Lymphedema is a condition that can significantly impact individuals, particularly those who have undergone cancer treatment, such as breast cancer surgery or radiation therapy. To effectively support a loved one dealing with this condition, family and friends must understand lymphedema, its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of lymphedema and how to educate your family and friends about this often-misunderstood condition.
What is Lymphedema and What are the Signs and Symptoms?
Understanding the Causes of Lymphedema
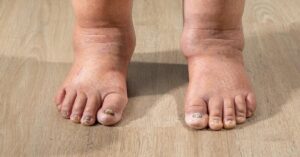
Lymphedema occurs when there is an accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, leading to swelling in the affected area, which is often an arm or leg. This condition can arise from various causes, including damage to the lymphatic system due to cancer treatment, surgery, or congenital issues. Primary lymphedema is a rare genetic condition that can develop at birth or later in life, while secondary lymphedema is more common and generally results from trauma to the lymphatic system, such as lymph node removal during cancer surgery. Understanding these causes is essential for recognizing the risk factors and signs of lymphedema.
Common Signs of Lymphedema
The signs and symptoms of lymphedema can vary, but they often include noticeable swelling in the affected limb, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, and restricted movement. Other symptoms of lymphedema may include discomfort or pain in the swollen area, and in some cases, skin changes such as thickening or hardening. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for effective management and treatment. People with lymphedema may also experience feelings of anxiety or depression due to the visible changes in their bodies and the challenges of living with this chronic condition.
Stages of Lymphedema: What to Look For
Lymphedema symptoms can progress through various stages, making it essential to monitor changes closely. In the early stage, swelling may be soft and can be reduced with elevation or compression. As the condition progresses, the swelling may become more pronounced and persistent, leading to fibrosis and skin changes in later stages. Understanding the stages of lymphedema can help individuals and their families identify the severity of the condition and seek appropriate treatment options sooner rather than later.
How Can I Help My Family and Friends Prevent Lymphedema?
Ways to Prevent Lymphedema in At-Risk Individuals
Preventing lymphedema is particularly important for individuals at risk, such as those who have undergone breast cancer treatment or lymph node removal. Simple lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of lymphedema occurrence. Encouraging regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good skincare can all contribute to lymphatic health. Families can play a supportive role by helping their loved ones incorporate these practices into their daily routines, thereby fostering a healthier lifestyle that may help prevent lymphedema from developing.
Reducing the Risk After Cancer Treatment
After cancer treatment, individuals may face an increased risk of lymphedema due to the removal or damage of lymph nodes during surgery or radiation therapy. It is vital for health care providers to educate patients about this risk and provide strategies to minimize it. For example, avoiding heavy lifting and extreme temperatures, and using compression garments when necessary can help reduce the risk of lymphedema. Family and friends can reinforce these recommendations and encourage their loved ones to stay vigilant about their health after cancer treatment.
Importance of Lymphatic Education in Families
Lymphatic education is essential for families to understand the complexities of lymphedema. By learning about the lymphatic system, how it functions, and the potential impacts of cancer treatment on this system, families can better support their loved ones. This education can take many forms, including attending workshops, reading literature, or consulting with a certified lymphedema therapist. By fostering an environment of understanding and support, families can help their loved ones manage this condition more effectively.
What are the Risk Factors for Developing Lymphedema?
Identifying Risk for Developing Lymphedema Post-Surgery
The risk of lymphedema is particularly heightened following cancer surgery that involves the removal of lymph nodes. Individuals who have had breast cancer surgery, for example, may experience swelling in the arm on the same side as the surgery. It’s essential for health care teams to assess each patient’s risk factors and provide tailored recommendations for monitoring and prevention. Understanding these risks allows individuals and their families to take proactive measures in managing their health.
Understanding Primary vs. Secondary Lymphedema
Distinguishing between primary and secondary lymphedema is crucial for understanding the condition and its management. Primary lymphedema may occur without any apparent cause and is typically hereditary. Conversely, secondary lymphedema develops as a complication of other medical conditions, particularly cancer treatments that impact the lymphatic system. By recognizing these differences, families can better understand their loved one’s condition and the necessary steps to prevent or manage lymphedema.
How Cancer Treatments Affect Lymphedema Risk
Cancer treatments, particularly those involving surgery or radiation therapy, can significantly increase the risk of lymphedema. The removal of lymph nodes and damage to lymph vessels during these procedures can disrupt normal lymphatic drainage, leading to a buildup of lymph fluid. Understanding how these treatments affect the lymphatic system is essential for families, as it can inform their approach to prevention and management. Open discussions with healthcare providers about these risks can foster a collaborative approach to care and support.
What are the Treatment Options for Lymphedema?
Exploring Decongestive Therapy and Its Benefits
Decongestive therapy is often the first-line treatment for managing lymphedema and includes techniques such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression bandaging, and exercise. This therapy aims to promote the drainage of lymph fluid from the affected area and reduce swelling. By regularly engaging with a certified lymphedema therapist, individuals can learn effective self-management techniques and improve their quality of life. Educating family members about these treatment options can empower them to support their loved ones in managing their condition.
The Role of a Qualified Lymphedema Therapist
A certified lymphedema therapist plays a critical role in the treatment and management of lymphedema. These healthcare professionals possess specialized knowledge and skills to assess the severity of lymphedema and create customized treatment plans. They help patients navigate their lymphedema management, including the fitting of compression garments and recommending exercises that promote lymphatic drainage. Families can support their loved ones by encouraging them to seek the services of a qualified lymphedema therapist, thereby enhancing their treatment experience.
When is Lymphedema Surgery Necessary?
In some cases, lymphedema surgery may be necessary for individuals who do not respond to conservative treatments. Procedures such as lymphovenous bypass or lymph node transfer can help restore normal lymphatic function and reduce swelling in the affected area. While surgery is not the first-line treatment for lymphedema, it can be a viable option for those with significant symptoms not responding to other methods. Discussing surgical options with a healthcare provider can lead to informed decisions about managing lymphedema effectively.
How to Support a Loved One Living with Lymphedema?
Understanding Life with Lymphedema: Emotional Support
Living with lymphedema can be emotionally challenging, impacting self-esteem and mental health. Providing emotional support is critical for individuals coping with this chronic condition. Family members and friends should be aware of the psychological effects of lymphedema and offer a listening ear, encouragement, and understanding. Engaging in open conversations about their experiences can foster a sense of community and reduce feelings of isolation.
Practical Ways to Assist with Lymphedema Management
There are numerous practical ways family and friends can assist in lymphedema management. Helping loved ones adhere to their treatment plans, such as wearing compression garments or attending therapy sessions, can significantly impact their overall well-being. Additionally, offering to accompany them to medical appointments or participating in educational sessions about lymphedema can demonstrate support and commitment to their health journey.
How to Encourage Adherence to Treatment Plans
Encouraging adherence to treatment plans is essential for effective lymphedema management. Family members can help by creating a supportive environment that emphasizes the importance of regular self-care routines, such as exercises and skin care practices. Additionally, setting reminders for appointments and advocating for their loved ones can help ensure they remain engaged in their lymphedema management. By taking a proactive role, family and friends can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with lymphedema.
FAQS
Q: What is the risk of lymphedema for individuals who have undergone cancer treatment?
A: Individuals who have undergone cancer treatment, especially those with breast cancer, face a higher risk for lymphedema due to potential damage to lymph nodes during surgery or radiation, which can lead to swelling caused by fluid accumulation in the arms and legs.
Q: What are the common symptoms of lymphedema that I should inform my family and friends about?
A: Common symptoms of lymphedema include noticeable swelling in the arms or legs, a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the affected limb, restricted range of motion, and recurring infections in the area.
Q: How can a physical therapist help in educating about lymphedema?
A: A physical therapist can provide valuable expertise in lymphedema treatment by teaching patients about self-care techniques, exercises to improve lymphatic flow, and how to manage symptoms effectively.
Q: What is primary lymphedema and how does it differ from secondary lymphedema?
A: Primary lymphedema is a rare genetic condition that results in lymphedema occurring without any prior surgery or injury, while secondary lymphedema is often caused by factors such as cancer treatment, infections, or trauma that affect lymphatic function.
Q: What is lymphovenous bypass and how might it be relevant to lymphedema treatment?
A: Lymphovenous bypass is a surgical procedure that creates a connection between lymphatic vessels and veins to help reduce swelling caused by lymphedema, offering a potential treatment option for patients with advanced lymphedema.
Q: How can I support a loved one who has lymphedema?
A: Supporting a loved one with lymphedema can involve educating yourself about the condition, encouraging adherence to complex decongestive therapy, and joining support groups where they can share experiences and coping strategies.
Q: What are the main causes of lymphedema that I can explain to my family and friends?
A: The main causes of lymphedema include damage to lymph nodes due to surgery or radiation, infections that affect lymphatic drainage, and certain medical conditions that impair lymphatic function, such as obesity or chronic venous insufficiency.
Q: Is lymphedema a lifelong condition, and what does that mean for treatment?
A: Yes, lymphedema is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management and treatment. This may include lifestyle changes, regular consultations with a physical therapist, and adherence to prescribed therapies to manage symptoms effectively.
Q: How does physical activity influence the risk of developing lymphedema?
A: Engaging in appropriate physical activity can help reduce the risk of developing lymphedema by promoting healthy lymphatic drainage and circulation, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine safe exercise options.