Our bodies undergo various changes as we age, and the lymphatic system is no exception. Lymphedema, a condition characterized by fluid retention and swelling, can significantly impact the quality of life for older adults. This article delves into the complexities of lymphedema and provides practical strategies for managing its symptoms as you age, ensuring a more comfortable and active lifestyle.
What is Lymphedema?
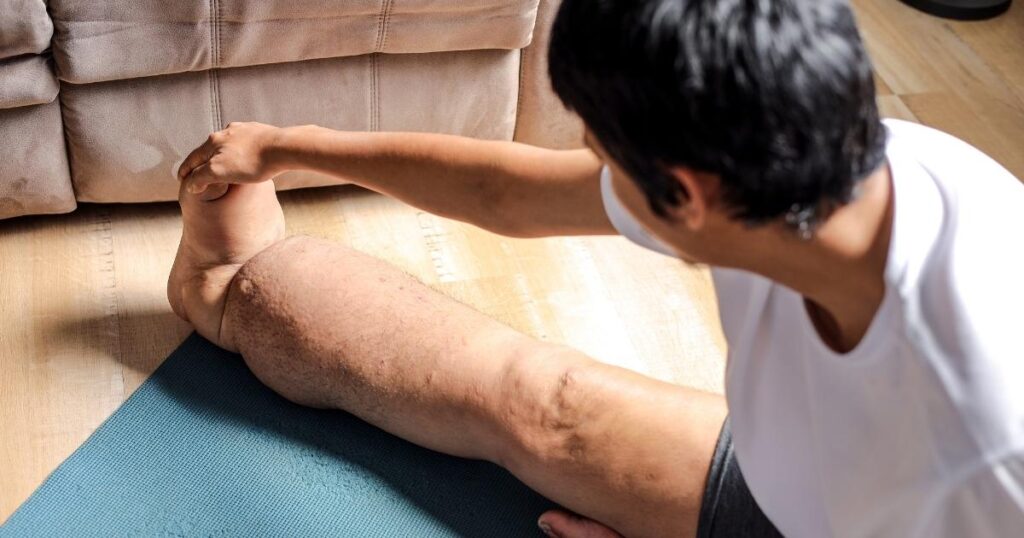
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that occurs when the lymphatic system is impaired, leading to a build-up of lymph fluid in the tissues. The lymphatic system, a crucial part of the immune and circulatory systems, is a network of vessels and lymph nodes that helps drain lymph fluid. When this system doesn’t function properly, lymph accumulates, causing swelling, typically in an arm or leg.
How Lymphedema Occurs
Lymphedema occurs when the lymphatic vessels are damaged or blocked, preventing the normal lymph flow. This blockage can lead to a build-up of fluid in the affected area, causing swelling and discomfort. There are two main types of lymphedema: primary lymphedema and secondary lymphedema. Understanding how lymphedema occurs is crucial for effective management and treatment of lymphedema. [Insert Internal Link]
Age of Onset and Risk Factors
The age of onset for lymphedema varies depending on the type and cause. Primary lymphedema, which is often genetic, may manifest at birth (congenital lymphedema) or later in life (lymphedema tarda). Secondary lymphedema, on the other hand, typically develops due to damage to the lymphatic system from cancer treatment, surgery, or infection. Our lymphatic system may become less efficient as we age, increasing the risk of developing lymphedema.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
Common Symptoms and Their Impact
The symptoms of lymphedema can vary in severity, ranging from mild swelling to severe lymphedema that significantly impairs mobility and quality of life. Common symptoms include swelling in an arm or leg, a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the limb, and skin changes such as thickening or hardening. These symptoms can impact daily activities, making it difficult to perform simple tasks or engage in social activities, affecting patients with lymphedema.
Recognizing Early Signs
Recognizing the early signs of lymphedema is crucial for prompt intervention and management. Early symptoms may include subtle swelling, a feeling of fullness in the limb, or changes in skin texture. It’s essential to pay attention to these signs and seek medical advice if you notice any persistent or unexplained swelling, especially if you have risk factors such as a history of cancer treatment. Early detection and treatment can help prevent the progression of lymphedema. [Insert Internal Link]
Symptoms Related to Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast cancer-related lymphedema is a common complication following breast cancer treatment, particularly after lymph node removal or radiation therapy. The symptoms of lymphedema in this context may include swelling in the arm, hand, or chest area on the affected side. Additionally, patients may experience pain, discomfort, and decreased range of motion in the affected limb, highlighting the challenges of living with lymphedema after breast cancer.
Causes of Lymphedema
Primary vs Secondary Lymphedema
Lymphedema is often classified into primary lymphedema and secondary lymphedema. Primary lymphedema is a rare, inherited condition caused by malformations in the lymphatic system. These malformations disrupt normal lymph flow, leading to swelling in the affected area. Primary lymphedema may manifest at birth (congenital lymphedema) or later in life (lymphedema tarda). It can cause lymphedema in the arm or leg. Understanding the cause of lymphedema is crucial for tailoring appropriate lymphedema treatment strategies.
Injury and Surgery as Triggers
Secondary lymphedema, on the other hand, is more common and develops due to damage to the lymphatic system. Common causes of secondary lymphedema include cancer treatment, surgery, radiation therapy, injury, or infection. Surgery, especially lymph node removal, can disrupt the lymphatic vessels, impairing lymphatic drainage and causing lymphedema to develop. Trauma or injury to the lymphatic system can also lead to lymphatic damage. Addressing wound care is essential in preventing secondary lymphedema.
Understanding Systematic Review Findings
Systematic reviews of lymphedema research provide valuable insights into the symptoms and causes of lymphedema. These reviews analyze data from multiple studies to identify risk factors, effective treatments for lymphedema, and management strategies. Understanding the findings of systematic reviews can help healthcare professionals and patients with lymphedema make informed decisions about their care. It’s important to note that venous insufficiency, which impacts veins, can sometimes be mistaken for lymphedema due to edema.
Management Strategies for Lymphedema
Wound Care Techniques
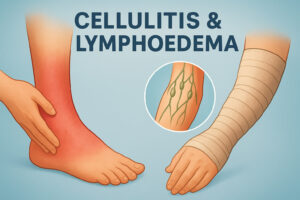
Effective wound care is crucial for managing lymphedema and preventing complications like cellulitis, a skin infection. People with lymphedema are at higher risk of developing diseases in the affected area due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Proper skin care involves keeping the skin clean and moisturized, protecting it from injury, and promptly treating any cuts or abrasions. Regular wound care, combined with other lymphedema treatment modalities, can improve the quality of life for patients with lymphedema.
Compression Therapy Options
Compression therapy is a cornerstone of lymphedema management. Compression garments, such as compression stockings or bandages, help to reduce swelling by supporting the lymphatic vessels and promoting lymph flow. Compression therapy can involve wearing compression stockings during the day and applying compression bandages at night. Pneumatic compression devices may also be used to enhance lymphatic drainage. Consistent compression therapy can significantly reduce lymphedema symptoms and improve limb function, helping patients with lymphedema live more comfortably.
Exercise and Lifestyle Modifications
Regular exercise and lifestyle modifications play a vital role in managing lymphedema. Exercise helps to improve lymph flow and reduce swelling, while lifestyle changes can minimize the risk of exacerbating lymphedema symptoms. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are generally recommended. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tight clothing, and protecting the affected limb from injury are necessary lifestyle modifications. Combining exercise and lifestyle adjustments with other treatments can enhance lymphedema treatment outcomes.
Living with Lymphedema as You Age
Emotional and Psychological Considerations
Living with lymphedema, particularly as you age, presents unique emotional and psychological challenges. The chronic nature of lymphedema, coupled with physical limitations and changes in body image, can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and social isolation for patients with lymphedema. Addressing these emotional and psychological aspects is crucial for overall well-being.
Seeking support from therapists, counsellors, or support groups can provide valuable coping strategies and emotional support for cases of lymphedema. Acknowledging and validating these feelings is essential, recognizing that they are a normal response to living with a chronic condition such as severe lymphedema. [Insert Internal Link] A proactive approach to mental health can significantly improve quality of life while living with lymphedema.
Support Networks and Resources
Building a strong support network is essential for managing lymphedema and enhancing overall quality of life. Support networks can include family members, friends, healthcare professionals, and other individuals with lymphedema. Participating in support groups or online forums can provide a sense of community and shared understanding. These platforms can offer practical advice, emotional support, and encouragement.
Various resources are available to assist individuals with lymphedema, including lymphedema associations, clinics specializing in lymphedema treatment, and educational materials. These resources can provide valuable information about lymphedema treatment options, self-management strategies, and financial assistance programs. Connecting with these networks and resources can empower patients to participate actively in their lymphedema care.
Future Trends in Lymphedema Management
The field of lymphedema management is continually evolving, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for improved treatment options. Future trends include the development of new surgical techniques, such as lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) and vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT), to restore lymphatic drainage. These procedures aim to create new pathways for lymph fluid to flow, reducing swelling and improving limb function. As medicine advances, treatment for lymphedema is becoming less invasive.
Additionally, advancements in imaging techniques, such as indocyanine green (ICG) lymphography, enhance the ability to visualize the lymphatic system and guide treatment decisions. Research into pharmacological agents that can stimulate lymphangiogenesis (forming new lymphatic vessels) is also underway. As our understanding of the lymphatic system deepens, we expect further innovations in lymphedema management, offering hope for more effective and less invasive therapies.
Recap of Key Points
Lymphedema is a chronic condition that can significantly impact the lives of older adults, but effective management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding the causes of lymphedema, recognizing early symptoms, and implementing appropriate treatment modalities are essential to managing this condition. Compression therapy, wound care, exercise, and lifestyle modifications are vital in reducing swelling and preventing complications like cellulitis.
Addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with lymphedema and building a strong support network are also crucial for overall well-being. As research advances, future trends in lymphedema management hold promise for more effective and less invasive therapies. Older adults can live more comfortably and actively by taking a proactive and comprehensive approach to lymphedema care.
Final Advice for Management
Living with lymphedema requires a proactive and consistent approach to self-care. To develop an individualized treatment plan, it is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals, including physicians, lymphedema therapists, and wound care specialists. Regular monitoring of symptoms, adherence to compression therapy, and diligent skin care are crucial for preventing complications. Seeking support from loved ones, support groups, and online resources can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice.
Remember, managing lymphedema is an ongoing process, and setbacks may occur. However, with perseverance, education, and a positive attitude, living well with lymphedema and maintaining an active and fulfilling lifestyle is possible. Stay informed about the latest advances in lymphedema management and advocate for your needs to ensure you receive the best possible care. Living with lymphedema can be a challenge, but by addressing these factors, you can live comfortably.
FAQs About Lymphedema
Below are some frequently asked questions about lymphedema, providing concise and informative answers to address common concerns. These FAQs are designed to enhance understanding and empower individuals to manage lymphedema symptoms actively. The following questions address different aspects of lymphedema management to help improve the quality of life for patients with lymphedema.
Q1: Can lymphedema be cured?
A1: There is currently no cure for lymphedema, but it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. Management strategies, such as compression therapy, exercise, and skin care, can help reduce swelling and improve quality of life.
Q2: Does cancer always cause lymphedema?
A2: No, lymphedema can be caused by various factors, including cancer treatment, surgery, injury, infection, and genetic conditions. While cancer-related lymphedema is common, it is not the only cause.
Q3: Can I exercise if I have lymphedema?
A3: Yes, exercise is beneficial for managing lymphedema. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can help improve lymph flow and reduce swelling. Consult with a lymphedema therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises.
Q4: What type of compression garment should I use?
A4: The type of compression garment depends on the location and severity of lymphedema. Compression stockings, sleeves, or bandages may be recommended. A lymphedema therapist can help determine the most suitable compression option.
Q5: How can I prevent infections in my affected limb?
A5: Prevent infections through diligent skin care, including keeping the skin clean and moisturized, protecting it from injury, and promptly treating any cuts or abrasions. Regular inspection of the skin and nails is also essential to identify any signs of infection early on.