Lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) are two conditions that affect the circulatory and lymphatic systems. Although they are separate issues, there is a growing understanding of how they are interconnected and can often coexist in individuals. Both conditions cause leg swelling, but the underlying causes and mechanisms differ. This article will explore the connection between lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency, how they are related, and how to manage and treat these conditions to improve patient outcomes.
What is Lymphedema?
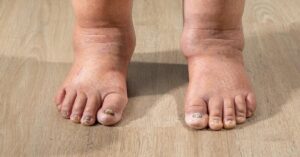
Lymphedema is a condition that occurs when the lymphatic system, responsible for draining excess fluid from tissues, becomes impaired. This can lead to the accumulation of lymph fluid in the affected areas, most commonly the arms or legs, causing swelling, discomfort, and in severe cases, skin changes or infections. Lymphedema can develop due to various factors, including surgery, radiation, disease, or as a congenital condition.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
The most noticeable symptom of lymphedema is swelling, but other symptoms can include:
- Heaviness or tightness in the affected limb
- Limited range of motion
- Skin changes such as thickening or hardening
- Frequent infections due to impaired immune function
- A feeling of discomfort or fullness in the affected area
What is Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
Chronic venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in the legs cannot efficiently return blood to the heart. The veins in the legs contain one-way valves that help blood flow upward against gravity. When these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can pool in the veins, leading to swelling, varicose veins, and even ulcers in the most severe cases.
Symptoms of Chronic Venous Insufficiency
CVI can present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Swelling in the legs, particularly around the ankles
- Pain or aching in the legs
- Heaviness or fatigue in the legs, especially after standing for long periods
- Varicose veins, which are enlarged, twisted veins
- Skin changes, including darkening or thickening of the skin around the ankles
- Venous ulcers in severe cases
How Are Lymphedema and Chronic Venous Insufficiency Connected?
While lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency are distinct, they often occur together. This is due to the complex relationship between the lymphatic and venous systems. The lymphatic and venous systems work together to manage fluid balance in the body, so when one system is compromised, the other can also suffer.
Fluid Retention and Swelling
Both conditions result in fluid buildup in the legs, but the causes differ. In lymphedema, the lymphatic system cannot drain fluid efficiently, accumulating lymphatic fluid in the tissues. In CVI, the veins cannot effectively return blood to the heart, causing blood to pool in the lower extremities, which results in swelling.
When both conditions coexist, the swelling from CVI can place additional pressure on the lymphatic system, further hindering its ability to drain fluid. This creates a vicious cycle of fluid retention and swelling, which can worsen the symptoms of both conditions.
Overlapping Symptoms
Swelling in the legs is a hallmark symptom of both lymphedema and CVI. However, the underlying causes of the swelling are different. In lymphedema, the swelling is primarily due to lymphatic fluid, while in CVI, it is caused by blood pooling in the veins. This can make it difficult to differentiate between the two conditions since they often co-occur in affected individuals.
Skin Changes and Infections
Both lymphedema and CVI can lead to skin changes, such as thickening, darkening, and ulcers. In addition, individuals with these conditions are at an increased risk of infections due to poor circulation and compromised immune function. Infections in the affected areas can complicate both conditions, leading to more severe swelling and discomfort.
How Does Chronic Venous Insufficiency Contribute to Lymphedema?
Chronic venous insufficiency can exacerbate lymphedema in several ways. First, the blood pooling in the veins increases the pressure in the affected tissues, which can further impair the function of the lymphatic system. This pressure can cause the lymphatic vessels to become less effective at draining lymphatic fluid, resulting in more significant swelling.
Additionally, the fluid buildup from CVI can lead to changes in the skin’s structure and underlying tissues. Over time, this can cause the lymphatic vessels to become even more obstructed, creating a compounding effect that worsens the symptoms of lymphedema.
Can Lymphedema Cause Chronic Venous Insufficiency?
While CVI typically results from weakened or damaged veins, lymphedema can contribute to its development in some cases. Chronic swelling from lymphedema can lead to increased pressure on the veins in the affected limb, which may contribute to the weakening of the venous valves over time. This can make it more difficult for the veins to return blood to the heart, leading to the development of CVI.
Diagnosis of Lymphedema and Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Accurately diagnosing both lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency is crucial for effective treatment. A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination to assess the degree of swelling, skin changes, and any signs of ulcers or infections. Diagnostic tests may include:
1. Ultrasound
An ultrasound can assess the condition of the veins and blood flow in the affected area. This test can help identify any blockages or venous function issues that may contribute to CVI.
2. Lymphoscintigraphy
This imaging test evaluates the function of the lymphatic system. It can help determine if lymphedema is present and assess the extent of lymphatic dysfunction.
3. Doppler Flow Studies
Doppler studies use sound waves to evaluate blood flow and can help determine the severity of CVI by assessing how well blood returns to the heart.
4. CT or MRI Scans
Sometimes, a CT or MRI scan may assess the lymphatic or venous systems for structural abnormalities contributing to both conditions.
Treatment for Lymphedema and Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Managing lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency often requires a multifaceted approach. Treatment aims to reduce swelling, improve circulation, and prevent further complications. Here are some standard treatment options for both conditions:
1. Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is often used for both lymphedema and CVI. In lymphedema, compression garments help promote lymphatic drainage by providing external pressure to the affected area. In CVI, compression stockings or bandages help improve venous return and reduce swelling. Both therapies can be used together to address the overlapping symptoms of these conditions.
2. Elevation and Exercise
Elevating the legs can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow. Regular exercise, such as walking or swimming, can also help improve circulation and lymphatic drainage, benefiting both lymphedema and CVI patients.
3. Medications
Medications like diuretics can help reduce fluid retention in both lymphedema and CVI. Additionally, pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to manage discomfort and inflammation associated with these conditions.
4. Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to treat CVI. This may involve procedures to remove varicose veins, repair damaged veins, or improve venous flow. Surgery may sometimes be required to treat lymphedema if other treatments are ineffective.
5. Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
For lymphedema patients, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique designed to encourage the flow of lymph fluid. MLD can be especially effective when combined with compression therapy to reduce swelling and improve overall function.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency may not always be preventable, specific lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing these conditions or manage existing symptoms. These include:
1. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can strain the venous and lymphatic systems. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can reduce the risk of lymphedema and CVI.
2. Avoiding Prolonged Standing or Sitting
Standing or sitting for long periods can exacerbate lymphedema and CVI symptoms. Taking regular breaks and moving around to improve circulation and reduce swelling is essential.
3. Skin Care
Proper skin care prevents infections in individuals with lymphedema and CVI. Keeping the skin clean, moisturized, and free from cuts or abrasions can help reduce the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency are two conditions that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, particularly when they occur together. Understanding the link between these two conditions is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Patients can manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being by combining compression, elevation, exercise, and manual lymphatic drainage therapies. With the right treatment plan and lifestyle modifications, individuals living with lymphedema and CVI can lead more active and fulfilling lives.
FAQs
Q1: Can chronic venous insufficiency cause lymphedema?
- Yes, chronic venous insufficiency can exacerbate lymphedema by increasing pressure in the veins, which can impair the function of the lymphatic system and lead to more fluid buildup.
Q2: What are the most effective treatments for lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency?
- Compression therapy, leg elevation, regular exercise, and manual lymphatic drainage are some of the most effective treatments for both conditions.
Q3: Is surgery ever needed for lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency?
- In severe cases, surgery may be required to treat varicose veins in CVI or to address lymphedema if other treatments have not been effective.
Q4: How can I prevent lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency?
- Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and caring for your skin can help reduce the risk of both conditions.
Q5: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage lymphedema and CVI?
- Regular movement, compression therapy, proper skin care, and weight management are key lifestyle changes that can help manage both conditions.