Lymphedema and Cancer: Understanding the Connection After Breast Cancer Treatment
Lymphedema is one of those conditions that can catch you off guard, especially when you’ve already faced the immense challenge of breast cancer treatment. As a survivor, your journey to recovery often includes learning about the potential long-term side effects, and lymphedema is a significant one. But what exactly is lymphedema, and how does it relate to cancer? Let’s dive in and explore how these two are connected, particularly for breast cancer survivors and others who have undergone cancer treatment.
What is Lymphedema, and How Does It Relate to Cancer?
Understanding Lymphedema and Its Causes
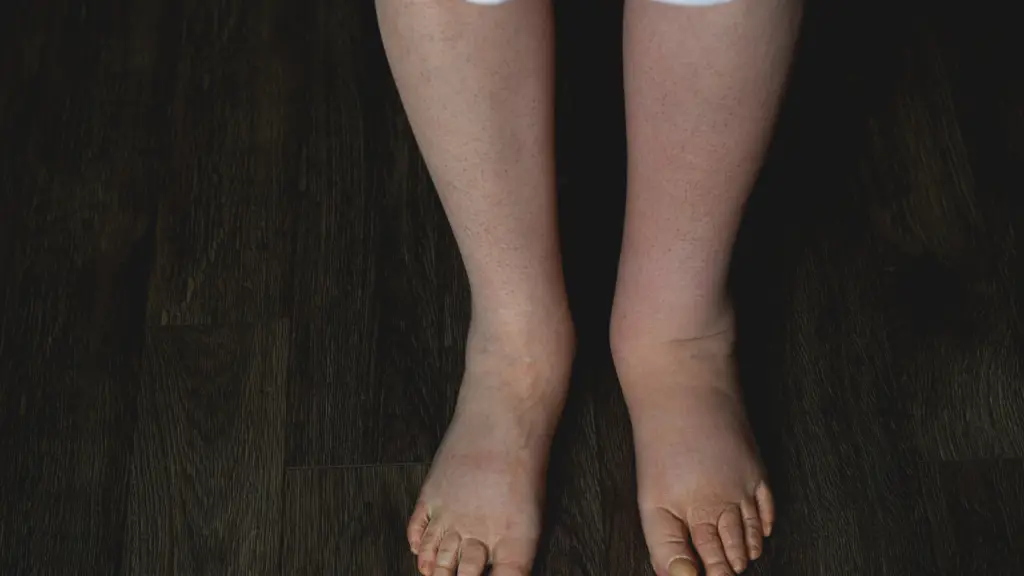
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by swelling, often in the arms or legs, caused by a build-up of lymph fluid. It occurs when the lymphatic system—which helps maintain fluid balance and supports immune function—becomes damaged or blocked. In cancer patients, lymphedema usually develops as a result of treatments like cancer surgery, radiation treatment, or the removal of lymph nodes. These treatments can inadvertently block the flow of lymph fluid, leading to painful and sometimes debilitating swelling.
The lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes and vessels, plays a crucial role in draining excess fluids and removing waste products. However, when the lymph nodes are removed or damaged during breast cancer surgery, the body struggles to manage fluid properly, which can cause lymphedema to develop. Though it is most commonly seen in breast cancer survivors, lymphedema can also affect those treated for other types of cancer.
The Link Between Lymphedema and Cancer Treatment
There’s no denying that cancer treatment saves lives, but the unfortunate reality is that these treatments can also have long-lasting side effects. Lymphedema is one of the most common complications, particularly after breast cancer treatment. Surgical procedures to remove cancer, especially when combined with radiation treatment, can damage the lymphatic system and increase the risk of lymphedema.
It’s important to note that not everyone who undergoes cancer treatment will develop lymphedema, but understanding the risks can help with prevention and early intervention. Women treated for breast cancer, in particular, may be at higher risk of developing lymphedema due to the removal of lymph nodes in the underarm area. As many as 30% of breast cancer survivors will experience some degree of lymphedema after surgery.
Types of Cancer Most Associated with Lymphedema
While breast cancer is the type most commonly linked to lymphedema, other types of cancer can also lead to the condition. Head and neck cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and melanoma are examples of cancers that can damage the lymphatic system and increase the risk of lymphedema. Any cancer that affects the lymph nodes or requires their removal has the potential to cause lymphedema. Understanding your risk factors and working with your medical team can help mitigate this risk.
What Are the Symptoms of Lymphedema in Cancer Patients?
Early Signs of Lymphedema After Cancer Treatment
In many cases, lymphedema develops gradually, so it’s crucial to recognize the early signs. Some common symptoms of lymphedema include a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb, swelling, and restricted movement. For those who have undergone breast cancer treatment, early signs of lymphedema often appear in the arm, hand, or chest area.
It’s important to be vigilant about these symptoms because early intervention can significantly improve lymphedema management. If you notice any of these signs of lymphedema after your cancer treatment, seek medical advice right away.
How Lymphedema Affects Arms and Legs
Lymphedema can occur in different body areas, but it’s most common in the arms or legs. After breast cancer, it typically affects the arm on the side where the lymph nodes are removed. In more severe cases, lymphedema can also impact your ability to move your limbs comfortably. Swelling can become so significant that it affects daily activities, from getting dressed to lifting objects.
For those who had pelvic or prostate cancer treatments, lymphedema may develop in the legs. This swelling can be painful and increases the risk of infection due to compromised lymph flow.
Recognizing Lymphedema in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors
Patients who survive head and neck cancer can experience a different form of lymphedema. The swelling here may not be as visible as in the arms or legs, but it can be just as uncomfortable, often causing swallowing, breathing, and speaking issues. Recognizing the unique symptoms in this population is vital for providing appropriate care. If you’re a you’re neck cancer survivor, be on the lookout for these symptoms.
Can Lymphedema Be Prevented During Cancer Treatment?
Strategies to Lower Your Risk of Developing Lymphedema
Preventing lymphedema isn’t always possible, but you can lower your risk. One of the most effective ways to prevent lymphedema is through careful monitoring and self-care during and after cancer treatment. Keeping the skin and nails clean, exercising regularly, and avoiding injury to the arm or leg at risk are all proactive measures.
Compression garments, which help prevent fluid build-up, can also be beneficial, especially for high-risk people. These strategies won’t eliminate your risk of lymphedema, but they can help you lower it.
The Role of Lymph Node Preservation in Cancer Surgery
Another critical aspect of prevention is lymph node preservation during cancer surgery. Today, surgeons aim to minimize the number of lymph nodes removed, especially during breast cancer surgeries. By preserving as many lymph nodes as possible, doctors can significantly reduce the likelihood of lymphedema. This approach, combined with early intervention, can make a substantial difference in whether or not a patient develops the condition.
Importance of Early Intervention and Education
Education and awareness are vital to preventing and managing lymphedema. Early detection and intervention can often prevent lymphedema from becoming severe. Many hospitals and cancer centres offer educational resources for cancer survivors, so take advantage of these programs. Knowing the signs of lymphedema and how to manage the condition from the start can significantly improve your quality of life.
What Are the Risk Factors for Developing Lymphedema After Cancer?
Impact of Different Cancer Treatments on Lymphedema Risk
Not all cancer treatments carry the same risk for lymphedema. Radiation treatment, surgery, and chemotherapy can all contribute to the development of lymphedema, but the exact risk factors vary depending on the type of cancer and the specific treatments used. For example, breast cancer survivors who undergo lymph node removal are at higher risk than those who don’t.
Understanding how cancer treatment impacts your risk of developing lymphedema can help you take proactive measures. Discussing your concerns with your oncologist can also clarify your risks.
Genetic and Lifestyle Factors Influencing Lymphedema Development
Certain genetic and lifestyle factors can also influence whether or not you develop lymphedema. For instance, people with a family history of the condition or other lymphatic disorders may be more prone to it. Additionally, being overweight or obese can increase your risk of lymphedema following cancer treatment. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and weight management, can reduce your chances of developing lymphedema.
Time Frame for Lymphedema Onset Post-Cancer Treatment
One of the challenging aspects of lymphedema is that it can develop at any time after cancer treatment—sometimes even months or years after treatment. This delayed onset makes it difficult for patients to know when to be vigilant. Even if you’ve been cancer-free for several years, it’s essential to remain aware of the potential for lymphedema and report any symptoms to your healthcare provider as soon as they arise.
How is Lymphedema Treated in Cancer Survivors?
Conservative Management Techniques for Lymphedema
For most cancer survivors, the treatment of lymphedema involves a combination of conservative management techniques. Compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage (a specialized type of massage), and exercise are all part of the standard care routine for managing lymphedema. These treatments help to move lymph fluid out of the affected area and prevent fluid build-up.
Good skin care is essential to avoid infections, which can worsen lymphedema. Although lymphedema isn’t cured, these management techniques can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
The Role of Certified Lymphedema Therapists in Treatment
A certified lymphedema therapist can be a crucial part of your treatment team. These professionals are trained in the latest techniques for treating lymphedema, including manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and exercise recommendations. If you’ve beeyou’venosed with lymphedema, working with a certified lymphedema therapist can help you develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs.
Innovative Treatments and Ongoing Research
Ongoing research is continually exploring new ways to treat lymphedema more effectively. From surgical interventions to medications, advancements in lymphedema treatment offer new hope to those affected. In some cases, microsurgery to restore lymphatic flow or remove excess tissue may be an option for those with severe or refractory cases. Staying informed about these emerging treatments is crucial for cancer survivors.
Living with Lymphedema: What Cancer Survivors Need to Know
Daily Management Strategies for Lymphedema
Living with lymphedema requires daily attention and care, but with the right strategies, the condition can be kept under control. Regular use of compression garments, staying active, and keeping the affected area clean and moisturized are all essential components of lymphedema management. If you’re struggling with managing the condition independently, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider for additional support.
Long-Term Effects of Lymphedema on Quality of Life
The long-term effects of lymphedema can vary from person to person. For some, the condition remains mild and manageable with routine care. However, in more severe cases of lymphedema, the swelling and discomfort can significantly impact your quality of life. Chronic pain, limited mobility, and the risk of infections can make daily activities more challenging, but with proper care, these issues can often be minimized.
Support Resources for Cancer Survivors with Lymphedema
If you’re living with lymphedema, you’re not you’re. Many support groups, both online and in person, can connect you with others who understand what you’re going through. Organizations like the National Cancer Institute and other cancer support services offer valuable resources for people with lymphedema. You can also ask your healthcare provider for recommendations on local support groups or counselling services to help you cope with the emotional and physical challenges of living with the condition.
Closing Thought
Lymphedema is a common yet often overlooked side effect of cancer treatment, particularly for breast cancer survivors. While there is no way to completely prevent or cure it, understanding the risk factors and early signs of lymphedema can empower you to take action and seek treatment immediately. With the right strategies, including working with a certified lymphedema therapist, maintaining an active lifestyle, and utilizing compression garments, it is possible to live well with lymphedema and improve your overall quality of life. If you or a loved one has been treated for breast cancer or any other type of cancer, it’s essential to stay informed and proactive about managing the condition.
FAQ
- What is lymphedema, and how do cancer treatments cause it? Lymphedema is swelling due to a build-up of lymph fluid when the lymphatic system is damaged. Cancer treatments, such as radiation or lymph node removal, can block the normal flow of lymph fluid, which can cause lymphedema to develop in the affected area.
- Can lymphedema be prevented during breast cancer treatment? While lymphedema cannot always be prevented, there are strategies to lower your risk. These include practising good skin care, exercising, using compression garments, and preserving lymph nodes during cancer surgery. Early intervention also plays a crucial role in preventing severe lymphedema.
- What are the early signs of lymphedema, and how can I recognize them? Early signs of lymphedema include swelling, a feeling of heaviness, tightness in the affected limb, and reduced flexibility. If you notice these signs of lymphedema in your arm or leg after cancer treatment, it’s essential to seek medical advice right away.
- How is lymphedema treated in cancer survivors? Treatment for lymphedema includes conservative management techniques such as compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, exercise, and skincare. Working with a certified lymphedema therapist can help you develop a personalized treatment plan that fits your needs.
- Can lymphedema develop years after cancer treatment? Yes, lymphedema can occur even years after cancer treatment. Although it often appears within a few months after cancer surgery, lymphedema can develop much later. This is why staying aware of the potential symptoms is essential, even long after your cancer treatment.