Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of lymphedema and lymphatic diseases. This article offers a detailed review, including a case report, to provide a thorough understanding of lymphedema, its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or someone seeking information about lymphedema, this guide aims to provide valuable insights and practical advice.
What is Lymphedema?
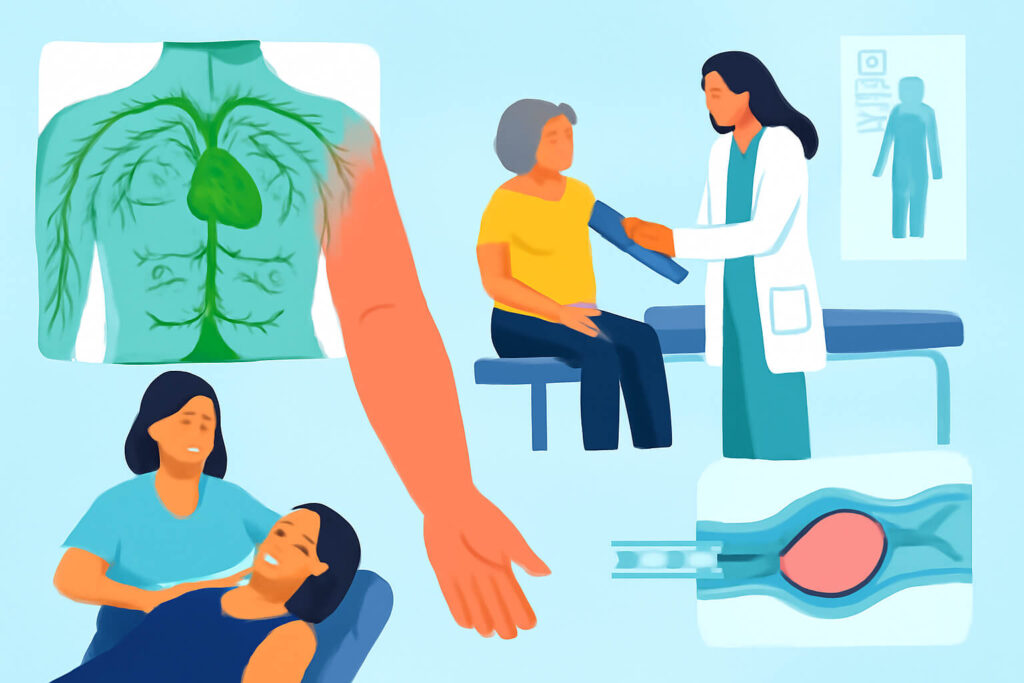
Lymphedema is swelling that generally occurs in an arm or leg due to a blockage in the lymphatic system. This condition arises due to a blockage in the lymphatic system, which prevents lymphatic fluid from draining adequately. The resulting accumulation of excess fluid leads to swelling in the affected area. Lymphedema may be a chronic condition, but effective lymphedema treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. [Insert Internal Link]
Symptoms of Lymphedema
The signs and symptoms of lymphedema can vary, but commonly include swelling in an arm or leg, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, and decreased range of motion. Patients affected by lymphedema may also experience recurring infections, such as cellulitis, due to the compromised lymphatic drainage. Increased swelling and discomfort often prompt individuals to seek treatment right away. Early detection of lymphedema symptoms is crucial for effective management.
Causes of Lymphedema
The cause of lymphedema can be broadly categorized into primary and secondary lymphedema. The underlying reasons for these types of lymphedema differ significantly:
- Primary lymphedema is rare and results from genetic conditions.
- Secondary lymphedema is more common and typically arises from damage to the lymphatic system due to cancer treatment, cancer surgery, or radiation.
Understanding the cause of lymphedema is essential for determining the appropriate treatment approach and to prevent lymphedema where possible.
The Lymphatic System and Its Importance
Overview of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a critical network that helps rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials. It includes the lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, and lymph fluid. The lymphatic system works closely with the vein system to maintain fluid balance. Lymphatic vessels collect lymph fluid, filtering it through lymph nodes, which trap and destroy bacteria and abnormal cells.
Role of the Lymphatic System in Health
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in immune function and fluid balance. It transports lymph, a fluid containing infection-fighting white blood cells, throughout the body. The lymphatic system also helps absorb fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the digestive system. A properly functioning lymphatic system is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing the accumulation of excess fluid. [Insert External Link]
Impact of Cancer on the Lymphatic System
Cancer and cancer treatment can significantly impact the lymphatic system, leading to lymphedema. Cancer cells can spread through the lymphatic system, leading to the involvement of lymph nodes. Surgical removal of lymph nodes or radiation therapy can damage lymphatic vessels, increasing the risk of lymphedema. For example, breast cancer treatment often involves the removal of axillary lymph nodes, which can contribute to developing lymphedema in the affected arm.
Types of Lymphedema
Primary vs. Secondary Lymphedema
Lymphedema is classified into two main types. The characteristics of each type are summarized below:
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Primary Lymphedema | Rare, inherited condition caused by malformations in the lymphatic system affecting the lymphatic vessels or lymph nodes. |
| Secondary Lymphedema | More common, develops as a result of damage to a previously healthy lymphatic system. Common causes include cancer treatment, cancer surgery, radiation therapy, and infections. |
Stages of Lymphedema
Here’s how lymphedema progresses, with early detection vital for symptom management. The stages involve a variety of symptoms, including:
- Stage 0: Subclinical lymphedema may present with heaviness or discomfort, but no visible swelling.
- Stage 1: Reversible swelling that pits with pressure and decreases with elevation of the affected limb.
- Stage 2: Irreversible swelling, tissue fibrosis, and minimal pitting.
- Stage 3: Significant swelling, skin changes like thickening and hardening, and an increased risk of infections.
Understanding these stages is crucial for appropriate lymphedema treatment.
Breast Cancer and Lymphedema
Breast cancer is a significant risk factor for secondary lymphedema due to lymph node removal or radiation. Breast cancer treatment often involves surgery to remove lymph nodes in the axilla (underarm), which can disrupt the lymphatic drainage pathway in the affected area. Radiation therapy can also damage the lymphatic vessels, increasing the risk of developing lymphedema in the arm or breast. The risk of lymphedema is elevated in women who undergo axillary lymph node dissection followed by radiation. Early detection and specialized lymphedema treatment is paramount to reduce swelling and manage symptoms.
Treatment for Lymphedema
Treatment Options Overview
Treatment for lymphedema focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life, as there is currently no cure. Treatment options range from conservative therapies to surgical interventions. Conservative lymphedema treatment typically includes manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy with compression garments, exercises, and meticulous skin care. Surgical treatments are reserved for more severe cases and may involve lymphaticovenous anastomosis or lymph node transfer. The specific treatment plan depends on the stages of lymphedema, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health.
Conservative Lymphedema Treatment
Conservative lymphedema treatment includes manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, exercise, and skin care. Conservative lymphedema treatment is often the first line of defense and is aimed at reducing swelling and preventing progression of the condition. Manual lymphatic drainage is a specialized massage technique that helps redirect lymph fluid around blocked areas, promoting drainage. Compression therapy, using compression garments, supports the lymphatic vessels and prevents fluid accumulation in the affected arm or leg. Regular exercise, particularly gentle aerobic activities and range-of-motion exercises, can also improve lymphatic drainage. Good skin care practices are essential to prevent infections like cellulitis.
Surgical Treatment for Lymphedema
Surgical treatment options include lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) and lymph node transfer. Surgical treatment for lymphedema is considered when conservative measures are insufficient to control symptoms or when the condition significantly impacts the patient’s quality of life. Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) involves connecting lymphatic vessels directly to nearby veins to improve lymph drainage. Lymph node transfer involves transplanting healthy lymph nodes from another part of the body to the affected area to restore lymphatic function. Debulking procedures may be performed to remove excess tissue and reduce swelling in severe cases of lymphedema. Patients with lymphedema secondary to cancer surgery may find these options beneficial.
Case Report: Lymphedema Treatment Outcomes
Patient Background and Diagnosis
In this case report and review, we delve into the details of a patient who presented with secondary lymphedema following breast cancer treatment, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis. The patient, a 62-year-old female, had undergone a mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection five years prior, a common cause of lymphedema. She initially noticed increased swelling in her affected arm, accompanied by a feeling of heaviness. Diagnostic imaging confirmed the presence of lymphedema, indicating lymphatic vessel damage and excess fluid accumulation in the lymphatic system. The patient’s medical history of cancer surgery and cancer treatment was significant in establishing the cause of lymphedema.
Treatment Plan and Execution
The treatment plan for this patient with lymphedema included a multi-faceted approach combining conservative and potentially surgical treatment options. Initially, the focus was on conservative lymphedema treatment, including manual lymphatic drainage to encourage lymphatic fluid movement and reduce swelling in the affected area. Compression therapy, utilizing a compression garment, was implemented to support lymphatic vessel function and prevent the accumulation of excess fluid. The patient was also educated on skin care to prevent cellulitis, a common infection in individuals affected by lymphedema. Regular monitoring ensured the treatment for lymphedema was effectively managing the symptoms. [Insert Internal Link]
Outcomes and Lessons Learned
This case highlights the importance of early intervention and comprehensive treatment. Following several months of consistent lymphedema treatment, the patient experienced a significant reduction in swelling and improved quality of life. The combination of manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy with a compression garment, and diligent skin care proved effective in managing her symptoms of lymphedema. This case highlights the importance of early intervention and comprehensive lymphedema treatment to prevent progression of the condition. It also underscores the need for ongoing monitoring and education to empower patients to manage their lymphedema effectively. If the swelling has not reduced sufficiently after conservative measures, surgical treatment may be considered.
Current Trends in Lymphedema Treatment
Innovative Therapies and Research
Innovative therapies such as lymphatic microsurgery and novel drug therapies are offering hope for improved outcomes. The field of lymphedema treatment is continuously evolving, with innovative therapies and ongoing research offering hope for improved outcomes. One promising area involves lymphatic microsurgery, such as lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA), which connects lymphatic vessels directly to nearby veins to improve lymphatic fluid drainage. Another technique, lymph node transfer, involves transplanting healthy lymph nodes from another part of the body to the affected area to restore lymphatic function. Researchers are also exploring novel drug therapies to reduce inflammation and promote lymphatic vessel regeneration. The aim is to treat lymphedema and eventually cure lymphedema. [Insert External Link]
Future Insights into Lymphedema Management
Future insights into lymphedema management are likely to focus on personalized treatment approaches and early detection strategies. Advances in genetic testing may help identify individuals at increased risk of developing lymphedema, particularly primary lymphedema cases. The use of advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance lymphangiography (MRL), may allow for earlier and more accurate diagnosis of lymphatic vessel dysfunction. Personalized treatment plans may incorporate a combination of conservative therapies, surgical interventions, and targeted drug therapies based on the individual patient’s needs and the cause of lymphedema.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Recap of Treatment Options
In summary, effective lymphedema treatment hinges on a multifaceted approach, tailored to the individual’s specific condition and stages of lymphedema. Conservative therapies, like manual lymphatic drainage and compression therapy with compression garments, remain the cornerstone for reducing swelling and managing symptoms of lymphedema. Surgical treatment options, such as lymphaticovenous anastomosis and lymph node transfer, offer promising avenues for restoring lymphatic function. Future advancements in innovative therapies aim to treat lymphedema. A holistic approach, integrating various treatment options and lifestyle adjustments, is key to improving the quality of life for those affected by lymphedema. The choice of treatment for lymphedema depends on the cause of lymphedema.
Final Advice for Patients
Proactive management, adherence to treatment, healthy lifestyle, and skin care are crucial for improving well-being. For patients grappling with lymphedema, know that proactive management is crucial in improving your well-being. Understand the signs and symptoms of lymphedema and seek treatment right away. Adhere to your prescribed treatment plan diligently, integrating compression garments and manual lymphatic drainage into your routine. Adopt healthy lifestyle choices, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, to support your lymphatic system. Maintain meticulous skin care to prevent cellulitis, and actively participate in support groups to share experiences. By understanding the cause of lymphedema and being proactive, you can treat lymphedema effectively and live a fulfilling life despite the challenges of lymphedema, whether it occurs in the arm or leg.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of lymphedema?
Early signs include heaviness, swelling, decreased flexibility, and pitting edema. Early signs and symptoms of lymphedema can be subtle but are essential to recognize for prompt treatment. These may include a feeling of heaviness or tightness in an arm or leg, swelling in the affected area, and decreased flexibility. You might also notice pitting edema, where pressing on the skin leaves a visible indentation. Some individuals also experience aching or discomfort in the affected limb. Any persistent changes in limb size or texture warrant a visit to a healthcare provider to rule out lymphedema or start treatment right away. Be aware that lymphedema may occur secondary to breast cancer or cancer surgery.
Can lymphedema be cured completely?
Currently, there is no cure, but effective treatment can manage the condition and improve quality of life. Currently, there is no definitive cure for lymphedema, but effective lymphedema treatment can significantly manage the condition and improve the quality of life. Lymphedema treatment focuses on reducing swelling, preventing infection, and maintaining skin integrity. Conservative therapies, such as manual lymphatic drainage and compression therapy with compression garments, can help control symptoms. Surgical treatment options, like lymphaticovenous anastomosis, may offer long-term benefits in select cases. Ongoing research explores innovative approaches to treat lymphedema, but, for now, focus on consistent management and early intervention.
How can I manage lymphedema at home?
Home management involves manual lymphatic drainage, compression, skin care, exercise, and elevation. Managing lymphedema at home involves a combination of self-care practices aimed at reducing swelling and preventing complications. Regularly perform manual lymphatic drainage techniques as instructed by your therapist to encourage lymphatic fluid movement. Wear compression garments as prescribed to support lymphatic vessel function and prevent the accumulation of excess fluid. Practice meticulous skin care to avoid infections like cellulitis. Engage in gentle exercises to promote lymphatic drainage and maintain mobility. Elevate the affected arm or leg whenever possible to reduce swelling. Adhering to these measures can prevent lymphedema from progressing, especially if it is secondary lymphedema.
What lifestyle changes can help treat lymphedema?
Lifestyle changes include maintaining a healthy weight, balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tight clothing. Several lifestyle adjustments can play a crucial role in the lymphedema treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the burden on the lymphatic system and helps manage symptoms. Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support overall health. Engage in regular, low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga to improve lymphatic drainage. Avoid tight clothing or jewelry that can constrict lymphatic vessels and exacerbate swelling. Staying hydrated by drinking enough water helps maintain optimal fluid balance, preventing the swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation throughout the body.
Are there support groups for lymphedema patients?
Yes, support groups offer emotional and practical support. Yes, numerous support groups are available for individuals affected by lymphedema, offering valuable emotional and practical support. These groups provide a safe space for patients to share experiences, exchange tips on managing symptoms, and learn about new lymphedema treatment options. Support groups can be found online or through local hospitals and lymphedema clinics. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of lymphedema can reduce feelings of isolation and empower individuals to navigate their condition more effectively. Sharing experiences can also help prevent lymphedema complications.