Ease Lymphedema Symptoms: How to Handle Lymphedema Flare-Ups
Lymphedema is a condition that occurs when the lymphatic system, responsible for transporting lymph (a fluid that contains white blood cells and helps fight infections), becomes damaged or impaired. This damage leads to an accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, causing swelling, typically in the arms or legs. While lymphedema is a chronic condition, it can also cause periods of flare-ups, where symptoms worsen and swelling becomes more pronounced. Managing these flare-ups effectively is crucial to preventing further complications and maintaining a good quality of life.
In this article, we’ll explore how to handle lymphedema flare-ups. We’ll cover common triggers, immediate actions you can take during a flare-up, long-term management strategies, and offer valuable insights for living well with lymphedema. Whether you’re new to lymphedema or have been managing it for years, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to ease symptoms and prevent flare-ups from becoming overwhelming.
Definition of Lymphedema and Its Impact on Daily Life
Lymphedema is most often caused by a disruption in the lymphatic system, either from surgery, radiation, or injury. In cases like secondary lymphedema, which frequently occurs after cancer treatment, including breast cancer surgery, the removal of lymph nodes can lead to swelling in the affected area. For people with lymphedema, this swelling can significantly impact their daily activities, making movement, exercise, and even regular self-care more difficult.
The condition is often painful and can lead to feelings of frustration and isolation, particularly during flare-ups. In the long term, lymphedema is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management to keep symptoms in check and avoid complications like infections and skin damage.
Importance of Managing Flare-Ups Effectively
Managing lymphedema flare-ups is crucial to maintaining a good quality of life. These flare-ups can lead to more severe swelling, discomfort, and potential tissue damage if left unchecked. Additionally, flare-ups can make lymphedema harder to manage overall, requiring more intensive treatment or even surgical interventions. By staying on top of flare-up management, you can prevent symptoms from worsening, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your long-term outcomes.
Overview of the Blog Post Structure
This blog post is structured to give you a comprehensive guide on managing lymphedema flare-ups, covering both immediate actions and long-term strategies. We’ll first examine the common triggers and symptoms of flare-ups. Then, we’ll discuss immediate actions you can take to reduce swelling during a flare-up, including the role of compression garments and manual lymphatic drainage. Lastly, we’ll explore the long-term management strategies that can help you prevent lymphedema flare-ups and live well with the condition.
Understanding Lymphedema Flare-Ups
Common Triggers of Flare-Ups
Various factors can trigger lymphedema flare-ups. Cancer treatment, especially breast cancer treatment, is one of the leading causes of secondary lymphedema. Removal of the lymph nodes during surgery for breast cancer or radiation therapy can interrupt the natural flow of lymph, making the affected area prone to swelling. Other triggers include infection, injury, or even changes in diet or exercise.
In addition, extreme weather conditions, such as excessive heat or cold, can also exacerbate lymphedema symptoms. Stress and hormonal changes—often experienced during menstruation or menopause—can also trigger flare-ups. Understanding these triggers is essential for managing lymphedema and preventing episodes of severe swelling.
Symptoms to Watch For
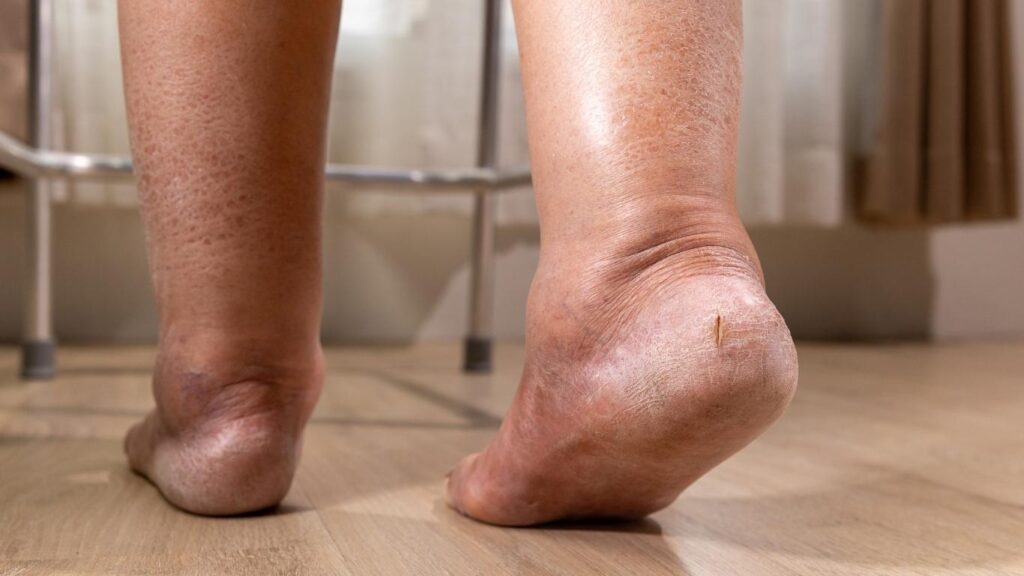
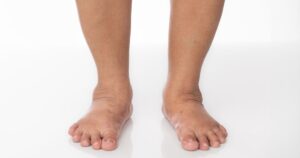
Symptoms of a lymphedema flare-up include increased swelling, a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected area, and changes in skin texture, such as thickening or hardening. Some individuals may also experience pain or discomfort, particularly when moving the affected limb. In severe cases, the skin may become red or inflamed, which could indicate an infection. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you take action before the flare-up worsens.
The Physiological Process Behind Flare-Ups
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic vessel system is damaged or blocked, preventing the proper drainage of lymph fluid. When this fluid builds up, it causes the tissues in the affected area to swell. During a flare-up, the lymphatic system struggles to keep up with the excess liquid, leading to noticeable swelling. The lymphedema is most often seen in the arms or legs, but it can also affect the lower body or abdomen, especially in those with advanced stages of lymphedema.
Immediate Actions to Take During a Flare-Up
Elevation Techniques to Reduce Swelling
Elevating the affected limb is one of the first actions to take when you notice the signs of a lymphedema flare-up. Elevation helps reduce swelling by allowing gravity to assist in the drainage of excess fluid. Aim to elevate the limb above heart level, propping it up with pillows or a cushion. This simple technique can provide immediate relief and prevent the swelling from getting worse.
Compression Garments and Their Role
Compression garments are one of the most effective tools in managing lymphedema symptoms, especially during a flare-up. These garments apply gentle pressure to the affected area, helping to stimulate lymphatic drainage and reduce symptoms. Depending on your needs, they prevent further swelling and can be worn throughout the day or night. Be sure to consult with your lymphedema therapist or healthcare provider to determine the correct size and type of garment for your condition.
Importance of Staying Hydrated
Hydration plays a crucial role in managing lymphedema flare-ups. When you are dehydrated, your body may retain more fluid, which can worsen lymphedema symptoms. Drinking plenty of water can help your body flush out excess fluids and reduce the swelling caused by the buildup of lymph fluid. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and consider incorporating foods high in water content, such as fruits and vegetables, into your diet.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Regular Exercise and Its Benefits
Exercise is essential for managing lymphedema in the long term. Regular physical activity helps promote lymphatic drainage by improving circulation and encouraging the flow of lymph fluid through the body. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can be particularly beneficial for people with lymphedema, as they reduce the risk of injury while stimulating the lymphatic system. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise routine to ensure it’s safe for your needs.
Dietary Considerations for Lymphedema Patients
Diet plays a significant role in managing lymphedema flare-ups. A healthy diet can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health, which is crucial for people with lymphedema. Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excess sodium, as it can cause your body to retain more water and worsen swelling. Some studies also suggest that anti-inflammatory foods—such as turmeric and ginger—may help alleviate lymphedema symptoms.
Importance of Routine Check-Ups with Healthcare Providers
Regular check-ups with a lymphedema specialist or healthcare provider are vital for tracking the condition’s progression and adjusting treatment plans. Routine visits can help identify any complications early and provide an opportunity to discuss new treatment options or interventions. Whether you’re managing lymphedema after breast cancer or another form of secondary lymphedema, staying in close contact with your healthcare team ensures you’re on the best path for effective management.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points Discussed
Managing lymphedema flare-ups requires both immediate action and long-term strategies. Immediate measures like elevation, compression garments, and staying hydrated can offer quick relief, while regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine healthcare visits help manage symptoms over time.
Encouragement to Seek Support and Resources
Living with lymphedema can be challenging, but you don’t have to navigate it alone. Numerous resources are available to help you manage the condition, including support groups, specialized therapists, and online communities. Contact a lymphedema therapist or your healthcare provider for personalized advice on treatment and ways to improve your daily life.
Final Thoughts on Living Well with Lymphedema
While lymphedema is a chronic condition, it’s possible to live well with it by staying proactive in your care. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can reduce the risk of flare-ups and continue to lead a fulfilling, active life. Early intervention and consistent management are key to easing symptoms and maintaining well-being.
FAQs
Q: What are the common symptoms of lymphedema?
A: The symptoms of lymphedema typically include swelling in the affected limb, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, recurring infections, and changes in the skin texture. In the early stages of lymphedema, the swelling may be soft and can be reduced with elevation, while in severe lymphedema, it may become stiff and fibrous.
Q: What is the cause of lymphedema?
A: Lymphedema can be caused by various factors, including damage to the lymphatic system caused by cancer treatment, such as surgery or radiation treatment, as well as certain infections or congenital conditions. Secondary lymphedema is often seen in patients who have undergone breast cancer treatment.
Q: How can I manage lymphedema at home?
A: Living with lymphedema involves adopting self-care practices such as wearing compression garments, engaging in exercises designed explicitly for lymphedema management, maintaining skin care to prevent infections, and following a healthy diet. It’s also essential to monitor for any changes in symptoms of lymphedema.
Q: What treatment options are available for lymphedema?
A: Treatment for lymphedema may include physical therapy with a certified therapist, manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and, in some cases, surgical treatment. Effective treatment focuses on reducing swelling and preventing complications.
Q: Can lymphedema develop after cancer treatment?
A: Yes, individuals who undergo cancer treatment, particularly those with breast cancer, are at risk for lymphedema. Removing lymph nodes or damaging the lymphatic system during surgery or radiation treatment can lead to lymphedema.
Q: What are the stages of lymphedema?
A: Lymphedema is often classified into stages. In the early stages, swelling may be reversible with elevation. As the condition progresses to moderate and severe lymphedema, the swelling becomes persistent, and skin changes may occur, indicating more advanced stages of the disease.
Q: Is there a cure for lymphedema?
A: Currently, there is no definitive cure for lymphedema. However, effective treatment for lymphedema can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Ongoing lymphedema management and self-care can significantly ease lymphedema symptoms.
Q: How can I prevent lymphedema if I am at risk?
A: To prevent lymphedema, individuals at risk, especially after cancer treatment, should avoid injury to the affected area, maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and follow skin care routines to prevent infections. Consulting with healthcare providers about risk factors can also be beneficial.
Q: What are the complications of lymphedema?
A: Complications of lymphedema can include recurrent infections, skin changes, and reduced mobility. Severe lymphedema can lead to more serious health issues, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Q: What role do healthy lymph nodes play in lymphedema?
A: Healthy lymph nodes are crucial for adequately functioning the lymphatic system. Damage or removal of lymph nodes during cancer treatment can impair lymphatic drainage, leading to lymphedema. Maintaining healthy lymph nodes is essential for minimizing the risk of developing lymphedema.