Understanding Lymphedema in the Hands: Comprehensive Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment
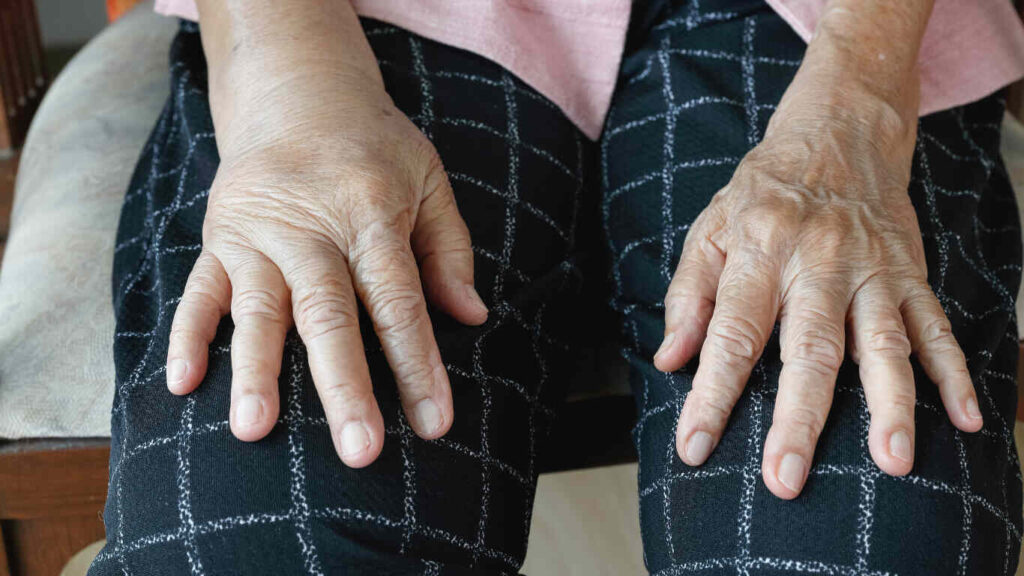
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that often results in swelling in various parts of the body due to issues within the lymphatic system. When it affects the hands, it can significantly impact daily life and quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is vital if you or a loved one manage lymphedema. Let’s explore this condition, from diagnosis to long-term management.
Key Takeaways
- Lymphedema is swelling caused by blockages in the lymphatic system, often resulting from surgery, radiation, or other cancer treatment.
- Early diagnosis and a combination of therapies can help manage symptoms effectively.
- Home-based strategies like skin care, exercise, and diet can reduce swelling and improve comfort.
- Advanced treatment options include manual lymphatic drainage, surgical, and lymph node transfer.
Lymphedema in Hands Treatment: What Are the Best Options?
Treating lymphedema often involves a combination of therapies tailored to individual needs. This ensures that the affected arm or hand receives the care necessary to reduce swelling and improve function.
What is the Most Effective Treatment for Lymphedema?
The effectiveness of treatment for lymphedema largely depends on the condition’s severity. Techniques like manual lymphatic drainage and compression therapy are highly effective in its early stages. These methods promote the movement of lymph fluid through the lymph vessels, helping to reduce swelling.
Vascularized lymph node transfer or other surgical options may be recommended in more advanced cases. These treatments aim to restore the function of the lymphatic system, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications. Your healthcare provider will assess the stages of lymphedema to recommend the best course of action.
How Does Manual Lymphatic Drainage Help?
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique that stimulates lymph flow through the lymph vessels. By targeting the affected arm or hand, MLD can alleviate the swelling caused by lymphedema and improve overall comfort. Regular sessions, often combined with compression garments, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of this treatment.
Can Surgical Treatment Cure Lymphedema?
While lymphedema surgery cannot completely cure the condition, it can significantly reduce its severity. Options like vascularized lymph node transfer involve transplanting healthy lymph nodes to the affected arm or hand, improving drainage, and reducing swelling. Surgery is usually reserved for severe cases of lymphedema, where other treatments have proven insufficient.
Living with Lymphedema: Daily Management Strategies
Managing lymphedema requires ongoing attention to prevent flare-ups and complications. The key is to incorporate a combination of medical therapies and home-based practices.
How Can I Manage Symptoms of Lymphedema at Home?
Home management involves wearing compression garments, elevating the affected arm, and engaging in light exercises to promote circulation. Avoid activities that strain the affected limb, as this can worsen swelling. Regularly practicing manual lymphatic drainage at home, as guided by a professional, is another effective way to manage your symptoms.
What Skin Care Practices Should I Follow?
Skin care is essential to prevent skin infections like cellulitis, which can occur in people with lymphedema. Keep your skin clean and moisturized to avoid cracks that may allow bacteria to enter. Use hypoallergenic lotions and avoid tight clothing or jewelry that could irritate the skin.
Can Diet Help Prevent Lymphedema Swelling?
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and low sodium can help manage swelling. Reducing salt intake minimizes water retention, while anti-inflammatory foods like berries and leafy greens support overall health. Staying hydrated and avoiding processed foods can help keep lymphedema symptoms in check.
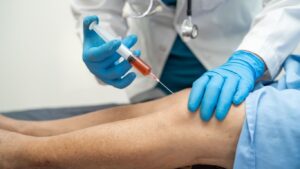
Lymphedema Diagnosis: How Is It Identified?
Accurately diagnosing lymphedema ensures timely treatment and better management outcomes. Medical professionals confirm the condition using a variety of tests and assessments.
What Tests Are Used to Diagnose Lymphedema?
Imaging tests like ultrasounds, MRIs, or lymphoscintigraphy are commonly used to examine the lymphatic system. These tests help identify blockages in the lymph vessels or lymph nodes, which could be causing the swelling. Advanced imaging, like an MRI, provides a detailed view of the affected arm and surrounding tissue.
What Are Common Symptoms of Lymphedema?
Signs and symptoms of lymphedema include persistent swelling, heaviness, and tightness in the affected arm or hand. In some cases, the skin may show changes like hardening or redness. Early detection of these symptoms can lead to more effective treatment.
How Do Medical Professionals Assess Lymphedema Severity?
Doctors assess the severity by evaluating the stages of lymphedema. This ranges from mild swelling that comes and goes to more severe cases involving tissue fibrosis and irreversible swelling. These assessments guide the choice of treatment, whether conservative or surgical.
Lymphedema Causes: What Triggers This Condition?
Understanding what causes lymphedema can help in prevention and management. Both primary and secondary factors play a role in its development.
How Does Breast Cancer Treatment Lead to Secondary Lymphedema?
Breast cancer treatment, particularly surgery and radiation, is a common cause of lymphedema. These procedures can damage or remove lymph nodes, leading to fluid buildup. This type, known as secondary lymphedema, often affects the arms after treatment for breast cancer.
What Are the Risk Factors for Developing Lymphedema?
The risk of developing lymphedema increases with factors such as obesity, repeated infections, and delayed treatment. Radiation treatment for cancer or multiple surgeries can also heighten the risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular monitoring can lower the risk of secondary lymphedema.
Can Primary Lymphedema Occur Without Any Known Cause?
Primary lymphedema can develop due to genetic mutations or congenital disabilities in the lymphatic system. Examples include lymphedema praecox (onset during adolescence) and lymphedema tarda (onset later in life). Although rare, primary lymphedema requires similar management strategies to prevent complications.
Lymphedema Complications: What Should You Be Aware Of?
Left untreated, lymphedema can lead to severe complications that affect both physical and mental well-being.
What Are the Potential Complications of Untreated Lymphedema?
Untreated lymphedema may include chronic swelling, limited mobility, and tissue hardening. In extreme cases, it can lead to lymphangiosarcoma, a rare but aggressive cancer. Regular medical care is essential to avoid these outcomes.
How Can Skin Infections Occur in People with Lymphedema?
Skin infections, such as cellulitis, are a common complication in patients with lymphedema. Swelling can stretch the skin, creating small tears that allow bacteria to enter. Preventing infections involves vigilant skin care and avoiding injuries to the affected arm.
Lymphedema Prevention: How Can It Be Avoided?
Prevention strategies focus on minimizing risk factors and maintaining healthy habits.
What Steps Can I Take to Prevent Lymphedema After Cancer Surgery?
If you’ve undergone cancer surgery, protect your affected limb by avoiding heavy lifting and wearing compression garments during air travel. Promptly treating infections or injuries in the affected arm can help prevent swelling.
Can Exercise Help in Preventing Lymphedema?
Gentle, regular exercise improves circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight, lowering the risk of lymphedema. Activities like swimming, yoga, or walking benefit at-risk individuals.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Reduce the Risk of Developing Lymphedema?
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding tight clothing, and reducing salt intake can significantly reduce the risk of developing lymphedema. Regular check-ups with your doctor ensure early detection and management of potential symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Are the Stages of Lymphedema?
The stages of lymphedema range from mild, intermittent swelling to severe, permanent tissue changes. Early treatment can prevent the progression to later stages.
Can Radiation Treatment Cause Lymphedema?
Yes, radiation treatment for cancer can damage the lymphatic system, leading to secondary lymphedema. Discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider if you’ve undergone such treatments.
What Is the Best Therapy for Lymphedema?
A combination of manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and regular exercise is often the most effective approach to treatment for lymphedema.