Primary lymphedema is a complex condition that significantly impacts the lymphatic system, leading to various complications for patients. Understanding the genetic factors that contribute to this disease is crucial for appropriate diagnosis, management, and treatment. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of primary lymphedema, the influence of genetics on its progression, and the available treatment options for lymphedema patients.
What is Primary Lymphedema and How Does It Affect the Lymphatic System?
Definition and Causes of Primary Lymphedema
Primary lymphedema is a type of lymphedema that occurs due to congenital malformations in the lymphatic system. It can manifest at different stages in life, with forms like lymphedema praecox, which typically appears during puberty, and primary congenital lymphedema that is evident at birth. The primary cause of lymphedema is often hereditary lymphedema, where genetic mutations lead to underdeveloped or dysfunctional lymphatic vessels, causing fluid accumulation in tissues. The condition can lead to swelling, particularly in the lower limbs, and may be associated with lymphatic anomalies, which further complicate the management of primary lymphedema.
The Function of the Lymphatic System in Health
The lymphatic system plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and the absorption of dietary fats. It consists of a network of lymphatic vessels that transport lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body. When the lymphatic system is functioning correctly, it helps remove excess interstitial fluid, proteins, and waste products from tissues. However, in patients with primary lymphedema, the lymphatic system is compromised, leading to fluid retention and swelling, primarily in the affected limbs. This dysfunction can cause significant physical discomfort and may result in further complications such as infections.
How Primary Lymphedema Differs from Secondary Lymphedema
Understanding the distinction between primary and secondary lymphedema is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Primary lymphedema arises from congenital defects in the lymphatic system, often influenced by genetics, while secondary lymphedema is usually caused by external factors such as surgery, radiation therapy, or trauma that damages lymphatic vessels. Patients with secondary lymphedema may not have the same hereditary predisposition as those with primary lymphedema, making the management and treatment approaches differ significantly. While both conditions lead to similar symptoms, the underlying causes and potential treatment options vary considerably.
What Are the Genetic Factors Contributing to Primary Lymphedema?
The Role of Hereditary Lymphedema and Family History
Genetics plays a crucial role in the development of primary lymphedema, particularly in hereditary cases. A family history of lymphedema can indicate a genetic predisposition, as certain genetic syndromes are associated with this condition. Familial lymphedema, often linked to specific genetic mutations, highlights the importance of understanding one’s family history when diagnosing and treating primary lymphedema. In many cases, patients with a known family history may experience a more severe form of lymphedema, indicating that genetics can significantly influence disease severity and progression.
Types of Genetic Mutations Associated with Lymphedema
Multiple genetic mutations have been identified in association with primary lymphedema. For instance, mutations in the FLT4 gene, which encodes for the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3), can lead to lymphatic vessel malformations and dysfunction. Additionally, mutations in other genes, such as the CCBE1 gene, are linked to various lymphedema syndromes. Understanding these genetic factors is essential for developing targeted therapies and improving outcomes for patients with primary lymphedema.
Understanding Milroy Disease and Meige Disease
Milroy disease and Meige disease are two well-known forms of primary lymphedema that illustrate the genetic basis of this condition. Milroy disease is characterized by congenital lymphedema, typically manifesting in infancy or early childhood, and is often caused by mutations in the FLT4 gene. In contrast, Meige disease, sometimes referred to as familial lymphedema, typically presents later in life and is associated with a milder lymphedema phenotype. Both conditions highlight the genetic underpinnings of lymphedema and underscore the critical role that genetics plays in the management of primary lymphedema.
How is Genetic Testing Used in the Management of Primary Lymphedema?
What to Expect from Genetic Testing for Lymphedema
Genetic testing has become increasingly important in the management of primary lymphedema. Patients seeking to understand the underlying causes of their condition can undergo genetic testing to identify specific mutations associated with hereditary lymphedema. This testing may include sequencing of relevant genes, providing valuable insights into the genetic basis of the patient’s lymphedema. With advances in genetic testing technology, patients can expect a more comprehensive understanding of their condition, which can guide treatment decisions and inform family planning.
Interpreting Genetic Test Results for Patients
Interpreting the results of genetic testing can be a complex process. A positive result indicating a known mutation associated with primary lymphedema can help confirm the diagnosis and provide a clearer prognosis for the patient. Conversely, negative results do not always rule out the presence of lymphedema, as there may be unidentified mutations or other contributing factors. Therefore, patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to understand the implications of their genetic test results and how they relate to their lymphedema management.
The Impact of Genetic Testing on Treatment Decisions
The results of genetic testing can significantly impact treatment decisions for patients with primary lymphedema. For instance, identifying specific genetic mutations can help clinicians tailor treatment strategies that address the underlying cause of the condition. Additionally, understanding the hereditary nature of lymphedema can guide patients in making informed choices about lifestyle modifications and preventive measures that may reduce the risk of disease progression. Genetic testing not only aids in the management of primary lymphedema but also enhances knowledge about potential complications and associated conditions.
What Are the Symptoms and Signs of Primary Lymphedema?
Common Symptoms in Patients with Primary Lymphedema
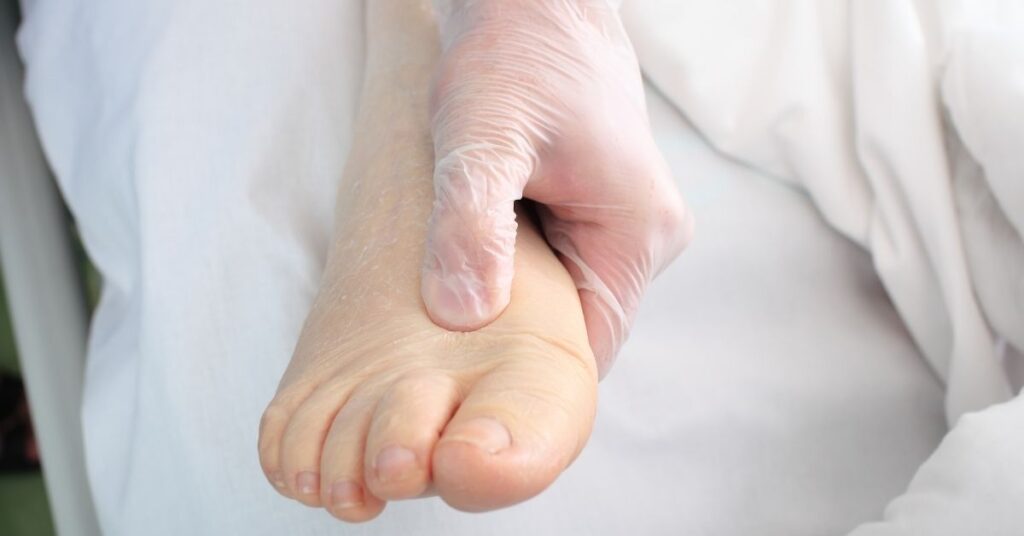
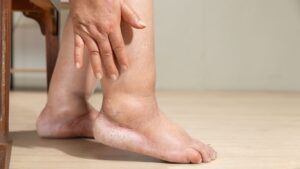
Patients with primary lymphedema typically present with swelling in the affected limbs, most commonly the lower limbs. This swelling, known as lymphedema, may be accompanied by discomfort, heaviness, and a sensation of tightness in the affected area. Over time, persistent swelling can lead to changes in skin texture, increased susceptibility to infections, and the development of lymphedema-related complications. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective management of primary lymphedema.
Identifying Lymphatic Anomalies and Malformations
Identifying lymphatic anomalies and malformations is essential for understanding the severity and potential complications of primary lymphedema. Healthcare professionals may conduct imaging studies to visualize the lymphatic vessels and assess their function. Patients with congenital lymphedema may exhibit distinct malformations in their lymphatic system, which can help in diagnosing the type of primary lymphedema present. Early identification of these anomalies can significantly improve the management of the condition and prevent further complications.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Lymphedema
Patients experiencing symptoms of lymphedema should seek medical advice promptly. Early consultation with a healthcare provider can lead to timely diagnosis and intervention, which is crucial for effective management. If swelling in the limbs increases, is accompanied by pain or redness, or if there is a sudden change in the condition of the skin, medical attention should be sought immediately. Understanding when to seek help is essential for preventing long-term complications associated with primary lymphedema.
How Can Patients Manage Primary Lymphedema Effectively?
Available Treatment Options for Lymphedema Management
The management of primary lymphedema involves a multifaceted approach that may include compression therapy, physical therapy, and manual lymphatic drainage. Compression garments are commonly used to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic drainage. Additionally, patients may benefit from specialized exercises designed to enhance lymphatic flow and reduce the risk of complications. It is essential for patients to work with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and condition.
The Importance of Lifestyle Changes and Support
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle changes play a vital role in the management of primary lymphedema. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing skin care can help minimize symptoms and prevent exacerbations. Support groups and educational resources can also provide valuable insights and emotional support for lymphedema patients. Engaging with a community of individuals facing similar challenges can foster resilience and empower patients in their management journey.
Emerging Therapies and Research in Lymphedema Treatment
Ongoing research into emerging therapies for primary lymphedema holds promise for improving patient outcomes. Innovations such as lymphatic surgery, which aims to restore lymphatic vessel function, and the exploration of gene therapy approaches are at the forefront of lymphedema research. These advancements could potentially offer new hope for patients with primary lymphedema, allowing for more effective management strategies and improved quality of life. Staying informed about new developments in lymphedema treatment is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike.
FAQS
Q: What is primary lymphedema and how does it relate to genetic factors?
A: Primary lymphedema is a condition that occurs due to congenital abnormalities of the lymphatic system, often attributed to genetic causes. These abnormalities can affect lymphatic endothelial cells and lead to insufficient lymphatic drainage, resulting in swelling, particularly in the lower limbs.
Q: What are the clinical features of primary lymphedema?
A: The clinical features of primary lymphedema include swelling of the affected limb, which may be present at birth or develop during puberty or adulthood. Other signs and symptoms can include a feeling of heaviness, recurrent infections, and skin changes in the affected area.
Q: How is the diagnosis of primary lymphedema made?
A: The diagnosis of primary lymphedema typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging studies to assess lymphatic channels. A diagnostic algorithm for primary lymphatic issues may also be employed to confirm the diagnosis.
Q: Can primary lymphedema occur in the absence of family history?
A: Yes, while many cases of primary lymphedema have a genetic basis, it can occur sporadically without a known family history. Genetic mutations are often involved, but not all patients with lymphedema have identifiable hereditary links.
Q: What are the treatment options for primary lymphedema?
A: The treatment of primary lymphedema focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Options include compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, exercise, and in some cases, surgical interventions to improve lymphatic drainage.
Q: What is lymphedema distichiasis and how does it relate to primary lymphedema?
A: Lymphedema distichiasis is a genetic syndrome that includes lymphedema as one of its manifestations. It is associated with the presence of an extra row of eyelashes and often involves primary lymphedema, typically affecting the lower limbs.
Q: Is lymphedema of the lower limb more common than in other areas?
A: Yes, lymphedema of the lower limb is more prevalent than in other areas of the body. This is largely due to the greater volume of lymphatic tissue and the higher incidence of primary lymphatic conditions affecting the legs.
Q: What are the potential causes of secondary lymphedema?
A: Secondary lymphedema can occur due to various causes, including trauma, infections, and cancer treatments such as surgery or radiation that damage lymphatic vessels. Secondary lymphedema following breast cancer is a well-known example.
Q: What role do genetic factors play in the progression of lymphedema?
A: Genetic factors can significantly influence the severity and progression of lymphedema. In cases of hereditary lymphedema, certain genetic mutations can lead to abnormal lymphatic development, which may worsen symptoms over time and affect treatment outcomes.