Lymphedema is a chronic condition that significantly impacts the lymphatic system, leading to swelling, skin changes, and potential ulceration. Effective skin and wound care is crucial in lymphedema management to prevent complications such as skin breakdown and infection. This article delves into the essential aspects of lymphedema care, focusing on ulcer prevention and comprehensive treatment strategies.
Understanding Lymphedema
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system is impaired, leading to an accumulation of lymph fluid in the interstitial spaces. This accumulation typically causes swelling, most commonly in the lower extremities. The lymphatic system, vital for maintaining fluid balance and immune function, relies on lymph nodes and vessels to transport lymph fluid. When this system fails, lymphedema develops, impacting the quality of life for patients with lymphedema.
Types of Lymphedema
Here are the primary categories of lymphedema. It is generally classified into:
- Primary lymphedema, which is often hereditary and stems from lymphatic system malformations.
- Secondary lymphedema, which is acquired and may arise due to surgery, radiation, infection, or trauma.
Understanding these types is essential for appropriate treatment and management, ensuring targeted care.
Diagnosis of Lymphedema
Diagnosing lymphedema typically involves a thorough physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history. Diagnostic imaging, such as lymphoscintigraphy, may be used to assess the lymphatic system and confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis is critical, as it allows for prompt initiation of lymphedema management strategies, including compression therapy and lymphatic drainage techniques, thereby minimizing the risk of complications like skin ulceration. [Insert Internal Link]
Lymphedema Management Strategies
Lymphedema Treatment Options
Lymphedema treatment involves various therapies to reduce swelling, improve lymph flow, and prevent complications. Key elements of this treatment include:
- Compression therapy, often using garments or bandages.
- Manual lymphatic drainage, performed by trained therapists.
Furthermore, exercise and proper skin care are also vital for improving circulation and preventing skin issues.
Skin Care Techniques for Lymphedema Patients
Good skin care is paramount for patients with lymphedema due to the increased risk of infection through breaks in the skin. Moisturizing the skin regularly helps to maintain skin integrity and prevent hardening of the skin and subsequent skin breakdown. Avoiding trauma, such as cuts or bruises, is essential, and any signs of infection, such as redness or warmth, should be promptly addressed. Effective skin care is a critical aspect of lymphedema management.
Wound Care Essentials
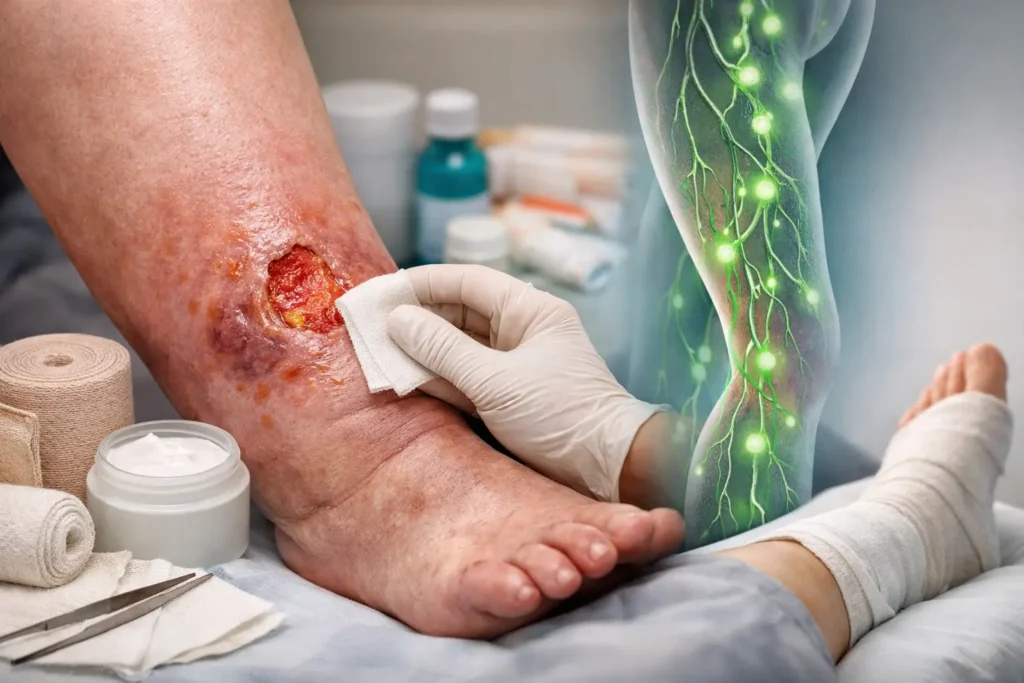
Effective wound care and lymphedema management are intrinsically linked, especially when addressing skin ulceration. If an ulcer develops, proper cleaning and dressing techniques are essential to prevent infection. Compression therapy should be continued to promote circulation and reduce swelling, facilitating healing. In some cases, advanced wound care products may be necessary to manage drainage and promote tissue regeneration, emphasizing the importance of specialized skin and wound care. [Insert Internal Link]
Preventing Skin Ulcers
Importance of Ulcer Prevention
Preventing skin ulcer formation in patients with lymphedema is critical due to the impaired lymphatic system and compromised skin integrity. Lymphedema causes swelling, which reduces blood flow and increases the risk of skin breakdown and infection. Early intervention with good skin care practices and effective lymphedema management can significantly lower the incidence of ulceration, thus enhancing the quality of life for patients with lymphedema.
Common Causes of Skin Ulcers in Lymphedema
Several factors contribute to skin ulcer development in lymphedema. Chronic swelling from impaired lymph flow leads to skin changes, including hardening of the skin and decreased elasticity, making it more susceptible to injury. Minor trauma, such as cuts or bruises, can easily progress to ulceration due to poor circulation and delayed healing. Additionally, infection and maceration from excessive moisture can further compromise skin integrity, emphasizing the need for meticulous skin care and wound care. [Insert Internal Link]
Practical Tips for Ulcer Prevention
To prevent skin ulcer formation, patients with lymphedema should adhere to a strict skin care regimen. Regularly moisturizing the skin helps maintain its barrier function, preventing breaks in the skin and reducing the risk of infection. Key components of this regimen include:
- Compression therapy with compression garments or bandages, essential for managing swelling and improving circulation.
- Protecting the skin from trauma, promptly treating any signs of infection, and ensuring proper wound care for any existing wounds to avoid developing lymphedema and wounds.
Patient Education and Support
Patient Education on Lymphedema
Patient education is a cornerstone of effective lymphedema management. Patients need to understand the importance of adhering to their treatment plan, including compression therapy, lymphatic drainage, and good skin care. They should also be educated about the early signs of infection and the steps to take to prevent ulceration. Empowering patients with knowledge enables them to actively participate in their care and improve their long-term outcomes with lymphedema therapy. [Insert Internal Link]
Support Resources for Lymphedema Patients
Navigating life with lymphedema can be challenging, making support resources invaluable for patients. Organizations like the National Lymphedema Network provide education, support groups, and referrals to certified lymphedema therapists. Online forums and communities offer a space for patients to share experiences and learn from others. Access to these resources can significantly enhance the quality of life for patients with lymphedema, fostering a sense of community and shared understanding.
Evaluating and Managing Skin and Wound Care
Regular evaluation of the skin is vital for identifying early signs of skin breakdown or infection. Healthcare providers should assess patients for skin changes, such as redness, warmth, or hardening of the skin. Proper wound care protocols should be in place to manage any existing ulcers, including cleaning, dressing, and monitoring for infection. A multidisciplinary approach involving physicians, nurses, and certified lymphedema therapists is essential for comprehensive skin and wound care.
Current Trends and Future Insights
Emerging Treatments in Lymphedema Care
The field of lymphedema treatment is continually evolving. Emerging therapies, such as supermicrosurgical lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA), aim to improve lymph flow by connecting lymphatic vessels to small veins. Other advancements include pharmacological interventions to reduce fibrosis and inflammation. These innovative approaches offer hope for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life for patients with lymphedema. These treatments will allow better treatment of lymphedema.
The Role of Technology in Wound Care
Technology is playing an increasingly significant role in wound care for lymphedema patients. Advanced wound dressings, such as those containing silver or growth factors, promote faster healing and reduce infection. Telemedicine allows for remote monitoring of wounds, enabling timely intervention and reducing the need for frequent clinic visits. These technological advancements enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of skin and wound care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and preventing venous leg ulcers.
Research Trends in Ulcer Prevention
Current research is focused on identifying novel strategies for ulcer prevention in lymphedema. Studies are investigating the use of biomarkers to predict the risk of skin breakdown and ulceration. Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of gene therapy and stem cell therapy to regenerate damaged lymphatic vessels and improve lymph flow. These research endeavors hold promise for developing more effective and personalized approaches to lymphedema management and skin care.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
In summary, effective lymphedema management is essential for preventing skin ulceration. Lymphedema, a chronic condition affecting the lymphatic system, leads to swelling and skin changes that increase the risk of infection. Comprehensive skin and wound care, including moisturizing the skin, using compression therapy with compression garments or bandages, and maintaining good skin hygiene, is critical. Early intervention and patient education can significantly enhance the quality of life for patients with lymphedema.
Final Advice for Patients
For patients with lymphedema, consistent adherence to a well-structured lymphedema treatment plan is vital. Regularly inspect your skin for any signs of infection or skin breakdown, and promptly address any concerns with your healthcare provider. Prioritize good skin care, wear compression garments as prescribed, and engage in lymphatic drainage exercises. By taking proactive steps in skin care and wound care, you can effectively manage your condition and minimize the risk of developing lymphedema and wound complications such as leg ulcers or skin ulceration.
FAQs
What are the early signs of lymphedema?
Early signs of lymphedema include persistent swelling in the affected limb, often accompanied by a feeling of heaviness or tightness. You may notice skin changes, such as hardening of the skin or pitting edema, where pressing on the skin leaves an indentation. It’s also important to watch for any unexplained discomfort or decreased range of motion. Recognizing these early indicators allows for prompt lymphedema treatment and intervention, which can prevent the progression of lymphedema and wounds and minimize long-term complications such as infection.
How can I manage lymphedema at home?
Managing lymphedema at home involves several key strategies, which include compression therapy with compression garments or bandages to reduce swelling and improve lymph flow. Practice meticulous skin care by keeping the skin clean and well-moisturized to prevent skin breakdown and infection. Perform lymphatic drainage exercises as instructed by a certified lymphedema therapist to encourage lymphatic fluid movement. Elevate the affected limb whenever possible to further reduce swelling. Good skin and wound care is key to preventing the development of lymphedema and wounds.
What should I do if I notice a skin ulcer?
If you notice a skin ulcer, it’s crucial to take immediate action to prevent infection and promote healing. Clean the wound gently with mild soap and water, then apply a sterile dressing. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scrubbing the area, as this can damage the tissue. Contact your healthcare provider or a wound care specialist promptly for further evaluation and treatment recommendations. Continue compression therapy, if appropriate, to support circulation and reduce swelling around the affected area.
Are there special products for skin care in lymphedema?
Yes, there are several specialized products designed for skin care for patients with lymphedema. Look for gentle, pH-balanced cleansers and moisturizers that are free from fragrances, dyes, and harsh chemicals to avoid irritating the skin. Emollients containing urea or lanolin can help to hydrate dry, hardened skin. Additionally, consider using barrier creams containing zinc oxide or petrolatum to protect the skin from maceration and infection. These products aid in good skin care and preserving the lymphatic system.
How often should I perform wound care?
The frequency of wound care depends on the severity and characteristics of the wound. In general, minor wounds should be cleaned and dressed daily to prevent infection and promote healing. More complex or draining wounds may require more frequent dressing changes, possibly two to three times per day. Always follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider or wound care specialist regarding wound care and dressing changes to ensure optimal healing and prevent complications such as cellulitis.