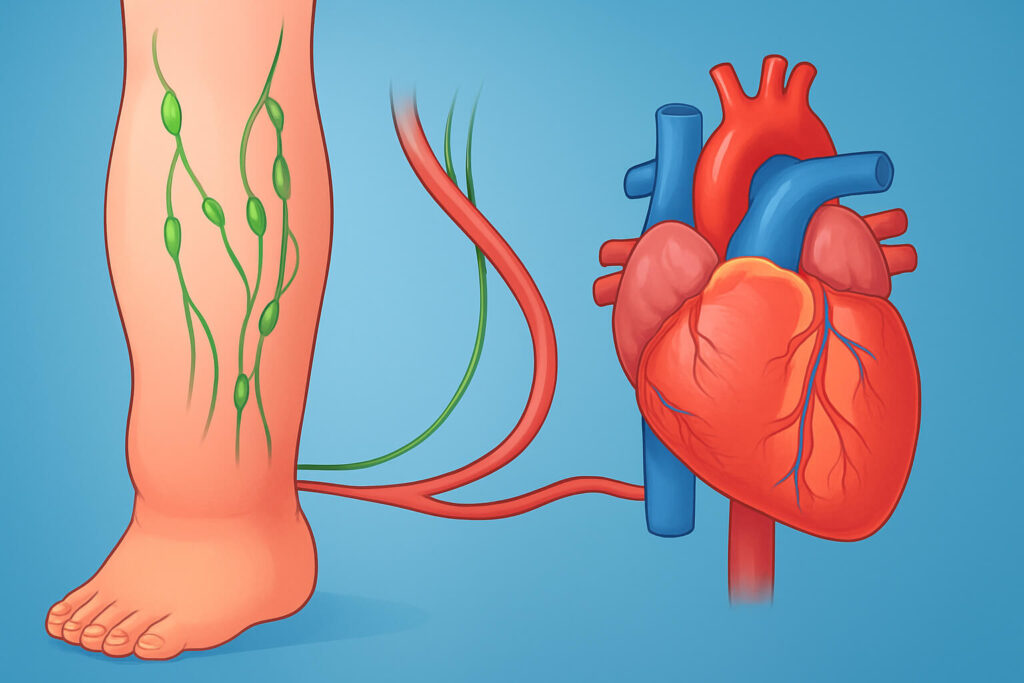
Explore the intricate relationship between lymphedema and cardiovascular health. This article delves into the vascular connections, offering insights for both beginners and experts. We will discuss how lymphedema affects the lymphatic system and its subsequent impact on heart health. Understanding the link is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life.
Introduction to Lymphedema
What is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a condition characterised by swelling, typically in the arms or legs, due to a blockage in the lymphatic system. This blockage prevents lymph fluid from draining properly, leading to accumulation in the tissue. Lymphedema affects millions worldwide and can significantly impact quality of life.
Types of Lymphedema: Primary vs. Secondary
Lymphedema can be broadly categorised into two main types. These types are:
- Primary lymphedema is a rare, inherited condition resulting from lymphatic system malformations.
- Secondary lymphedema, which is more common and stems from damage to the lymphatic vessels, is frequently due to cancer treatment or surgery.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
Lymphedema symptoms can vary but often include swelling in an affected limb, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, and skin changes. The affected area may also experience recurring infections. Early detection and management are crucial to reducing swelling and preventing complications associated with lymphedema.
The Lymphatic System and Its Role
Understanding the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the vascular and circulatory system, responsible for maintaining fluid balance and immune function. Lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, travels through lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes, filtering out waste and pathogens. Proper lymphatic drainage is essential for overall health.
How the Lymphatic System Affects Cardiovascular Health
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in cardiovascular health by managing fluid levels and preventing inflammation. Impaired lymphatic function, as seen in lymphedema, can lead to fluid accumulation and increased pressure on blood vessels and the heart. This can contribute to cardiovascular disease and high blood pressure.
The Vascular Connection Between Lymphedema and Heart Health
The connection between lymphedema and heart health is rooted in the shared vascular pathways. When lymphatic drainage is compromised, the resulting fluid build-up can strain the circulatory system. This strain can exacerbate existing venous insufficiency or heart failure, highlighting the need for comprehensive management of lymphedema and cardiovascular risk factors.
Impact of Lymphedema on Cardiovascular Health
How Lymphedema Affects Heart Failure Risk
Lymphedema affects heart failure risk through several mechanisms. The lymphatic system’s impaired lymphatic drainage leads to fluid accumulation in the tissue, increasing blood volume and putting extra strain on the heart. This added stress can exacerbate existing cardiovascular issues and contribute to the development of heart failure. Manage lymphedema effectively to mitigate these risks and support cardiovascular health.
The Link Between Insufficiency and Lymphedema
Venous insufficiency and lymphedema are interconnected conditions. Insufficiency in the vascular system can lead to fluid build-up in the limbs, overwhelming the lymphatic vessels and the lymphatic system. This overload impairs lymphatic drainage, contributing to lymphedema. Addressing venous issues is crucial in managing lymphedema and preventing further complications in the affected limb.
Cardiovascular Disease and Lymphedema: What You Need to Know
Lymphedema and cardiovascular disease share a complex relationship. Cardiovascular diseases can compromise blood flow and circulation, affecting lymphatic function and potentially leading to secondary lymphedema. Conversely, chronic lymphedema can strain the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications such as high blood pressure. Understanding the link is vital for comprehensive care.
Treatment Options for Lymphedema
Managing Lymphedema: Lifestyle Changes and Home Care
Managing lymphedema involves several lifestyle changes and home care strategies. To significantly improve quality of life, consider incorporating these measures:
- Regular exercise, especially activities that promote lymphatic drainage, can help reduce swelling.
- A balanced diet low in sodium supports overall vascular and circulatory health.
- Proper skin care is essential to prevent infections in the affected area.
- Compression garments.
Medical Treatments for Lymphedema
Medical treatments for lymphedema encompass a range of therapies aimed at reducing swelling and improving lymphatic function. Key components of lymphedema management include:
- Compression therapy, often using garments or bandages, is used to reduce swelling.
- Manual lymphatic drainage, a specialised technique performed by trained therapists.
Pneumatic compression devices can also aid lymphatic circulation, but should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Surgical Treatment for Lymphedema
Surgical treatment for lymphedema is considered when conservative treatments are insufficient. Lymphedema surgery options include lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA), which connects lymphatic vessels to veins to improve lymphatic drainage, and lymphatic vessel bypass. In some cases, liposuction may be used to remove excess tissue and reduce swelling in the affected arm or leg. Surgical treatment is a consideration to improve lymphatic function and quality of life.
Specific Cases: Lymphedema in Breast Cancer Survivors
The Risk of Lymphedema After Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast cancer survivors often face the risk of developing secondary lymphedema as a result of cancer treatment. The removal or radiation of lymph nodes during treatment can disrupt the lymphatic drainage in the affected arm, leading to swelling. Understanding the link between breast cancer treatment and lymphedema is crucial for early detection and effective management of the condition. Lymphedema may significantly impact the quality of life of breast cancer survivors.
Managing Lymphedema in Cancer Survivors
Managing lymphedema in cancer survivors requires a comprehensive approach. Compression garments are essential to reduce swelling and support lymphatic circulation in the affected limb. Manual lymphatic drainage, performed by trained therapists, can help improve lymphatic drainage. Regular exercise and proper skin care are also vital components of treatment options for managing lymphedema, supporting heart health, and improving the quality of life for those living with lymphedema.
Success Stories: Overcoming Lymphedema
Many breast cancer survivors have successfully overcome lymphedema through dedicated management strategies. These success stories often involve early intervention, consistent use of compression, and a proactive approach to lymphatic drainage. By sharing these experiences, we can inspire hope and provide practical advice for others facing similar challenges with lymphedema. These stories highlight that living with lymphedema can include a high quality of life.
Future Insights and Trends in Lymphedema Treatment
Innovative Research and Developments
Innovative research is continuously advancing treatments for lymphedema, offering hope for improved outcomes. Current studies are exploring new surgical techniques to enhance lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling. Additionally, researchers are investigating pharmacological approaches to stimulate lymphatic function and prevent the progression of lymphedema. These developments are important to cardiovascular health and lymphedema and cardiovascular health.
Emerging Treatment Options
Emerging treatment options for lymphedema include advanced therapies that target the underlying causes of lymphatic dysfunction. Gene therapy and regenerative medicine hold promise for repairing damaged lymphatic vessels and restoring lymphatic function. Furthermore, new imaging techniques are improving the ability to diagnose lymphedema early, allowing for timely intervention and better management of the condition and improving heart health.
Importance of Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection and prevention are paramount in managing lymphedema and mitigating its impact on cardiovascular health. Regular monitoring of at-risk individuals, such as those who have undergone cancer treatment, can help identify early signs of swelling. Preventative measures, including proper skin care and avoiding trauma to the affected arm or leg, can reduce the risk of developing lymphedema and can improve circulation.
Conclusion and FAQs
Recap of Key Points
In summary, lymphedema is a condition characterised by swelling due to impaired lymphatic drainage, impacting cardiovascular health. The lymphatic system’s vascular connection to the heart means that lymphatic dysfunction can strain the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart failure. Effective management of lymphedema, including compression, exercise, and proper skin care, is crucial for improving quality of life. The management of lymphedema affects the vascular system and lymphatic system, which subsequently affects cardiovascular health.
Final Advice for Managing Lymphedema
For those living with lymphedema, proactive management is key. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses your specific needs. Incorporate regular exercise, maintain a healthy diet, and prioritise proper skin care to minimise swelling and prevent complications. Remember, early intervention and consistent self-care can significantly improve your quality of life. This will help you manage lymphedema more effectively.
FAQs About Lymphedema and Cardiovascular Health
Q1: Can lymphedema cause heart problems?
Yes, impaired lymphatic drainage from lymphedema can increase fluid volume and strain the cardiovascular system, potentially leading to or exacerbating heart conditions.
Q2: How does compression help with lymphedema?
Compression garments support lymphatic drainage by applying external pressure, reducing swelling, and preventing fluid accumulation in the affected limb.
Q3: What lifestyle changes can improve lymphedema symptoms?
Regular exercise, a balanced low-sodium diet, and proper skin care can improve lymphatic function and reduce swelling associated with lymphedema.
Q4: Is there a cure for lymphedema?
While there’s no definitive cure for lymphedema, effective treatments can manage symptoms, improve lymphatic drainage, and enhance quality of life.
Q5: How can I prevent lymphedema after cancer treatment?
Monitor for early signs of swelling, protect your affected arm or leg from injury, and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for lymphatic care and exercise.