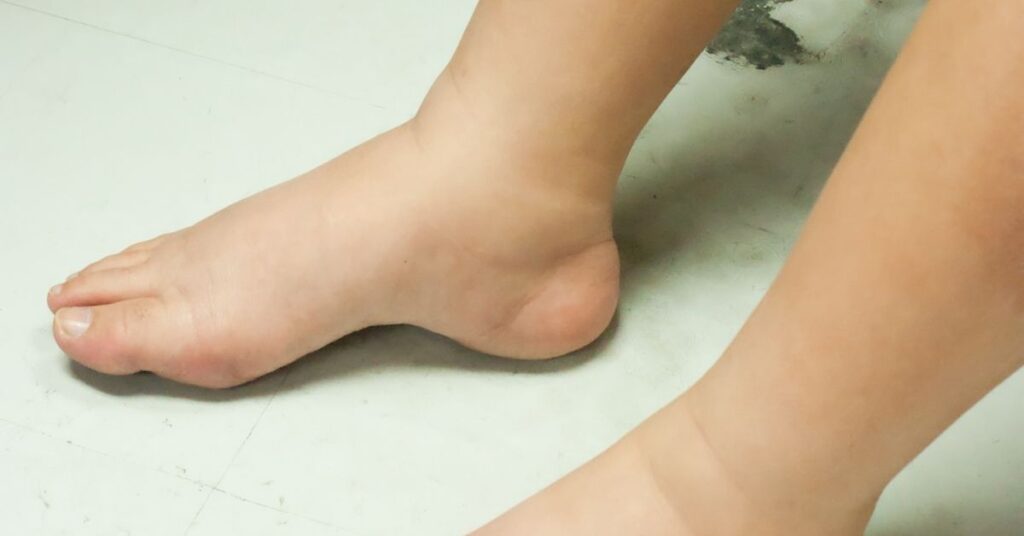
Lymphedema, a condition characterized by swelling due to lymphatic dysfunction, has significant implications for diabetic patients, particularly those managing type 2 diabetes. This article will delve into the relationship between lymphedema and diabetes, exploring how these conditions impact the lower limbs and detailing effective management strategies to improve outcomes for patients affected by both ailments.
What is Lymphedema and How Does it Relate to Diabetes?
Defining Lymphedema and Its Causes
Lymphedema is defined as the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, typically in the lower limbs, leading to swelling and discomfort. This condition can arise from various factors, including lymphatic injury, surgical interventions, or radiation therapy, particularly in cases of breast cancer-related lymphedema. Secondary lymphedema, which is often seen in patients with diabetes, occurs when the lymphatic system is compromised due to underlying health issues. In individuals with diabetes, the risk of developing lymphedema is heightened due to potential complications such as poor circulation and damage to the lymphatic vessels, which can impede lymph flow and contribute to tissue swelling.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Types
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to produce or utilize insulin effectively. There are two primary types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes, which is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin, and type 2 diabetes, which often develops due to insulin resistance. The management of blood sugar levels is essential in both types, as elevated glucose levels can lead to significant complications, including neuropathy, cardiovascular disease, and complications of the lymphatic system. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are particularly susceptible to these complications, making it crucial to understand how diabetes can exacerbate the risk of lymphedema.
How Diabetes Affects the Lymphatic System
The relationship between diabetes and the lymphatic system is complex. Diabetes can lead to lymphatic dysfunction, which impairs lymphatic function and can cause damage to the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes. Additionally, hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels, can lead to inflammation and tissue damage, further complicating the management of lymphedema. Patients with diabetes often experience reduced blood flow and impaired healing, making them more vulnerable to the effects of lymphedema in the lower limbs. Understanding this connection is vital for developing effective strategies to manage lymphedema and mitigate its impact on diabetic patients.
How Can Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Manage Lymphedema?
Effective Strategies for Managing Lymphedema
Managing lymphedema in patients with type 2 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach. Effective strategies include regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy diet, and engaging in physical activity to improve circulation. Compression therapy is also essential, as it helps maintain lymph flow and reduces swelling in the lower limbs. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans that address both their diabetes and lymphedema. Education on self-care techniques, such as skin care and proper foot hygiene, is also critical in preventing complications associated with diabetes and lymphedema.
The Role of Compression Therapy in Diabetes
Compression therapy plays a pivotal role in the management of lymphedema, particularly for diabetic patients. By applying controlled pressure to the affected limbs, compression garments can enhance lymphatic drainage and reduce swelling. This therapy also aids in improving blood circulation, which is often compromised in individuals with diabetes. It is important for patients to consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate type of compression therapy, as improper use can lead to further complications. Regular use of compression garments, in conjunction with other treatment modalities, can significantly improve the quality of life for patients managing lymphedema and diabetes.
Importance of Blood Sugar Control in Managing Lymphedema
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial in managing lymphedema for patients with diabetes. Elevated blood sugar can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms by increasing inflammation and impairing lymphatic function. Implementing lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adherence to prescribed medications can help regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, monitoring and managing blood sugar can prevent further complications, such as diabetic foot ulcers, which are common in patients with diabetes and can be exacerbated by lymphedema.
What Are the Effects of Intermittent Pneumatic Compression on Lymphedema?
How Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Works
Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) is a therapeutic technique that utilizes a device to apply sequential pressure to the affected limbs. The mechanism involves inflating and deflating compartments within a sleeve, which promotes lymphatic flow and reduces swelling in the lower limbs. IPC can be particularly beneficial for patients with lymphedema, as it enhances lymphatic function and alleviates discomfort associated with fluid accumulation. This treatment modality is often integrated into comprehensive care plans for individuals managing lymphedema and diabetes.
Benefits for Patients with Diabetes
For diabetic patients, the benefits of intermittent pneumatic compression extend beyond merely reducing lymphedema. IPC can help improve overall circulation, which is crucial for patients experiencing complications related to diabetes. By enhancing lymphatic flow and reducing swelling, IPC can also alleviate pressure on nerves and improve mobility. These advantages contribute to better overall health outcomes for patients managing both diabetes and lymphedema, making IPC a valuable component of their treatment plan.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Despite its benefits, there are potential risks associated with the use of intermittent pneumatic compression for patients with diabetes. It is essential for healthcare providers to assess the individual needs and health status of patients before implementing IPC. Conditions such as severe peripheral vascular disease or active infections may contraindicate the use of IPC. Therefore, careful evaluation and monitoring are paramount to ensure safe and effective treatment. Patients should be educated about the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms or changes in their condition while undergoing IPC therapy.
What is the Connection Between Diabetes and Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
The Impact of Hyperglycemia on Foot Health
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common and serious complication of diabetes that can have devastating consequences. Hyperglycemia can impair circulation and lead to neuropathy, reducing sensation in the feet and increasing the risk of injury. When combined with lymphedema, the risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers escalates significantly. The swelling associated with lymphedema can create pressure points on the feet, leading to skin breakdown and ulcer formation. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies.
Preventing Foot Ulcers in Diabetic Patients
Preventing foot ulcers in diabetic patients involves a proactive approach that includes regular foot inspections, proper footwear, and maintaining optimal blood sugar levels. Patients should be encouraged to keep their feet clean and dry and to seek medical attention for any signs of wounds or infections. Additionally, managing lymphedema through compression therapy and other modalities can significantly reduce the risk of ulcer development by minimizing swelling and improving overall foot health. Education on foot care is essential for all diabetic patients, particularly those also dealing with lymphedema.
Managing Diabetic Foot Ulcers with Lymphedema
When diabetic foot ulcers occur in patients with lymphedema, management becomes more complex. The presence of lymphedema can impede healing and increase the risk of infection, necessitating a comprehensive treatment approach. Collaboration between healthcare providers, including wound care specialists and lymphedema therapists, is essential to address both conditions effectively. Treatment may involve advanced wound care techniques, lymphatic drainage therapies, and strict blood sugar control to promote healing and prevent further complications.
How Can Manual Lymphatic Drainage Be Beneficial for Diabetic Patients?
What is Manual Lymphatic Drainage?
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique designed to promote lymphatic flow and reduce swelling in affected areas. The gentle, rhythmic strokes employed in MLD stimulate the lymphatic system and help facilitate the removal of excess fluid from the tissues. For patients with lymphedema, especially those with diabetes, MLD can be an integral part of their management plan, aiding in reducing lower limb lymphedema and improving overall well-being.
Benefits of Manual Lymphatic Drainage for Lymphedema
The benefits of manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema are manifold. By enhancing lymphatic function and reducing swelling, MLD can alleviate discomfort and improve mobility for patients. Additionally, the calming nature of MLD can provide psychological benefits, helping to reduce stress and anxiety often associated with chronic health conditions like diabetes and lymphedema. Integrating MLD into a comprehensive care plan can significantly enhance the quality of life for diabetic patients managing lymphedema.
Integrating Manual Lymphatic Drainage into Diabetes Care
Integrating manual lymphatic drainage into diabetes care requires collaboration between healthcare providers and therapists specialized in lymphatic health. Patients should be educated about the benefits of MLD and how it can complement other treatment modalities, such as compression therapy and blood sugar management. Regular sessions of MLD can help maintain lymphatic function and improve overall health outcomes for patients dealing with both diabetes and lymphedema. This holistic approach not only addresses the physical aspects of these conditions but also supports the emotional and psychological well-being of patients.
FAQS
Q: How does lymphedema and diabetes affect the lower limbs?
A: Lymphedema and diabetes can significantly impact the lower limbs by causing swelling due to impaired lymphatic system function. People with diabetes are at a higher risk for lymphedema, especially if they have diabetes complications that affect blood vessels and circulation.
Q: What is the relationship between diabetes complications and lymphedema?
A: Diabetes complications, such as diabetic neuropathy, can lead to reduced sensation and mobility in the lower limbs, increasing the risk for lymphedema. The impaired blood flow and nerve function can hinder lymphatic transport, exacerbating swelling.
Q: What are some common symptoms of lymphedema in people with diabetes?
A: Common symptoms include swelling in the lower limbs, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, and restricted movement. Skin changes and infections may also occur due to compromised lymphatic contractile function.
Q: What are the treatment options for lymphedema and diabetes?
A: Treatment of lymphedema may include compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), and intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC). These methods can enhance lymphatic pump function and improve lymphatic contraction.
Q: How can living with diabetes affect the development of lymphedema?
A: Living with diabetes can increase the risk for lymphedema due to factors such as poor circulation and nerve damage. These conditions can impair lymphatic system function, leading to the development of lymphedema.
Q: What is primary lymphedema, and how does it relate to diabetes?
A: Primary lymphedema is a genetic condition that affects lymphatic system function. While it is not directly related to diabetes, individuals with diabetes may experience secondary lymphedema due to additional complications affecting their lymphatic and vascular systems.
Q: Can vascularized lymph node transfer help individuals with lymphedema and diabetes?
A: Yes, vascularized lymph node transfer can be a surgical option for treating lymphedema in people with diabetes. This procedure aims to restore lymphatic transport by introducing healthy lymph nodes that can enhance lymphatic contractility.
Q: How does IPC in reducing lower limb lymphedema work?
A: Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) works by applying pressure to the lower limbs, promoting lymphatic pump action and improving lymphatic contractile function. This can help reduce swelling and improve overall lymphatic drainage in individuals with lymphedema and diabetes.
Q: Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage lymphedema in people with diabetes?
A: Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active, and managing blood sugar levels are important lifestyle changes that can help manage lymphedema. Regular exercise can improve blood circulation and lymphatic function, reducing the risk of swelling.