Lymphedema, a chronic condition causing swelling due to lymphatic system dysfunction, significantly impacts patients’ quality of life. Fortunately, various treatment options exist, including pneumatic compression therapy. This article explores how pneumatic compression pumps aid in lymphedema management and compression.
Understanding Lymphedema
What is Lymphedema?
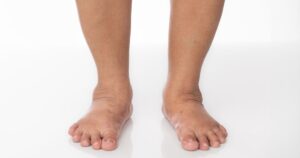
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by swelling, typically in the arms or legs, resulting from a blockage or damage to the lymphatic system. This system, crucial for immune function and fluid balance, becomes impaired, leading to fluid accumulation. Without adequate management, lymphedema can progress.
Causes of Lymphedema
Lymphedema can be primary, due to congenital lymphatic abnormalities, or secondary, resulting from damage to the lymphatic system. Secondary lymphedema is often caused by surgery, radiation therapy, or infection, particularly in cancer-related lymphedema cases, such as breast cancer treatment. It is a common issue for individuals with lymphedema.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of lymphedema include swelling, a feeling of heaviness, and skin changes. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective lymphedema management. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging techniques to assess lymphatic function. Proper diagnosis allows for timely initiation of appropriate conservative treatment and other lymphatic therapy.
The Role of Compression in Lymphedema Management
Importance of Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is a cornerstone in lymphedema management, aiming to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic drainage. By applying external pressure, compression helps move fluid out of the affected limb, preventing further accumulation. The use of compression is vital in controlling lymphedema and improving the quality of life of patients with lymphedema.
Types of Compression Garments
Various compression garments are available, including compression bandages, sleeves, and stockings, each designed to provide specific levels of compression. Compression bandage application requires skill, ensuring even pressure distribution. Custom-fitted compression garments offer tailored support for individual needs of patients with lymphedema, complementing other forms of compression treatment.
How Compression Affects Lymphedema
Compression affects lymphedema by increasing tissue pressure, which supports lymphatic vessels and enhances fluid movement. This reduces swelling and improves overall lymphatic function. Regular compression therapy can prevent lymphedema progression and maintain limb size, making it a crucial component of complete decongestive therapy.
Pneumatic Compression Pumps: An Overview
What is a Pneumatic Compression Pump?
A pneumatic compression pump is a medical device consisting of an inflatable sleeve connected to a pump that cyclically inflates and deflates. This creates intermittent pneumatic compression, mimicking the natural muscle contractions that promote lymphatic drainage. These devices are increasingly used in lymphedema treatment and lymphedema management.
How Pneumatic Compression Works
Pneumatic compression works by applying sequential pressure to the affected limb, moving fluid proximally towards the body’s core. This action enhances lymphatic and venous flow, reducing swelling and preventing fluid stagnation. The types of pneumatic compression offered vary, catering to different needs in lymphedema treatment.
Benefits of Using Pneumatic Compression Devices
Here’s how pneumatic compression devices can help: they offer several benefits.
- Reduced swelling
- Improved limb comfort
- Enhanced lymphatic drainage
Pneumatic compression pump therapy can be administered at home, offering convenience and promoting self-management of lymphedema. These devices offer a valuable treatment option in managing limb lymphedema.
Types of Pneumatic Compression Pumps
Different Models and Features
Pneumatic compression pumps come in various models, each offering unique features to cater to different needs in lymphedema management. Some models provide sequential compression, while others offer gradient compression. The intensity and duration of the compression cycles can also vary, allowing for personalized treatment of lymphedema to manage limb lymphedema.
Choosing the Right Pneumatic Compression Pump
Choosing the right pneumatic compression pump involves considering factors such as the severity of lymphedema, the area affected, and individual preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most suitable compression device for effective lymphedema treatment. The correct compression pump helps manage cancer-related lymphedema.
Comparison of Pneumatic Compression Pumps
Comparing different pneumatic compression pumps requires evaluating their features, ease of use, and cost. Some pumps are designed for home use, while others are intended for clinical settings. Understanding the pros and cons of each compression pump ensures informed decision-making in lymphedema management and improving lymphatic therapy, including complete decongestive therapy.
Using a Pneumatic Compression Pump for Lymphedema
How to Use a Pneumatic Compression Pump
Using a pneumatic compression pump involves placing the affected limb into the compression garment connected to the pump. The device is then turned on, and the compression cycles begin, typically lasting for a set duration. Following the manufacturer’s instructions and healthcare provider’s guidance is crucial for safe and effective treatment of lymphedema and the use of compression.
Best Practices for Treatment
Best practices for treatment with a pneumatic compression pump include ensuring proper fit of the compression garment and monitoring the skin for any signs of irritation. Maintaining a consistent treatment schedule and combining compression therapy with other lymphedema management strategies optimizes outcomes. This is vital when seeking ways to treat lymphedema.
Frequency and Duration of Use
The frequency and duration of pneumatic compression pump therapy vary based on individual needs and the severity of lymphedema. Typically, treatments last from 30 minutes to several hours, performed once or twice daily. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is essential for achieving optimal results in lymphedema management and improved lymphatic therapy.
Integrating Pneumatic Compression with Other Treatments
Combining with Compression Garments
Combining pneumatic compression with compression garments can enhance the effectiveness of lymphedema treatment. Using compression garments between pump sessions helps maintain reduced swelling and supports lymphatic drainage. This combination is a cornerstone of comprehensive lymphedema management, offering continuous benefit for patients with lymphedema.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Integrating physical therapy and exercise with pneumatic compression can further improve lymphatic function and reduce swelling. Exercises designed to promote lymphatic drainage, combined with compression therapy, enhance overall treatment outcomes. Tailored physical therapy complements the benefits of compression treatment to manage limb lymphedema.
Addressing Cancer-Related Lymphedema
Addressing cancer-related lymphedema requires a comprehensive approach, including pneumatic compression, compression garments, and specialized exercises. Early intervention and consistent adherence to a treatment plan are crucial for managing cancer-related lymphedema effectively. This holistic approach aims to improve the quality of life for individuals with lymphedema after breast cancer treatment.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Patient Testimonials
Patient testimonials often highlight the positive impact of pneumatic compression pump therapy on their quality of life. Many report reduced swelling, improved comfort, and increased mobility, underscoring the benefits of this treatment option. These personal accounts provide valuable insights into the real-world effectiveness of lymphedema management with pumps for treatment of lymphedema.
Statistical Outcomes
Statistical outcomes from clinical studies demonstrate the effectiveness of pneumatic compression in reducing lymphedema-related swelling. Research consistently shows significant improvements in limb volume and patient-reported outcomes, supporting the use of compression therapy. These statistics underscore the importance of pneumatic compression devices in conservative treatment.
Real-Life Applications
Real-life applications of pneumatic compression span various settings, from hospitals and clinics to patients’ homes. The versatility and ease of use of these devices make them a valuable tool in managing lymphedema across different patient populations. These applications highlight the broad utility of pneumatic compression pumps for treatment of lymphedema, including secondary lymphedema.
Future Trends in Lymphedema Treatment
Innovations in Compression Technology
Innovations in compression technology are continually improving the effectiveness and convenience of lymphedema management. The development of more sophisticated pneumatic compression devices and compression pump designs offers enhanced precision and customization. Advanced pneumatic compression device features could include biofeedback mechanisms, allowing for personalized pneumatic compression therapy. These advancements are aimed at providing better compression treatment and outcomes for patients with lymphedema, particularly in limb lymphedema cases.
Research and Development in Lymphedema Management
Research and development efforts in lymphedema management are focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease and identifying new treatment approaches. Studies are exploring the potential of pharmacological interventions, gene therapy, and advanced imaging techniques to improve lymphatic function. These advances can complement existing therapies, like compression therapy, and ultimately improve the lives of individuals with lymphedema.
Potential New Treatment Options
Potential new treatment options for lymphedema include lymphatic microsurgery, which aims to restore lymphatic flow by connecting lymphatic vessels to veins. Additionally, research into stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine holds promise for repairing damaged lymphatic tissue. These innovative approaches, combined with conservative treatment and the use of compression, could revolutionize lymphedema treatment and management of lymphedema.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
In summary, lymphedema is a chronic condition requiring comprehensive management, with compression as a cornerstone of treatment. Pneumatic compression pump therapy offers a valuable tool for reducing swelling and improving lymphatic drainage. Integrating pneumatic compression with other therapies, such as compression garments and exercise, optimizes outcomes for individuals with lymphedema. Early intervention and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for effective lymphedema management.
Final Advice for Managing Lymphedema
For those managing lymphedema, remember that consistency and proactive care are key. Work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes pneumatic compression, compression garments, and lifestyle modifications. Stay informed about the latest advancements in lymphedema treatment and explore all available resources to support your journey. With proper management, you can maintain your quality of life while living with lymphedema. The correct pneumatic compression pump can assist significantly.
FAQs
What is the best way to treat lymphedema?
Here’s how to treat lymphedema effectively, using an approach tailored to the needs of each patient. This often involves several key components, including:
- Compression therapy, which might use garments or bandages.
- Pneumatic compression pump therapy, designed to improve lymphatic drainage.
- Exercises that encourage fluid movement.
- Skin care, carefully done to help prevent infections.
Complete decongestive therapy, which combines these elements, is often regarded as the gold standard in conservative treatment and lymphedema management.
How often should I use a pneumatic compression pump?
The frequency of using a pneumatic compression pump varies depending on the severity of lymphedema and individual treatment plans. Typically, treatments range from 30 minutes to two hours, once or twice daily. Always follow your healthcare provider’s specific recommendations to ensure safe and effective use of compression and optimize the benefits of pneumatic compression pump therapy for treatment of lymphedema.
Are there risks associated with compression therapy?
While compression therapy is generally safe, potential risks include skin irritation, discomfort, and, in rare cases, impaired circulation. It is crucial to ensure proper fit of compression garments and pneumatic compression devices and to monitor the skin for any signs of redness or breakdown. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as peripheral artery disease, should consult their doctor before starting compression treatment.
Can pneumatic compression help with lower extremity lymphedema?
Yes, pneumatic compression can be highly effective in managing lower extremity lymphedema. The sequential compression action of the pneumatic compression pump helps move fluid from the lower limbs towards the body’s core, reducing swelling and improving lymphatic drainage. Combining pneumatic compression with compression garments and exercises can further enhance treatment outcomes for lower extremity lymphedema, managing limb lymphedema, and improving lymphatic therapy.
What are the differences between pneumatic compression and compression garments?
Pneumatic compression involves using a pump to cyclically inflate and deflate a compression sleeve, providing intermittent pressure to enhance lymphatic drainage. Compression garments, on the other hand, provide continuous, static pressure to support lymphatic vessels and prevent fluid accumulation. While pneumatic compression offers active drainage, compression garments provide ongoing support. Both play vital roles in comprehensive lymphedema management, either as conservative treatment or lymphatic therapy.