Lymphedema is a condition that leads to the swelling of certain areas in the body, often in the arms or legs, due to the buildup of lymphatic fluid. This condition can be physically and emotionally taxing for individuals, affecting their mobility, quality of life, and overall well-being. Physical therapy plays a vital role in treatment for those managing lymphedema, helping to reduce swelling, improve movement, and prevent further complications. In this article, we will explore the significance of physical therapy in managing lymphedema and how it can provide relief and improve the lives of individuals living with this condition.
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system, responsible for transporting lymph fluid throughout the body, becomes impaired. This can happen for several reasons, including the removal or damage of lymph nodes during surgery, injury, or radiation therapy, typically related to cancer treatments. The lymphatic system’s inability to drain excess fluid causes it to accumulate in the tissues, leading to swelling, discomfort, and potential skin changes.
Types of Lymphedema
There are two main types of lymphedema:
- Primary Lymphedema: This form is rare and results from genetic abnormalities that affect the lymphatic system’s development. It can be present at birth or develop later in life.
- Secondary Lymphedema: This is the more common form and usually occurs due to external factors, such as surgery, radiation therapy, or injury, that affect the lymphatic system.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
The most common symptom of lymphedema is swelling in the affected area, typically in the arms or legs. Other symptoms may include:
- Heaviness or tightness in the limb
- Pain or discomfort in the swollen area
- Skin changes such as dryness, tightness, or thickening
- Reduced range of motion or flexibility in the affected area
- Increased risk of infections in the affected limb
How Physical Therapy Helps with Lymphedema
Physical therapy is essential to managing lymphedema, as it helps improve lymphatic drainage, reduce swelling, and increase mobility. A trained physical therapist can develop a personalized plan that targets the specific needs of the individual. Below are the primary ways in which physical therapy helps manage lymphedema:
1. Lymphatic Drainage Massage
One key component of physical therapy for lymphedema is lymphatic drainage massage, also known as manual lymphatic drainage (MLD). This specialized technique uses gentle, rhythmic strokes to encourage the flow of lymph fluid away from the swollen area and into healthy lymph nodes. By promoting the movement of lymph, MLD helps reduce swelling and alleviate the discomfort associated with lymphedema.
How MLD Works
The therapist uses a series of precise techniques to stimulate the lymphatic system. These movements are typically performed sequentially, starting from areas of the body where lymph nodes are functioning well and moving toward the swollen regions. This method can help improve circulation and reduce the buildup of lymphatic fluid.
2. Exercise Therapy
Physical therapy for lymphedema often includes specific exercises designed to improve the function of the affected limb and enhance lymphatic drainage. Gentle exercises, such as stretching, light strengthening, and aerobic activities, can promote fluid movement and improve circulation in the swollen area.
The Role of Exercise in Lymphedema Management
Exercise helps increase muscle contractility, which in turn helps the lymphatic system function better. For example, simple movements like arm or leg lifts can stimulate lymphatic flow, while strengthening exercises can improve overall muscle tone, reducing the likelihood of further fluid retention. Regular exercise also helps improve flexibility and mobility, which can be compromised due to swelling.
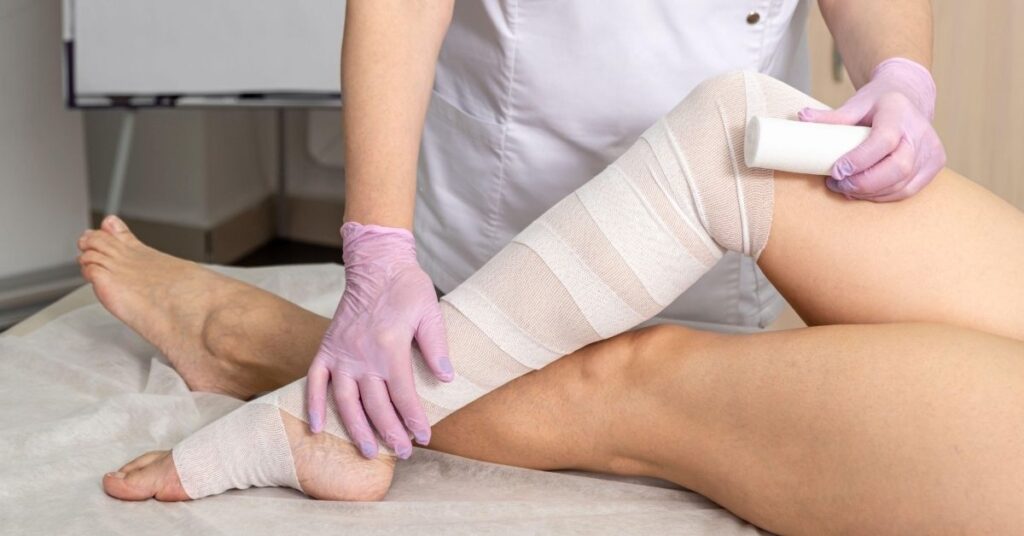
3. Compression Therapy
Compression therapy, in combination with manual lymphatic drainage and exercise, is crucial for managing lymphedema. Compression garments, such as sleeves, stockings, or bandages, apply controlled pressure to the affected area. This pressure helps prevent fluid from accumulating and supports the lymphatic system in draining excess fluid from the tissues.
The Importance of Compression in Lymphedema Treatment
Compression therapy applies consistent pressure to the swollen area, encouraging the lymph fluid to move through the lymphatic vessels and back into the bloodstream. Physical therapists will often work with patients to ensure they are using the appropriate compression garments and applying them correctly.
4. Education and Self-Management
A significant part of physical therapy for lymphedema involves educating patients on managing their condition at home. This includes teaching individuals about proper skin care to prevent infections, how to monitor swelling, and when to seek additional medical help. Patients are also trained in performing lymphatic drainage massage on themselves, allowing them to maintain fluid movement between therapy sessions.
Empowering Patients for Better Outcomes
Self-management is a powerful tool in the fight against lymphedema. By equipping individuals with the knowledge and techniques to manage their symptoms independently, physical therapists help reduce the need for frequent medical visits and improve long-term outcomes. Patients who are proactive in their care often experience better control over their symptoms.
5. Pain Management
Lymphedema can often be accompanied by discomfort or pain, particularly as swelling increases. Physical therapy can help alleviate this pain by improving circulation and reducing fluid accumulation. Techniques such as massage, gentle stretching, and heat or cold therapy may reduce pain and increase comfort.
Reducing Pain and Inflammation
Physical therapy can improve overall comfort by targeting the root cause of pain, which is often related to fluid buildup and poor circulation. For many individuals, managing pain effectively through physical therapy can make daily activities easier and improve quality of life.
6. Improving Mobility and Function
As lymphedema progresses, it can restrict movement, making simple tasks difficult. Physical therapy helps improve the range of motion in the affected area, allowing individuals to perform daily activities more easily. Stretching exercises, joint mobilization, and strength training are all part of a comprehensive plan to regain mobility.
Restoring Function and Independence
The primary goal of physical therapy is to restore function for people with lymphedema. Whether regaining the ability to walk comfortably, lift objects, or move limbs freely, physical therapy is vital for helping individuals return to their everyday lives and activities.
The Benefits of Physical Therapy for Lymphedema
Physical therapy offers a wide range of benefits for people with lymphedema. These include:
- Reduced swelling and fluid retention: Techniques like MLD and compression therapy help manage fluid buildup.
- Improved circulation: Exercise and movement enhance lymphatic flow and overall circulation.
- Pain relief: Therapy can help alleviate the discomfort associated with lymphedema.
- Restored mobility: Physical therapy helps improve joint flexibility and muscle strength, aiding movement.
- Empowerment: Self-management techniques teach patients how to care for their condition independently.
When Should You Seek Physical Therapy for Lymphedema?
It is advisable to consult a physical therapist if you have been diagnosed with lymphedema, particularly if you are experiencing persistent swelling, discomfort, or reduced movement in a limb. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from worsening and lead to better long-term management.
Conclusion
Physical therapy is crucial in managing lymphedema, helping individuals reduce swelling, alleviate pain, and regain mobility. Through a combination of lymphatic drainage massage, exercise therapy, compression therapy, and education, physical therapists empower patients to take control of their condition and improve their quality of life. If you or someone you know is living with lymphedema, working with a physical therapist can provide significant relief and support throughout the management process.
FAQs
Q1: Can physical therapy cure lymphedema?
Physical therapy cannot cure lymphedema, but it can help manage the symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Q2: How long does physical therapy for lymphedema take?
The duration of physical therapy varies depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment plan. Many individuals benefit from regular sessions over several weeks to months.
Q3: Is manual lymphatic drainage painful?
No, manual lymphatic drainage should not be painful. It is a gentle technique designed to promote fluid movement and reduce swelling.
Q4: Can I do lymphatic drainage massage on my own at home?
Yes, after being trained by a physical therapist, you can perform self-massage techniques at home to help manage lymphedema.
Q5: What types of compression garments are best for lymphedema?
The best compression garments depend on the area affected by lymphedema. A physical therapist can help you select the right type and fit for your needs.