Understanding Lymphedema After Breast Cancer Treatment
Lymphedema is a condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for those who have undergone cancer treatment, particularly breast cancer. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lymphedema, its causes, risk factors, treatment options, and prevention strategies. By gaining insights into this condition, cancer patients and survivors can better manage their health and well-being.
What is Lymphedema, and How is it Related to Cancer Treatment?
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to swelling in an arm or leg. This condition is often seen in cancer patients, particularly those who have undergone surgery or radiation therapy as part of their cancer treatment. During such procedures, lymph nodes may be removed or damaged, disrupting the normal flow of lymphatic fluid and causing lymphedema to develop. This is particularly common in breast cancer survivors who have had surgery to remove breast tissue and nearby lymph nodes.
What Causes Lymphedema in Cancer Patients?
The primary cause of lymphedema in cancer patients is the disruption of the lymphatic system. When lymph nodes are removed or irradiated during cancer surgery, the body’s ability to drain lymph fluid effectively is compromised. This can lead to an accumulation of fluid in the surrounding tissues, resulting in swelling. In breast cancer-related lymphedema, the removal of axillary lymph nodes is a common surgical procedure that can increase the risk of developing lymphedema. Additionally, radiation therapy can also cause inflammation and scarring in the lymphatic vessels, further exacerbating the risk of lymphedema.
How is Lymphedema Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of lymphedema typically involves a thorough clinical assessment by healthcare providers. They will evaluate the patient’s medical history, specifically focusing on any history of cancer treatment, and perform a physical examination to assess any swelling in the affected limb. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, may also be utilized to visualize the lymphatic system and rule out other potential causes of swelling. Early diagnosis is crucial, as prompt management can prevent the progression of symptoms of lymphedema.
What are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
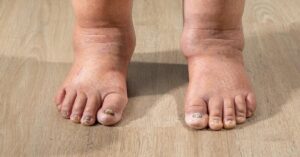
The symptoms of lymphedema can vary widely among individuals but often include noticeable swelling in the arm or leg, a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb, and changes in skin texture. Patients may also experience discomfort or pain, reduced range of motion, and an increased susceptibility to infections in the affected area. Recognizing these signs and symptoms is vital for early intervention and effective lymphedema management.
What are the Risk Factors for Developing Lymphedema After Breast Cancer?
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing lymphedema after breast cancer treatment. Understanding these risk factors is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to implement preventive measures.
Who is at Risk for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema?
Breast cancer survivors who have undergone lymph node removal or radiation therapy are at heightened risk for developing lymphedema. Other risk factors include age, body mass index (BMI), and the extent of cancer surgery. Research indicates that younger patients and those with a higher BMI may have an increased risk of lymphedema. Additionally, individuals who have received chemotherapy may also be more susceptible to this condition.
How Does Cancer Surgery Impact the Risk of Lymphedema?
Cancer surgery plays a crucial role in the risk of lymphedema, particularly in breast cancer patients. The extent of surgical intervention, such as the number of lymph nodes removed during axillary dissection, directly correlates with the likelihood of developing lymphedema. Studies have shown that patients who undergo more extensive surgical procedures have a higher risk of lymphedema. Furthermore, surgical complications, such as infections or delayed healing, can further increase the risk of developing this condition.
Can Head and Neck Cancer Patients Develop Lymphedema?
Yes, patients with head and neck cancer can also develop lymphedema. This condition, often referred to as cervical lymphedema, can occur following surgery or radiation treatment, affecting the lymphatic drainage system in the neck. Similar to breast cancer-related lymphedema, the removal of lymph nodes in the neck region can disrupt normal lymphatic flow, leading to swelling. Patients should remain vigilant about monitoring for signs of lymphedema in these areas post-treatment.
What are the Treatment Options for Lymphedema After Cancer Treatment?
Managing lymphedema effectively is crucial for improving the quality of life for cancer survivors. Various treatment options are available, and tailored approaches are often necessary for optimal results.
What is the Role of a Certified Lymphedema Therapist?
A certified lymphedema therapist plays a vital role in the treatment and management of lymphedema. These specialized therapists are trained to provide comprehensive care, which may include manual lymphatic drainage techniques, compression therapy, and education on self-care practices. Working closely with patients, certified lymphedema therapists develop personalized treatment plans that address individual needs and help reduce swelling effectively. Their expertise is essential in helping patients manage the physical and emotional challenges associated with lymphedema.
What Types of Lymphedema Treatment Are Available?
Several treatment options are available for lymphedema, ranging from conservative to more invasive methods. Conservative treatments often include compression garments, which help prevent fluid accumulation in the affected limb, and exercises aimed at promoting lymphatic flow. Manual lymphatic drainage performed by a certified lymphedema therapist is also a common practice. In more severe cases, surgical options such as lymphatic bypass or lymph node transfer may be considered to improve drainage. Each treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s specific condition and lifestyle.
How Effective is Treatment for Lymphedema?
Treatment for lymphedema can be highly effective when initiated early and managed appropriately. Many patients experience significant improvements in swelling and overall limb function through a combination of therapies. However, it is important to note that while treatment can greatly alleviate symptoms, it may not completely eliminate lymphedema. Ongoing lymphedema management is crucial, and patients should remain proactive in monitoring their condition and adhering to recommended treatment protocols.
How Can Lymphedema Be Prevented in Cancer Survivors?
Prevention plays a critical role in managing the risk of lymphedema among cancer survivors. By implementing proactive strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
What Strategies are Effective in Preventing Lymphedema?
Several strategies can help prevent lymphedema in cancer survivors. Early detection and intervention are paramount; patients should be educated about the signs and symptoms of lymphedema so that they can seek timely medical attention. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding injuries in the affected limb are also important preventive measures. Additionally, patients should consult with their healthcare providers about the appropriate use of compression garments during high-risk activities.
Are There Lifestyle Changes That Can Reduce the Risk of Lymphedema?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of lymphedema. Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in low-impact exercises can promote overall health and support lymphatic function. Furthermore, avoiding heavy lifting, excessive heat exposure, and tight clothing can minimize the risk of triggering lymphedema symptoms. These lifestyle modifications should be discussed with healthcare professionals to ensure they align with individual circumstances and treatment plans.
How Important is Early Detection in Preventing Lymphedema?
Early detection of lymphedema is crucial in preventing the condition from worsening. By recognizing the early signs of lymphedema, patients can seek immediate evaluation and initiate treatment promptly. This proactive approach can significantly alter the course of the condition, leading to better management outcomes and improved quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers can aid in monitoring for any signs of lymphedema, allowing for timely intervention when necessary.
What Should Cancer Patients Know About the Signs and Symptoms of Lymphedema?
Awareness of the signs and symptoms of lymphedema is essential for cancer patients and survivors. Understanding what to look for can empower individuals to seek treatment early and effectively manage their condition.
How to Recognize the Early Signs of Lymphedema?
The early signs of lymphedema may include subtle changes such as a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the arm or leg, a noticeable increase in limb size, and changes in skin texture. Patients might also experience discomfort or a decrease in flexibility. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for prompt evaluation and potential treatment, which can mitigate the progression of lymphedema.
What Symptoms Indicate a Need for Immediate Medical Attention?
Certain symptoms of lymphedema warrant immediate medical attention. These include sudden swelling, increased pain, warmth, or redness in the affected limb, as these may indicate the presence of an infection or an acute exacerbation of lymphedema. If any of these symptoms arise, patients should seek medical evaluation without delay to address potential complications and ensure appropriate management.
How Can Patients Monitor Their Condition Post-Treatment?
Patients can effectively monitor their condition post-treatment by regularly assessing their limbs for any changes in size, shape, or texture. Keeping a daily log of any symptoms, such as swelling or discomfort, can provide valuable information for healthcare providers during follow-up visits. Additionally, engaging in self-care practices, such as prescribed exercises and wearing compression garments as recommended, can help maintain lymphatic function and reduce the risk of lymphedema. Ongoing communication with healthcare professionals is essential for effective lymphedema management, allowing patients to remain informed and proactive about their health.
FAQS
Q: What is the link between lymphedema and cancer?
A: Lymphedema can occur as a result of cancer or cancer treatment, particularly after surgeries or radiation that affects lymph nodes. This condition, known as cancer-related lymphedema, can develop in the arms, legs, or other areas, depending on the location of the cancer.
Q: What are the risk factors for lymphedema in cancer patients?
A: Risk factors for lymphedema include having surgery or radiation therapy that affects lymph nodes, obesity, infections, and a family history of lymphedema. Patients treated for breast cancer or gynaecological cancer are particularly at risk for developing secondary lymphedema.
Q: How is lymphedema diagnosed in cancer patients?
A: Diagnosing lymphedema typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who may assess swelling, skin changes, and other symptoms. Imaging tests such as MRI or lymphoscintigraphy may also be used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate lymphatic function.
Q: What are the symptoms of lymphedema?
A: Symptoms of lymphedema include swelling in the affected area, feelings of heaviness or tightness, restricted range of motion, and recurrent infections. In some cases, the skin may become thickened or hard.
Q: How can lymphedema be treated?
A: The treatment of lymphedema may include compression garments, manual lymph drainage, exercise, and skin care. Some patients may benefit from specialized physical therapy focused on managing lymphedema. In severe cases, surgical options may be considered.
Q: Can lifestyle changes help manage lymphedema?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes can help manage lymphedema. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding tight clothing can reduce the risk for lymphedema. Proper skin care is also crucial in preventing infections.
Q: Is there a connection between gynaecological cancer and lymphedema?
A: Yes, gynaecological cancer treatments, particularly those involving lymph node removal or radiation, can increase the risk of developing lymphedema, particularly in the lower extremities. Patients should discuss lymphedema risk with their cancer care team.
Q: What is the role of cancer centres in managing lymphedema?
A: Cancer centres often have specialized programs to address lymphedema related to cancer treatment. They may offer comprehensive care that includes education, physical therapy, and support services to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Q: How can patients with lymphedema find support?
A: Patients with lymphedema can find support through support groups, online forums, and organizations dedicated to cancer care and lymphedema awareness. Consulting with healthcare providers can also connect patients to resources and specialists.