Dealing with both lymphedema and joint pain can be incredibly challenging. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of lymphedema, its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. We will explore the intricate relationship between the lymphatic system and lymphedema, offering practical advice for those affected by this condition.
Understanding Lymphedema
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the build-up of lymph fluid in the body’s tissues, leading to swelling, typically in the arms and legs. Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining this fluid, is impaired or blocked. This impairment prevents the proper drainage of lymph fluid, leading to persistent swelling and discomfort.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
Lymphedema presents with a range of symptoms. Some of the more common signs include:
- Swelling in an arm or leg
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness
- Decreased range of motion
Other symptoms of lymphedema may involve aching or discomfort in the affected limb, recurring infections, and skin changes such as thickening or hardening. Early detection of these lymphedema symptoms is essential for effective management.
Cause of Lymphedema
The cause of lymphedema can be categorized as primary or secondary. Primary lymphedema is rare and results from genetic abnormalities that affect the development of the lymph vessels. Secondary lymphedema, on the other hand, is more common and often results from damage to the lymph nodes or lymph vessels due to cancer treatment, surgery, or infection. Cancer surgery, especially breast cancer surgery, is a significant risk factor.
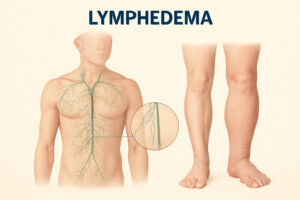
The Lymphatic System’s Role
How the Lymphatic System Works
The lymphatic system is an integral part of the immune system, working throughout the body to maintain fluid balance and fight infection. It consists of a network of lymph vessels and lymph nodes that transport lymph fluid, a clear fluid containing white blood cells. The lymphatic system collects excess fluid, proteins, and waste products from the body’s tissues, filtering them through the lymph nodes before returning the cleansed fluid to the bloodstream.
Impact of Cancer Treatment on Lymphedema
Cancer treatment, including cancer surgery and radiation therapy, can significantly increase the risk of developing lymphedema. When lymph nodes are removed during cancer surgery, or when lymph vessels are damaged, it disrupts the normal flow of lymph fluid, causing it to accumulate in the tissues. This is particularly common after breast cancer, where axillary lymph nodes are often removed.
Stages of Lymphedema
Lymphedema progresses through several stages, each characterized by different symptoms. These stages can be generally understood as follows:
- Stage 0, also known as the latent stage, where underlying lymphatic damage may be present without visible swelling.
- Stage 1, involving reversible swelling that decreases with elevation.
Further progression includes Stage 2, characterized by spontaneous, irreversible swelling, and Stage 3, the most severe form, which involves significant swelling, skin changes, and potential complications.
Identifying Symptoms and Causes
Common Symptoms of Lymphedema
Early recognition of lymphedema symptoms is vital for effective management. Individuals affected by lymphedema might notice several indicators, including:
- Persistent swelling, often in the arm or leg
- A sensation of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb
The condition can also lead to discomfort or aching, decreased range of motion, and in some instances, skin alterations like thickening or hardening.
Areas of the Body Affected
Lymphedema may affect various parts of the body, though it commonly targets the arms and legs. The area affected by lymphedema is often determined by the location of the initial lymphatic damage. For instance, breast cancer surgery can lead to lymphedema in the arm on the same side as the surgery, as the lymph nodes are often removed. Secondary lymphedema may affect other regions depending on the cause of swelling.
Risk Factors for Lymphedema
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing lymphedema. Cancer treatment, particularly cancer surgery and radiation therapy, is a significant risk. Removing lymph nodes during surgery disrupts the normal flow of lymph fluid. Other risk factors include obesity, infections, and certain medical conditions that affect the lymph vessels. Being aware of these risk factors can help people with lymphedema take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent lymphedema from occurring.
Managing Lymphedema
Treatment for Lymphedema
Treatment for lymphedema focuses on reducing swelling and managing symptoms to improve the patient’s quality of life. There are several effective treatment options available. These include manual lymphatic drainage, a specialized massage technique performed by lymphedema therapists to encourage the flow of lymph fluid. Compression therapy, involving wearing compression garments, is another cornerstone of lymphedema treatment, helping to reduce swelling and support the lymph system.
Lymphedema Management Techniques
Effective lymphedema management techniques involve a combination of professional therapies and self-care strategies. Manual lymphatic drainage helps move excess fluid from the affected area. Compression garments provide support and reduce swelling, helping the fluid move throughout more efficiently. Exercise, particularly exercises that promote lymphatic drainage, is also beneficial. Good skin care is also crucial to prevent infections. These methods assist in managing lymphedema.
Living with Lymphedema: Daily Tips
Living with lymphedema requires incorporating specific daily habits to manage the condition effectively. One essential tip is to wear compression garments as prescribed to control swelling and support the lymphatic system. Regular, gentle exercise can promote lymph fluid drainage and overall well-being. Maintaining a healthy weight is also important, as obesity can exacerbate lymphedema. Paying meticulous attention to skin care helps prevent infections, which are a risk for developing lymphedema.
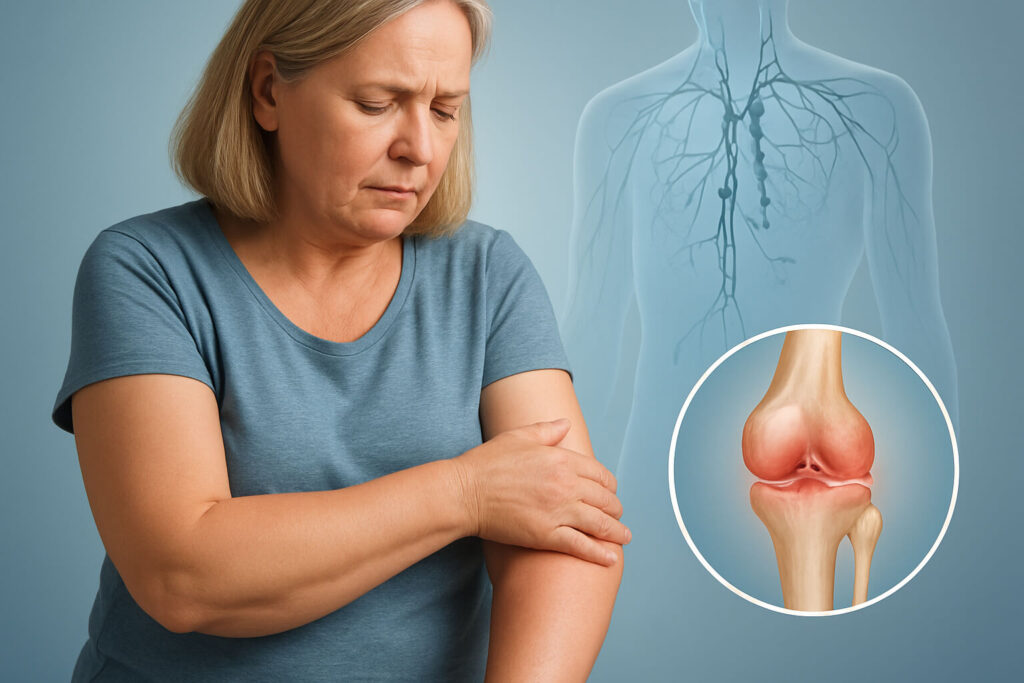
Lymphedema Can Be Painful
Understanding Joint Pain in Relation to Lymphedema
Joint pain can be a significant and often overlooked symptom associated with lymphedema. When lymphedema occurs, the accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues can cause inflammation and pressure on nearby joints, leading to discomfort and pain. People with lymphedema in the arm or leg may experience stiffness, reduced range of motion, and aching sensations in the adjacent joints, further complicating their daily lives and overall quality of life, especially in severe cases of lymphedema.
Strategies for Coping with Joint Pain
Several strategies can help manage joint pain related to lymphedema. Gentle exercises, such as range-of-motion exercises and low-impact activities, can help improve joint mobility and reduce stiffness. Applying warm compresses to the affected joints can also provide relief by increasing blood flow and reducing muscle tension. In addition, manual lymphatic drainage performed by lymphedema therapists can help reduce swelling and alleviate pressure on the joints. These strategies assist in treatment for lymphedema.
When to Seek Professional Help
It’s essential to seek professional help if joint pain becomes severe or persistent, or if it interferes with your daily activities. A healthcare provider can evaluate your condition and determine the underlying cause of the pain, whether it’s directly related to lymphedema or another issue. They may recommend additional treatment options, such as pain medication or physical therapy, to help you manage your symptoms and improve your overall well-being. Early intervention can prevent severe cases of lymphedema.
Conclusion and FAQs
Recap of Key Points
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by swelling due to impaired lymphatic drainage, leading to various symptoms, including joint pain. The lymphatic system plays a crucial role throughout the body in maintaining fluid balance and immune function. Cancer treatment, particularly cancer surgery, is a significant risk factor for developing lymphedema. Managing lymphedema involves a combination of therapies such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression garments, and lifestyle adjustments.
Final Advice for Managing Symptoms
Living with lymphedema requires a proactive and consistent approach to manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. Wear compression garments as prescribed by your healthcare provider to control swelling and support lymphatic drainage. Incorporate regular, gentle exercise into your routine to promote lymph fluid movement. Pay meticulous attention to skin care to prevent infections, which are a common risk of developing lymphedema. Seek support from lymphedema therapists.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main cause of lymphedema?
The cause of lymphedema is often due to damage or blockage in the lymphatic system, which can result from cancer treatment, surgery, or genetic conditions, leading to a buildup of lymph fluid and swelling in the affected area.
How can I reduce lymphedema swelling at home?
To reduce swelling from lymphedema at home, elevate the affected limb, perform gentle exercises to promote lymph drainage, wear compression garments as prescribed, and practice good skin care to prevent infections, which can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms.
Is lymphedema curable, or is it a lifelong condition?
Lymphedema is typically a chronic condition without a definitive cure. However, with proper management techniques such as manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, and lifestyle adjustments, people with lymphedema can effectively control their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Can massage help with lymphedema?
Yes, massage, specifically manual lymphatic drainage performed by trained lymphedema therapists, can be highly beneficial. This specialized massage technique helps to move excess lymph fluid from the affected area, reducing swelling and improving lymphatic flow throughout the body.
What type of exercises are recommended for people with lymphedema?
Gentle, low-impact exercises that promote lymphatic drainage are recommended for people with lymphedema. These may include range-of-motion exercises, walking, swimming, and specialized lymphedema exercises prescribed by a therapist to improve lymphatic function and reduce swelling in the affected arm or leg.