Understanding Compression Bandaging in Lymphedema Management
Living with lymphedema can be challenging, but the proper treatment methods, like compression bandaging, can make a difference. Understanding how compression works is essential whether you’re new to this condition or looking to refine your current approach.
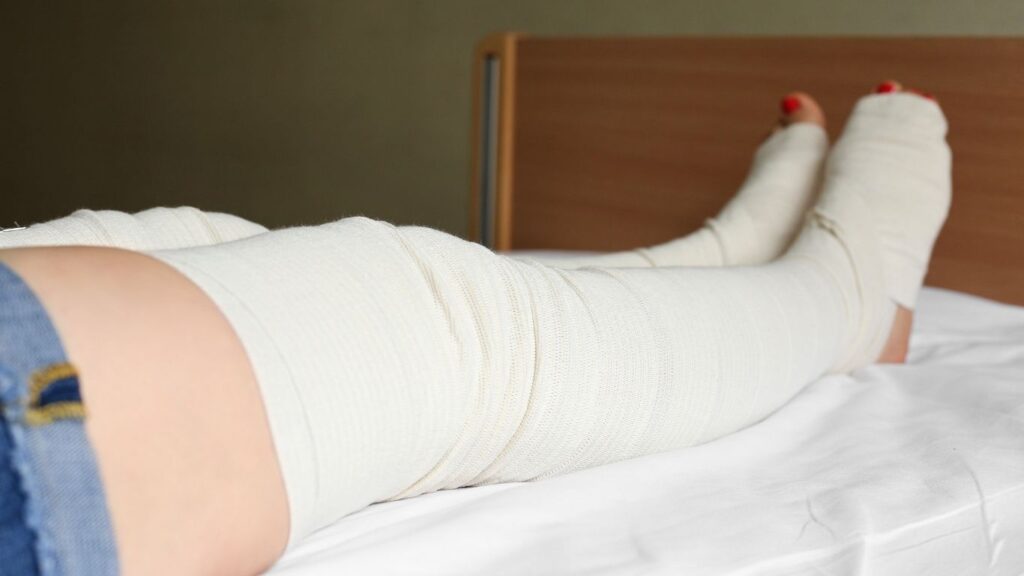
Compression bandages help manage the symptoms of lymphedema by improving lymphatic flow, reducing swelling, and supporting the limb. They are a key component of lymphedema treatment, often used alongside other therapies like compression sleeves, stockings, and pneumatic compression devices. This article will explain everything you need to know, from the types of compression bandages available to proper application techniques and common complications.
What is Lymphedema and How Can Compression Bandages Help?
Defining Lymphedema and Its Causes
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by the buildup of lymph fluid in tissues, leading to swelling, usually in the arms or legs. This happens when the lymphatic system is damaged or blocked, often due to surgery, radiation, or injury. Primary lymphedema is inherited, while secondary lymphedema results from external factors like breast cancer treatment or trauma.
Patients with lymphedema experience swelling, discomfort, and limited mobility. Effectively managing lymphedema requires reducing fluid retention and improving lymph flow, which is where compression bandages come into play. These specialized bandages provide graduated compression, helping to move lymph fluid out of swollen areas.
How Do Compression Bandages Work?
Compression bandages are designed to apply pressure to the affected limb, supporting the lymphatic system and promoting fluid drainage. When properly applied, these bandages create pressure gradients that encourage lymph flow from swollen tissues back into the lymphatic vessels.
Short-stretch bandages are commonly used in lymphedema bandaging because they offer low-stretch compression. This means they provide high working pressure when muscles contract and low resting pressure when muscles are relaxed. This dynamic pressure helps stimulate lymphatic flow without restricting blood circulation, making them effective for both upper-limb and lower-limb lymphedema.
The Role of Compression in Lymphedema Treatment
Compression therapy plays a crucial role in reducing swelling and maintaining long-term control of lymphedema symptoms. By applying compression wraps and bandages, patients can minimize fluid buildup, reduce discomfort, and improve mobility. Compression treatment also helps prevent complications like fibrosis and infections, common in severe lymphedema.
Medical compression garments like compression stockings and compression sleeves are often used for long-term maintenance, but compression bandages are essential during the intensive phase of treatment. Multilayer compression bandaging, which involves applying multiple layers of compression bandages, provides consistent pressure to help reduce swelling more effectively.
What Types of Compression Garments Are Available for Lymphedema?
Types of Compression Bandages and Their Uses
There are several types of compression bandages used in the treatment of lymphedema, each with unique properties:
- Short-stretch bandages: Provide low-stretch compression, making them ideal for reducing swelling in both upper and lower limbs.
- Two-layer compression systems: Combine a comfort layer with a compression layer to provide adjustable compression for different levels of swelling.
- Multicomponent compression bandaging: This involves applying multiple layers of bandages to provide consistent pressure and support.
Compression wraps and bandages for lymphedema are typically used during the intensive phase of treatment to reduce swelling before transitioning to compression garments like stockings and sleeves.
Benefits of Multilayer Compression
Multilayer compression offers several advantages for patients with lymphedema:
- Enhanced pressure control: Multiple layers of bandages allow for better pressure distribution, ensuring consistent compression across the limb.
- Improved lymphatic flow: Graduated compression helps stimulate lymph flow, reducing swelling and discomfort.
- Long-lasting compression: Multilayer systems maintain their compression pressures longer than single-layer bandages.
Choosing the Right Compression Wrap for Your Needs
Selecting the right compression wrap depends on your lymphedema’s severity and treatment goals. Patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema may benefit from adjustable compression wraps that provide customizable pressure. Inelastic compression wraps offer firm support for leg lymphedema and help maintain fluid balance.
Consulting a lymphedema specialist is crucial to ensure you choose the correct compression type for your condition. A properly fitted compression garment can significantly improve your quality of life and help you manage lymphedema more effectively.
How to Properly Apply and Remove Compression Garments
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying Compression Bandages
- Prepare the skin: Clean and dry the skin to prevent irritation.
- Apply padding: Use soft padding to protect bony areas and ensure even pressure.
- Wrap from the bottom up: Begin wrapping at the foot or hand and move upward, maintaining consistent tension.
- Overlap each layer: Overlap each layer of bandage by about 50% to ensure even compression.
- Secure the bandage: Use tape or clips to secure the bandage without restricting blood flow.
Best Practices for Removing Compression Garments
- Remove slowly: Unwrap the bandage gently to avoid damaging the skin.
- Check for skin changes: Look for signs of irritation, redness, or blisters, which may indicate complications of compression.
- Reapply as needed: Compression bandages should be reapplied daily or as instructed by your lymphedema therapist.
What Are the Benefits of Compression Therapy in Lymphedema Management?
Improving Lymphatic Flow with Compression
Compression therapy can improve lymphatic flow by applying graduated pressure to the limb. This process encourages lymph fluid to move from swollen tissues back into the lymphatic vessels, helping reduce swelling and prevent fluid buildup, improving overall lymph circulation.
Reducing Swelling and Discomfort in Lymphedema Patients
Compression treatment is highly effective in reducing swelling and alleviating the discomfort associated with lymphedema. Compression wraps and bandages allow patients to experience reduced limb volume, improved mobility, and less pain. Regular compression garments can also help maintain these benefits and prevent swelling from returning.
What Are Common Complications of Compression Treatment?
Recognizing Complications of Compression Bandaging
While compression therapy is generally safe, it can sometimes cause complications, mainly if the bandages are misapplied. Common issues include:
- Skin irritation and blisters: Caused by excessive pressure or improper bandaging techniques.
- Restricted blood flow: Compression pressures that are too high can impair circulation, leading to numbness and tingling.
- Allergic reactions: Some patients may be sensitive to the materials used in compression bandages.
How to Address Issues with Compression Garments
- Adjust compression levels: Ensure the compression system is properly adjusted for the correct pressure.
- Use padding: Adding padding can help prevent pressure points and improve comfort.
- Consult a lymphedema specialist: If you experience persistent issues, seek advice from a healthcare professional experienced in lymphedema management.
How Does Compression Bandaging Compare to Other Lymphedema Treatments?
Bandaging vs. Compression Garment Usage
Compression bandaging and compression garments both play essential roles in lymphedema treatment, but they are used at different stages:
- Compression bandaging: Used during the intensive phase to reduce swelling and restore limb volume.
- Compression garments: Worn during the maintenance phase to prevent swelling from returning.
Effectiveness of Compression Devices and Wraps
Compression devices like pneumatic compression pumps can complement bandaging and garments by providing intermittent pneumatic compression. These devices apply controlled pressure to the limb, further promoting lymph flow. Compression pumps offer a more automated approach than short-stretch bandages, but their effectiveness depends on consistent use.
Conclusion
Compression bandaging is a cornerstone of lymphedema management, offering a proven way to reduce swelling, improve lymphatic flow, and enhance mobility. By understanding how compression works and choosing the right type of compression for your needs, you can take control of your lymphedema symptoms and enjoy a better quality of life. Whether you’re using compression bandages, wraps, or garments, proper application and regular use are key to maximizing the benefits of compression therapy.
FAQs
Q: What is the role of compression bandaging in lymphoedema management?
A: Compression bandaging plays a crucial role in the management of lymphoedema by helping to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic drainage. It is often used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance efficacy.
Q: How do I use compression garments for lymphoedema?
A: To effectively use compression garments for lymphoedema, it is important to wear them consistently throughout the day. Ensure that your compression garment is fitted correctly to provide the necessary support and pressure.
Q: How is a compression garment fitted for lymphoedema treatment?
A: A compression garment fitted for lymphoedema treatment should be tailored by a healthcare professional who can assess the severity of your condition and recommend the appropriate size and level of compression needed.
Q: What are lymphoedema compression bandages and how do they work?
A: Lymphoedema compression bandages are specialized bandages designed to apply controlled pressure to swollen limbs. They work by promoting lymphatic flow and preventing the accumulation of lymphatic fluid.
Q: Can wraps and pumps be used in conjunction with compression bandaging?
A: Yes, wraps and pumps can be used alongside compression bandaging to enhance lymphatic drainage. These devices can provide additional compression and assist in the management of swelling.
Q: What is breast cancer-related lymphedema and how can compression help?
A: Breast cancer-related lymphedema is a common condition that can occur after breast cancer treatment. The application of compression, such as lymphoedema compression bandages or garments, can help manage swelling and improve quality of life.
Q: What should I consider when choosing a compression garment for the treatment of breast lymphedema?
A: When choosing a compression garment for treating
Q: Is compression therapy contraindicated for certain conditions?
A: Yes, compression therapy is contraindicated for certain conditions, such as untreated heart failure or infections. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any compression regimen.
Q: What is a bandaging regimen for lymphoedema management?
A: A bandaging regimen for lymphoedema management typically involves applying multi-layer compression bandages to the affected limb. This regimen helps to reduce swelling and prevent fluid buildup.
Q: How often should I wear my compression garment for effective lymphoedema management?
A: For effective lymphoedema management, it is recommended to wear your compression garment for most of the day, usually 20-24 hours, and to follow your healthcare provider’s specific guidelines.