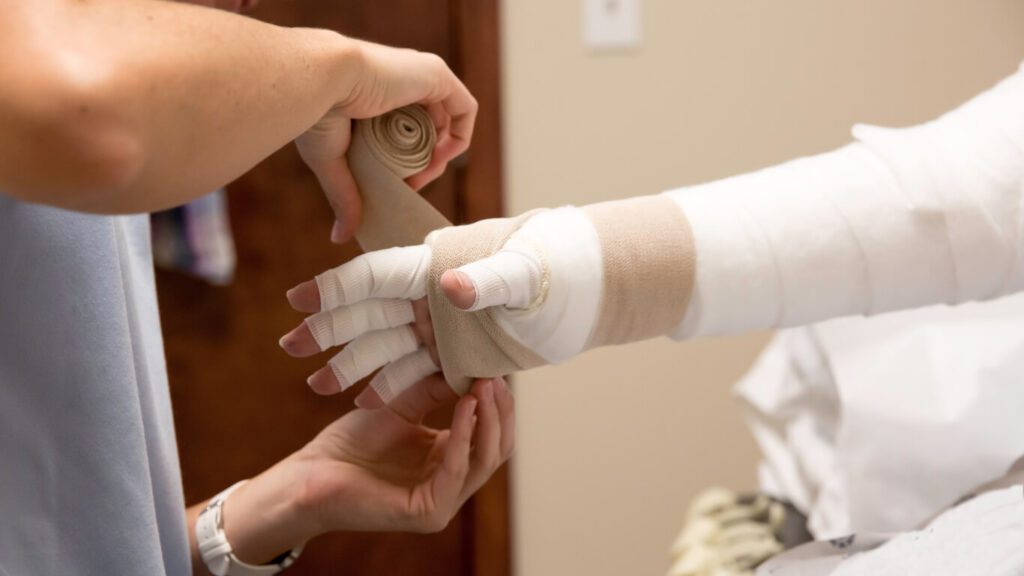
- Compression garments: Wearing a compression sleeve or bandage can help reduce swelling and promote proper lymphatic drainage.
- Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD): This specialized massage technique encourages lymph fluid to flow properly through the body.
- Physical therapy: A trained therapist can guide you through exercises and techniques that help reduce swelling and improve mobility.
- Skincare: Proper skincare is essential to prevent infections and manage swelling. Keeping your skin moisturized and avoiding injury is key.
Final Thoughts
Living with lymphedema can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that you are not alone. Many breast cancer survivors deal with this condition, and with the right care, it is manageable. Early detection and consistent treatment are your best tools for preventing lymphedema from worsening. If you experience any symptoms, contact your healthcare provider for advice and support. With the right care, you can continue to live a full and active life, even with lymphedema.