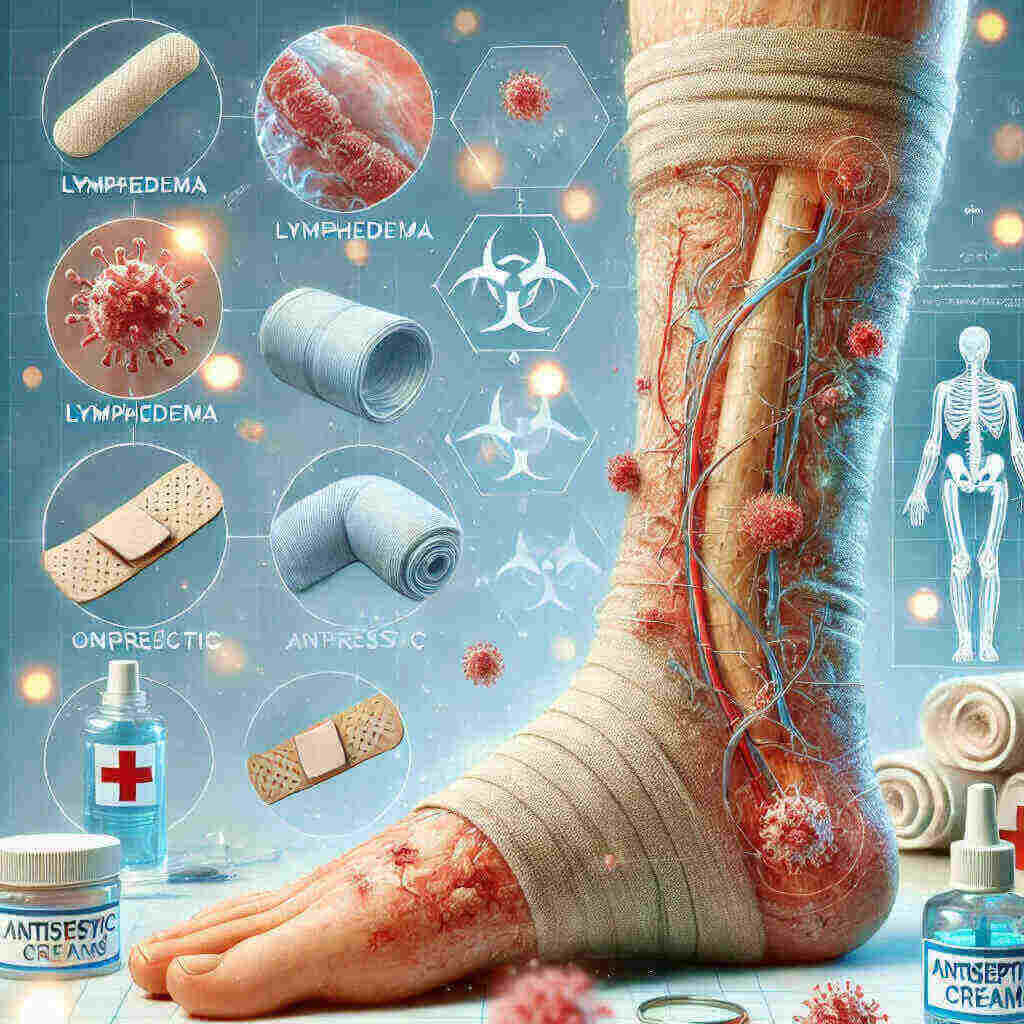
Lymphedema and Infection: Understanding the Risks and Protecting Your Health
Living with lymphedema can be challenging, particularly when it comes to managing the risk of infection. If you’re one of the many people affected by lymphedema, it’s essential to understand the connection between lymphedema and infection and how to protect your health. In this blog post, we’ll explore what causes infections in lymphedema patients, how to recognize the signs of an infection and the best prevention and treatment strategies. Let’s dive into understanding the risks and protecting your health.
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphedema increases the risk of infection, particularly in the arms and legs.
- Cellulitis is a common skin infection in lymphedema patients.
- Early intervention and lymphedema treatment can help prevent complications.
- Proper skin care, the use of compression garments, and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
- Breast cancer treatment or surgery can increase the risk of developing secondary lymphedema, making infection prevention critical.
What causes infections in lymphedema patients?
How does lymphedema increase the risk of infection?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system cannot properly drain tissue fluid, leading to swelling in the arms and legs. This swelling, particularly in the soft tissue, can cause the skin to stretch, making it more susceptible to injury. When the skin is compromised, bacteria and other pathogens can easily enter the body, leading to infections. Additionally, the impaired flow of lymph vessels means that the body’s immune system cannot effectively clear infections from the affected areas, further increasing the risk of infection.
The chronic nature of lymphedema often leads to skin infections, particularly in areas that are frequently exposed to friction or injury. If not properly managed, lymphedema can result in recurrent infections that can worsen the condition over time, leading to a more severe form of lymphedema. Early intervention and consistent care are critical to managing this risk.
What types of infections are common in lymphedema?
One of the most common skin infections in lymphedema patients is cellulitis, a bacterial infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin. Cellulitis often occurs when bacteria enter the body through breaks in the skin, such as cuts or insect bites. The swelling associated with lymphedema can create tiny cracks in the skin, allowing bacteria to enter more easily. Other infections that may affect lymphedema patients include fungal and viral infections, although cellulitis remains the most prevalent and dangerous.
In addition to cellulitis, infections in lymphedema patients can also lead to the development of abscesses or more severe complications like sepsis if left untreated. Preventing disease is vital for maintaining overall health and preventing further complications related to lymphedema.
Can cancer treatment lead to lymphedema-related infections?
Yes, cancer treatments like breast cancer treatment or cancer surgery can significantly increase the risk of developing lymphedema and subsequently lead to infections. Radiation treatment for cancer, in particular, can damage lymph nodes, causing secondary lymphedema. When the lymph nodes are damaged or removed during cancer surgery, the lymphatic system becomes impaired, making it difficult for the body to drain fluids effectively.
Secondary lymphedema is a common complication for cancer survivors, particularly those who have had breast cancer surgery or radiation. This condition increases the risk of infection in affected limbs, making regular monitoring and early intervention essential.
How can I recognize signs of infection in lymphedema?
What are the early symptoms of cellulitis in lymphedema?
Recognizing the early signs of infection is crucial for preventing serious complications. Cellulitis is often one of the first signs of a disease in lymphedema patients, and its symptoms may include:
- Redness or warmth in the affected area
- Increased swelling or pain
- Blisters or sores on the skin
- Fever or chills
If you notice any of these symptoms, seeking immediate medical attention is important to prevent the infection from spreading. Ignoring the early signs of cellulitis can lead to more severe infections that may require hospitalization and intensive treatment.
When should I seek medical attention for lymphedema-related infections?
You should seek medical attention as soon as you notice any signs of infection. If you experience persistent swelling, redness, warmth, or pain, especially in lymphedema, consult your doctor or a therapist. Early diagnosis and treatment can help fight infection and prevent complications. In some cases, if the disease worsens or spreads rapidly, antibiotics may be required to treat the infection.
Regular monitoring and prompt action are key to managing lymphedema complications and preventing life-threatening infections. If you have any doubts about experiencing an infection, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and seek professional medical help.
What are the best prevention strategies for lymphedema-related infections?
How can proper skin care reduce the risk of infection?
Proper skin care is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of infection in lymphedema patients. Keeping the skin clean, moisturized, and protected from injury can help prevent breaks in the skin that provide a pathway for bacteria. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers to avoid irritating the skin, and always avoid cuts, scrapes, or other injuries.
If you have lymphedema, it’s also important to avoid scratching the skin, damaging the surface and increasing the risk of infection. Regularly check your skin for signs of injury or infection and take immediate action if you notice anything unusual.
Are compression garments effective in preventing infections?
Compression garments are an important part of lymphedema treatment and can help reduce swelling, improve lymphatic flow, and reduce the risk of infection. Compression garments help prevent excessive swelling and encourage fluid movement through the lymph vessels by providing gentle pressure. This helps with lymphedema symptoms and reduces the likelihood of infection by improving the body’s ability to clear waste and harmful bacteria.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent lymphedema complications?
In addition to wearing compression garments and practising good skin care, lifestyle changes can also help reduce the risk of developing lymphedema complications. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting can all help manage lymphedema symptoms and improve overall circulation.
Regular exercise, particularly low-impact activities like walking or swimming, can help reduce swelling and improve the function of the lymphatic system. Staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet also supports overall health and helps prevent lymphedema flare-ups.
What treatment options are available for infections in lymphedema?
How are antibiotics used to treat lymphedema-related infections?
Antibiotics are often the first line of defence when treating cellulitis and other infections in lymphedema patients. If you develop an infection, your doctor will likely prescribe an oral or intravenous antibiotic to help eliminate the bacteria. In more severe cases, hospitalization and IV antibiotics may be required.
What role does manual lymphatic drainage play in infection treatment?
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique that can help improve lymphatic flow and reduce swelling. MLD is often used in lymphedema treatment to help patients manage swelling and prevent infection. By improving the function of the lymphatic system, MLD helps the body clear waste and bacteria, reducing the likelihood of infection.
Can lymphedema-related infections be life-threatening?
What are the potential complications of untreated infections?
If left untreated, lymphedema-related infections can lead to severe complications, such as sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by widespread infection. Other complications include abscesses, tissue necrosis, and further damage to the lymphatic system, which can worsen lymphedema.
How quickly can cellulitis progress in lymphedema patients?
Cellulitis can progress rapidly in lymphedema patients, especially if the infection is untreated. In some cases, cellulitis can spread within hours, leading to more severe infections and complications. This is why seeking medical attention immediately if you suspect an infection is important.
Are there specific considerations for breast cancer survivors with lymphedema?
How does radiation treatment affect infection risk in lymphedema?
Radiation treatment for breast cancer increases the risk of developing lymphedema and can also damage the lymph nodes, making the body more vulnerable to infection. Cancer survivors who have undergone radiation or surgery should be extra cautious about infection prevention and work closely with their healthcare team to manage lymphedema and minimize the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Managing lymphedema and infection risks requires a proactive approach. Understanding the connection between lymphedema and infection, recognizing early signs, and implementing effective prevention strategies can protect your health and reduce the risk of serious complications. Regular lymphedema treatment, including compression garments, skincare, and lifestyle modifications, can help you manage the condition and maintain your overall well-being.
If you have lymphedema, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for infection prevention. Early intervention and regular care can help keep you healthy and reduce the impact of lymphedema on your daily life.