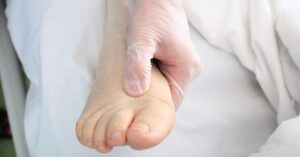
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, which can lead to swelling in the affected limbs, typically an arm or a leg. This condition can significantly impact the immune system, as the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in our body’s defense mechanisms. Understanding the intricacies of lymphatic dysfunction, its causes, and its effects on immune function is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike. In this article, we will explore the relationship between lymphedema and the immune system, providing insights into the management and long-term effects of this condition.
What is the Risk for Lymphedema and How Does It Affect the Immune System?
What Causes Lymphedema?
Lymphedema can be classified into primary and secondary forms. Primary lymphedema is often caused by developmental abnormalities in the lymphatic system, while secondary lymphedema is typically a result of factors such as cancer treatment, trauma, or infections that damage lymphatic vessels. A common cause of secondary lymphedema includes surgeries for breast cancer, where lymph nodes are removed or damaged, leading to impaired lymphatic function. Patients with lymphedema may also experience exacerbations due to infections, obesity, or prolonged immobility, all of which can further compromise lymphatic drainage.
How Does Lymphatic Dysfunction Occur?
Lymphatic dysfunction occurs when there is damage to lymphatic vessels, leading to the failure of the lymphatic system to transport lymphatic fluid effectively. This dysfunction can arise from congenital issues, surgical interventions, or trauma. Additionally, conditions such as lymphatic filariasis can cause significant damage to the lymphatic vasculature, resulting in severe lymphedema symptoms. When the lymphatic system is unable to function properly, lymphatic fluid accumulates in the interstitial spaces, causing swelling and inflammation in the affected limb.
What are the Common Symptoms of Lymphedema?
Common symptoms of lymphedema include swelling in the affected arm or leg, a feeling of heaviness, discomfort, and restricted range of motion. Early-stage lymphedema may be characterized by reversible swelling that is soft to the touch, but as the condition progresses, the swelling can become more pronounced and harden, indicating chronic lymphedema. Patients with lymphedema may also notice changes in skin texture and color, which can complicate the management of this condition. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of further complications.
How Does Lymphatic Dysfunction Influence Immune Function?
What is the Role of the Lymphatic System in Immune Response?
The lymphatic system is integral to the immune response, serving as a conduit for immune cells and lymphatic fluid. It transports lymph containing lymphocytes and other immune cells throughout the body, facilitating adaptive immune responses to pathogens. When lymphatic dysfunction occurs, the impaired lymphatic vessels hinder the transport of immune cells, leading to a diminished immune response. This can predispose patients with lymphedema to recurrent infections, particularly in the affected limb, highlighting the importance of maintaining optimal lymphatic function for overall immune health.
How Does Inflammation Affect Immune Cells?
Inflammation is a key component of the immune response; however, chronic inflammation associated with lymphedema can adversely affect immune cells. The accumulation of lymphatic fluid can lead to an inflammatory environment, which may alter the function of immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages. This dysfunction in lymphedema can result in impaired immune function, making it more challenging for the body to respond effectively to infections and other threats. Furthermore, persistent inflammation can contribute to the pathogenesis of lymphedema, creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates both swelling and immune dysfunction.
What are the Effects of Immune Cells in Lymphedema?
In patients with lymphedema, the distribution and function of immune cells can be significantly impacted. The presence of inflammatory cells in the affected limb may contribute to tissue damage and fibrosis, further complicating the condition. Additionally, the altered immune environment can lead to an imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory signals, perpetuating a state of chronic inflammation. Understanding the role of immune cells in lymphedema is essential for developing targeted therapies aimed at restoring lymphatic function and improving immune responses in affected patients.
What is the Connection Between Secondary Lymphedema and Immune Dysfunction?
How Can Cancer Treatment Lead to Secondary Lymphedema?
Cancer treatment, particularly surgical interventions and radiation therapy, is a well-documented cause of secondary lymphedema. The removal or damage of lymph nodes during surgery can disrupt the normal flow of lymphatic fluid, leading to swelling and an increased risk of infection in the affected limb. Breast cancer-related lymphedema is a common example, where patients often experience swelling following axillary lymph node dissection. The resulting lymphatic dysfunction not only causes physical symptoms but also poses a risk for compromised immune function, making vigilant monitoring and management essential.
What is the Impact of Lymphatic Injury on Immune Function?
Lymphatic injury, whether due to surgery, trauma, or infection, can have profound effects on immune function. When lymphatic vessels are damaged, the body’s ability to transport immune cells is compromised, leading to impaired immune responses. Inflammation may also increase as a result of lymphatic dysfunction, further contributing to immune cell dysregulation. This disruption can make patients more susceptible to infections, underscoring the importance of addressing lymphatic health as part of overall immune system care.
Can Lymphatic Filariasis Cause Lymphedema?
Lymphatic filariasis, a parasitic infection caused by filarial worms, is a significant cause of lymphedema in endemic regions. The infection leads to damage of lymphatic vessels and nodes, resulting in severe swelling and chronic inflammation. This condition exemplifies how infectious agents can induce lymphatic dysfunction, ultimately leading to compromised immune function. Managing lymphedema in patients with lymphatic filariasis requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the underlying infection and the resulting lymphatic impairment.
How Can Lymphedema Management Improve Immune System Health?
What Are Effective Treatments for Managing Lymphedema?
Effective treatment for lymphedema often involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing swelling and improving lymphatic function. Compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and exercises designed to stimulate lymphatic flow are commonly employed. Additionally, skin care is crucial for preventing infections, which can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms and compromise immune function. By implementing a comprehensive management plan, patients can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with lymphedema.
How Does Lymphatic Drainage Help in Lymphedema Management?
Lymphatic drainage is a specialized technique that involves gentle manipulation of the skin and underlying tissues to encourage lymphatic fluid movement. This therapy can significantly help in managing lymphedema by promoting the reabsorption of lymphatic fluid and reducing swelling in the affected limb. By enhancing lymphatic function, lymphatic drainage not only alleviates physical symptoms but also supports immune health by facilitating the movement of immune cells throughout the body. Regular sessions can play a vital role in maintaining optimal lymphatic function for patients with lymphedema.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Support Lymphatic Function?
In addition to clinical treatments, lifestyle changes can significantly impact lymphatic function and overall immune health. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing good skin care can all contribute to the management of lymphedema. Additionally, staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate the effects of chronic inflammation associated with lymphedema. These proactive measures empower patients to take control of their health and support their immune system.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Lymphedema on the Immune System?
How Can Chronic Inflammation Affect Immune Response?
Chronic inflammation resulting from lymphedema can have detrimental effects on the immune response over time. An ongoing inflammatory state may lead to immune cell exhaustion, reducing the body’s ability to effectively respond to infections. Furthermore, persistent inflammation can contribute to tissue damage and fibrosis, compounding the challenges associated with managing lymphedema. Awareness of these long-term effects is essential for both patients and healthcare providers in order to implement strategies to mitigate the complications of chronic inflammation on immune function.
What Role Do Affected Limbs Play in Overall Immune Health?
The affected limb in patients with lymphedema plays a critical role in overall immune health. As swelling persists, the risk of infections increases, which can further compromise the immune system. The skin barrier may become disrupted, allowing pathogens to enter more easily. Effective management of lymphedema is therefore vital not only for alleviating physical discomfort but also for protecting the integrity of the immune system. This highlights the interconnectedness of lymphatic health and immune function in patients with lymphedema.
How Can Individuals with Lymphedema Monitor Their Immune Function?
Monitoring immune function in individuals with lymphedema can be achieved through regular check-ups with healthcare providers, who can assess for signs of infection or other complications. Patients should be educated on recognizing changes in their symptoms, such as increased swelling, redness, or pain, which may indicate an underlying issue. Maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals and adhering to prescribed management strategies can empower patients to proactively manage their condition and support their immune health effectively.