Lymphedema is a condition that causes swelling due to the buildup of lymphatic fluid in the tissues. While it can affect anyone, specific populations are at higher risk of developing the condition. For those in high-risk groups, prevention is key to reducing the severity and impact of lymphedema. This article will explore how to prevent lymphedema in high-risk populations, providing practical tips and strategies to manage and reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
Understanding Lymphedema and Its Causes
Before discussing prevention strategies, it is essential to understand lymphedema and why certain individuals are more susceptible to it. Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system, which is responsible for transporting lymph fluid, becomes compromised. This can be due to damage to lymphatic vessels, nodes, or tissues, leading to fluid accumulation and swelling, usually in the arms, legs, or other areas of the body.
Types of Lymphedema
Lymphedema is generally classified into two types:
- Primary Lymphedema: This form is congenital, which is present at birth or develops later in life due to genetic factors affecting the lymphatic system.
- Secondary Lymphedema: This is more common and occurs due to an injury or damage to the lymphatic system. Common causes include surgery (especially cancer treatments), radiation therapy, or infections that impact the lymphatic system.
Who Are the High-Risk Populations?
Certain groups of people are at a higher risk of developing lymphedema. Understanding these high-risk populations is crucial for targeting preventive measures effectively.
Cancer Patients and Survivors
Cancer treatments, particularly surgery and radiation, can damage or remove lymph nodes, leaving the lymphatic system vulnerable to fluid buildup. Individuals undergoing treatments for breast cancer, melanoma, or prostate cancer, for instance, are particularly at risk.
Obese Individuals
Obesity is another significant risk factor for developing lymphedema. Excess weight can put extra pressure on the lymphatic system, making it harder for the body to drain excess fluid. This pressure can lead to swelling and increase the risk of fluid retention in the tissues.
People with Vascular Disease
Conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), varicose veins, or other circulatory issues can impair the proper flow of lymphatic fluid. Due to poor circulation and fluid buildup in the affected areas, individuals with these vascular diseases are more likely to develop lymphedema.
Post-Surgical Patients
Surgeries that involve the removal of lymph nodes or vessels can leave the body at risk for lymphedema. Patients who have undergone procedures such as mastectomies, prostate surgeries, or pelvic surgeries should be particularly cautious, as these procedures often affect the lymphatic system.
People with Infections or Trauma
Infections, such as cellulitis, or physical trauma to the skin and underlying tissues, can damage the lymphatic system. This damage may lead to swelling and fluid retention in the affected areas.
Prevention Strategies for High-Risk Populations
Taking steps to prevent lymphedema is essential for those in high-risk groups. While lymphedema cannot always be avoided, several strategies can significantly reduce the risk of its development or progression.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity increases the likelihood of developing lymphedema, as the excess weight can impede the lymphatic system’s ability to drain fluid effectively. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is one of the best ways to prevent lymphedema, particularly for those at a higher risk due to obesity.
The Role of Exercise in Prevention
Regular physical activity, especially exercises that promote circulation and lymphatic flow, is highly beneficial. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and yoga can help enhance fluid movement throughout the body, reducing the risk of fluid retention and swelling.
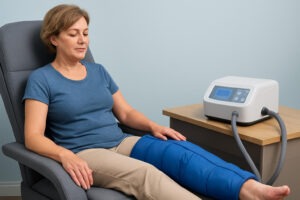
2. Compression Therapy
Compression garments, such as sleeves, stockings, or bandages, are often used to prevent or manage lymphedema. These garments apply controlled pressure to the affected areas, helping to reduce swelling and prevent fluid buildup. For high-risk individuals, wearing compression garments during high-risk activities, such as long periods of standing or sitting, may help prevent lymphedema from developing.
When to Use Compression Garments
Compression garments are beneficial for recovering from surgery or cancer treatments, as they help maintain proper lymphatic drainage. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the correct type of compression garment and ensure it is used correctly.
3. Lymphatic Drainage Massage
Lymphatic drainage massage is a specialized technique performed by trained therapists that encourages the flow of lymphatic fluid. It stimulates the lymphatic system by using gentle, rhythmic strokes, helping the body remove excess fluid before it builds up and causes swelling.
Benefits of Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic drainage massage can be an effective preventive measure for high-risk individuals. It helps prevent lymphedema and promotes overall wellness by improving circulation and reducing fluid retention.
4. Skin Care and Hygiene
Proper skin care is essential for preventing infections, which can worsen or trigger lymphedema. Individuals at high risk should keep their skin clean and moisturized, especially in areas prone to swelling. Avoiding cuts, scratches, or other injuries that can lead to infections is equally essential, as these can increase the risk of developing lymphedema.
Preventing Infections
Daily skin checks and proper wound care are essential for those in high-risk groups. Promptly cleaning and treating cuts or abrasions can help prevent infection and the subsequent development of lymphedema.
5. Elevating the Affected Area
For individuals at high risk, elevating the affected limb or area of the body when possible can help reduce swelling and encourage fluid drainage. Sleeping with the head elevated or propping up a swollen arm or leg during rest can also help reduce the development of lymphedema.
6. Avoiding Heat and Extreme Temperatures
Excessive heat can dilate blood vessels and increase fluid retention, making it harder for the lymphatic system to drain excess fluid. High-risk individuals should avoid hot showers, saunas, or other activities that expose the body to extreme heat. On the other hand, cold compresses can help reduce swelling and prevent the progression of lymphedema.
7. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Living a healthy lifestyle can play a crucial role in preventing lymphedema. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients, staying hydrated, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle factors help support the lymphatic system and promote overall health.
8. Regular Monitoring and Early Intervention
For individuals at high risk, regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential. Early detection of swelling or fluid retention signs can help prevent lymphedema from worsening. Routine monitoring, particularly after surgery or cancer treatment, can ensure that potential issues are addressed before they become more severe.
9. Psychological Support and Stress Management
Dealing with the risk of lymphedema can be emotionally challenging, especially for individuals who have undergone cancer treatments or surgery. Psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, can help individuals cope with the stress and anxiety that may accompany the possibility of developing lymphedema.
10. Educating at-Risk Populations
One of the most effective prevention strategies is educating high-risk individuals about lymphedema and how to manage it. Providing information on the importance of self-care, early warning signs, and prevention techniques can empower individuals to take proactive steps in their health care.
Conclusion
While lymphedema cannot always be prevented entirely, there are several steps that high-risk populations can take to minimize their chances of developing the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, using compression garments, and engaging in lymphatic drainage massage are all effective prevention methods. With the right approach, individuals in high-risk groups can manage their health and reduce the likelihood of lymphedema affecting their lives.
FAQs
Q1: Can I prevent lymphedema if I’ve already had surgery that affected my lymphatic system?
You can still reduce the risk by following preventive measures such as wearing compression garments, engaging in lymphatic drainage massage, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Q2: How often should I use compression garments?
It depends on your risk and the advice of your healthcare provider. Typically, wearing compression garments during high-risk activities or throughout the day can be helpful.
Q3: Is exercise essential for preventing lymphedema?
Regular exercise helps improve circulation and lymphatic flow, significantly reducing the risk of fluid retention and swelling.
Q4: Can lymphedema be treated once it develops?
While lymphedema cannot be cured, it can be managed effectively with compression therapy, massage, and lifestyle adjustments.
Q5: What should I do if I notice swelling in my arms or legs after surgery?
If you notice any swelling, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Early intervention can help prevent the development of lymphedema.