Managing Lymphedema and Diabetes: Effective Strategies for Patients
Managing lymphedema in patients with diabetes is a complex task that requires careful attention to both conditions. These two chronic health issues often coexist, and when combined, they can lead to a more significant challenge in overall health management. However, with the proper knowledge and strategies, patients can live healthier lives, minimizing the complications and risks associated with both. This article will explore the effective strategies for managing lymphedema and diabetes together, from treatment options to lifestyle adjustments.
What is Lymphedema and How Does it Relate to Diabetes?
Understanding Lymphedema and its Causes
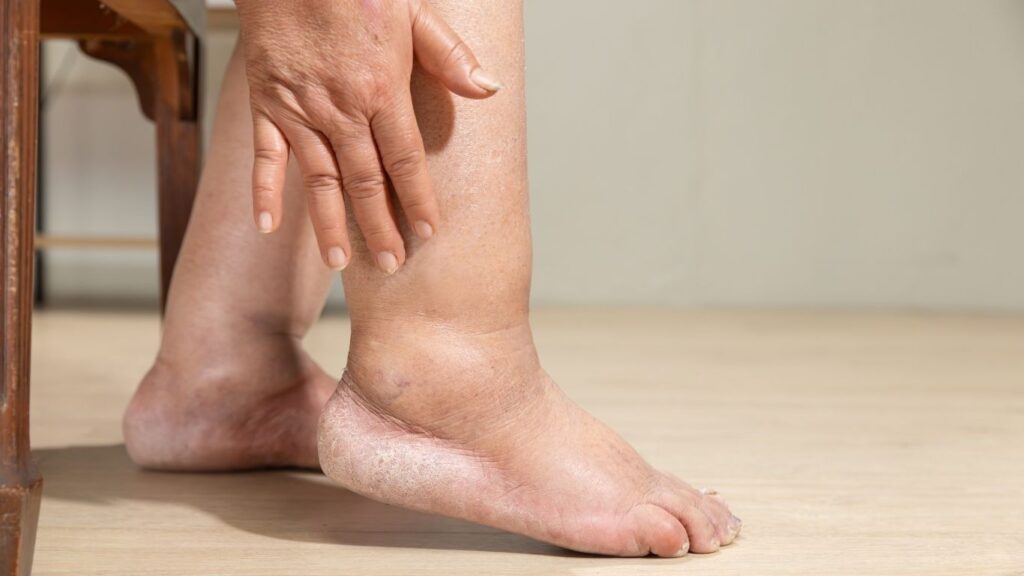
Lymphedema is a condition resulting from the lymphatic system’s failure to properly drain lymphatic fluid, which can lead to abnormal swelling, usually in the limbs. It can be caused by a blockage in the lymphatic vessels or damage to the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is responsible for maintaining the fluid balance in the body, carrying lymph—a colourless fluid containing white blood cells—through lymphatic vessels and nodes. When this system is compromised due to injury, disease, or surgery, excess fluid builds up in the tissue, causing swelling and discomfort.
The Connection Between Diabetes and Lymphedema
Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, can exacerbate the development of lymphedema. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels and nerves, making it difficult for the lymphatic system to function correctly. People with uncontrolled diabetes are more likely to suffer from poor circulation, which further hinders the body’s ability to drain lymphatic fluid. The combination of impaired circulation, increased blood sugar, and nerve damage contributes significantly to the risk of developing lymphedema in diabetic patients.
How Lymphedema Occurs in Patients with Diabetes
In patients with diabetes, especially those with type 2 diabetes or who have had diabetes for many years, there is a higher risk of developing both primary and secondary lymphedema. Secondary lymphedema occurs due to another condition, such as surgery or trauma, that affects the lymphatic system. For individuals with diabetes, the added strain on the vascular and lymphatic systems can lead to the development of secondary lymphedema, often in the lower limbs. This creates a cycle where poor lymphatic flow, combined with high glucose levels, accelerates the progression of both conditions.
How Can You Manage Lymphedema with Diabetes?
Effective Treatment of Lymphedema for Diabetic Patients
Managing lymphedema in patients with diabetes involves a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Compression therapy is one of the most effective treatments for lymphedema, as it helps reduce swelling by applying consistent pressure to the affected limb, encouraging the lymphatic fluid to drain more efficiently. Patients should also consider manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) techniques, where a trained therapist gently massages the lymphatic system to promote lymphatic flow and reduce swelling.
Importance of Compression Therapy in Managing Lymphedema
Compression therapy is essential for reducing swelling in patients with lymphedema. It applies controlled pressure to the affected areas, encouraging the lymphatic vessels to pump more effectively and preventing fluid buildup in the tissue. In diabetic patients, compression therapy can also help manage the swelling in the lower limbs, a common problem. Special compression garments, such as stockings, sleeves, or bandages, are commonly used. Patients must work with a healthcare provider to determine the best compression level for their needs.
Role of Manual Lymphatic Drainage in Lymphedema Management
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is another crucial component in managing lymphedema. This hands-on technique involves gentle, rhythmic massage movements stimulating the lymphatic system to promote fluid drainage. MLD can be especially beneficial for diabetic patients because it aids in improving lymphatic flow, reducing swelling, and easing discomfort. Studies have shown that MLD effectively treats primary and secondary lymphedema, helping alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
What are the Best Practices for Managing Blood Sugar Levels in Patients with Lymphedema?
Understanding the Impact of Blood Sugar Levels on Lymphedema
In diabetic patients, managing blood sugar levels is crucial for the overall success of lymphedema treatment. Uncontrolled blood glucose levels can impair the lymphatic system’s function, exacerbate tissue swelling, and increase the risk of infection. High glucose levels contribute to poor circulation and can damage blood vessels, hindering the lymphatic system’s ability to function effectively. This underscores the importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels through proper diet, exercise, and medication.
Dietary Recommendations for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
For patients with type 2 diabetes, a balanced and controlled diet plays a key role in managing both blood sugar levels and lymphedema. A fibre-rich diet, low in processed sugars and high in lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, can help regulate glucose levels. Additionally, foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as omega-3 fatty acids, can aid in reducing swelling and improving overall health. Patients should avoid excessive sodium, which can lead to fluid retention and worsening lymphedema symptoms.
Monitoring and Controlling Glucose Levels Effectively
To manage lymphedema effectively, patients with diabetes should regularly monitor their blood glucose levels and follow their doctor’s recommendations for insulin use or other medications. The goal is to keep blood sugar levels within a target range to reduce the risk of complications. Proper diabetes management not only helps control swelling but also decreases the risk of developing secondary conditions like diabetic neuropathy and cardiovascular issues that could further exacerbate lymphedema.
What Surgical Treatments Are Available for Lymphedema?
Overview of Surgical Options for Managing Lymphedema
In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions may be considered for managing lymphedema. Several options are available, including lymphatic venous anastomosis (LVA), vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT), and liposuction. These procedures aim to improve lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling by creating new lymph flow pathways or removing excess tissue. Surgical treatments are typically reserved for severe cases of lymphedema where other therapies have not been successful.
When to Consider Surgical Treatment for Patients with Diabetes
For patients with diabetes, surgery is usually a last resort when conservative treatments such as compression therapy and manual lymphatic drainage fail to provide relief. Due to the risks associated with diabetes, including poor wound healing and infection, surgical interventions must be carefully considered. However, if a patient suffers from severe lymphedema affecting their quality of life, surgery may provide long-term benefits.
Risks and Benefits of Surgical Intervention
While surgical treatments for lymphedema can be effective, they come with potential risks, particularly for diabetic patients. The primary risks include infection, poor healing, and complications arising from impaired circulation. However, the benefits include significantly reduced swelling and improved limb function, which can drastically enhance the quality of life. Patients should consult their healthcare team to weigh the pros and cons before surgery.
How Does Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Help in Managing Lymphedema?
Effects of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression on Lymphedema
Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses inflatable sleeves or cuffs to apply pressure to the affected limbs. It helps stimulate the lymphatic vessels to promote the drainage of lymphatic fluid. Studies have shown that IPC can reduce swelling and improve lymphatic flow, making it an effective tool in managing lymphedema in patients with diabetes. The periodic compression cycles enhance the movement of lymph, which prevents the buildup of excess fluid in the tissue.
Research Findings: Randomized Controlled Trials on Compression Therapy
Several randomized controlled trials have confirmed the benefits of intermittent pneumatic compression in managing lymphedema. These studies have shown that IPC significantly reduces limb volume and improves overall limb function in primary and secondary lymphedema patients. For diabetic patients who may also suffer from poor circulation, the use of IPC can provide an effective and non-invasive treatment option for managing swelling and improving lymphatic flow.
Integrating Intermittent Pneumatic Compression into Treatment Plans
For optimal results, intermittent pneumatic compression should be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan that includes compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and blood sugar management. By combining these therapies, patients with diabetes can effectively manage lymphedema, reduce swelling, and enhance their overall quality of life.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Help in Managing Both Conditions?
Exercise and Physical Activity Recommendations
Regular exercise is vital for managing both lymphedema and diabetes. It helps improve circulation, manage blood sugar levels, and maintain a healthy weight. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for patients with lymphedema, as they encourage lymphatic flow without putting undue stress on the affected limbs.
Stress Management Techniques for Diabetic Patients
Stress can negatively impact both blood sugar levels and the progression of lymphedema. Therefore, managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga, is essential for patients with diabetes and lymphedema. Lowering stress levels can help stabilize glucose levels and reduce swelling-related inflammation.
Importance of Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular check-ups are crucial for patients managing both lymphedema and diabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels, assessing the progression of lymphedema, and adjusting treatment plans as necessary can help prevent complications. Regular visits to healthcare professionals ensure that the patient’s treatment is on track and that both conditions are effectively managed.
Conclusion
Managing lymphedema in patients with diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and careful monitoring of blood sugar levels. Individuals can effectively manage both conditions by incorporating therapies like compression, manual lymphatic drainage, and intermittent pneumatic compression, along with making key lifestyle adjustments. With the right strategies, patients with diabetes can reduce swelling, improve lymphatic function, and enjoy a better quality of life.
FAQs
Q: What is lymphedema, and what are its common causes?
A: Lymphedema is a condition characterized by swelling due to the accumulation of lymph fluid, often caused by a blockage in the lymphatic system. Common causes include primary lymphedema, cancer treatment (especially for breast cancer), and damage to the lymphatic vessels due to injury or surgery.
Q: How is breast cancer related to lymphedema?
A: Breast cancer-related lymphedema occurs when lymph nodes are removed or damaged during cancer treatment, affecting the drainage of lymph fluid and leading to swelling, particularly in the upper extremities.
Q: What are the effective strategies for managing lymphedema?
A: Effective strategies for managing lymphedema include compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage, exercises to promote lymph flow, and skin care to prevent infections. Patients should consult a healthcare professional for personalized lymphedema care.
Q: Can diabetes mellitus affect the risk of developing lymphedema?
A: Yes, people with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, may have a higher risk of developing lymphedema due to possible damage to the lymphatic vessels and poor circulation, which can impede the healing process.
Q: What is the connection between diabetes and lymphedema treatment?
A: Lymphedema treatment in patients with diabetes may require special considerations, such as careful monitoring of blood sugar levels and ensuring that compression therapies do not impede circulation, as this can affect the healing process.
Q: Are there preventative measures for lymphedema in patients with breast cancer?
A: Yes, preventative measures for lymphedema may include educating patients about the risk of lymphedema associated with breast cancer treatment, encouraging exercise, and advising on skin care to prevent infections that could exacerbate lymphedema.
Q: What types of lymphedema are most common in diabetes patients?
A: Lower limb lymphedema and bilateral lower extremity lymphedema are commonly observed in diabetes patients, as the condition can lead to swelling in the legs and feet due to fluid retention.
Q: How can patients recognize the signs of lymphedema?
A: Patients should look for signs such as swelling in the arms or legs, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, restricted range of motion, and changes in skin texture. Early recognition is crucial for effective lymphedema treatment.
Q: What lifestyle changes can help manage lymphedema symptoms?
A: Lifestyle changes that can help manage lymphedema symptoms include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, following a balanced diet, and practising good skin care to minimize the risk of infections.