Lymphedema is a chronic condition that can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected. Understanding how to track and record lymphedema symptoms is essential for effective management and treatment. In this article, we will explore the signs and symptoms of lymphedema, how it is diagnosed, its causes, treatment options, and how to prevent complications associated with this condition.
What are the Common Signs and Symptoms of Lymphedema?
What are the early symptoms of lymphedema?
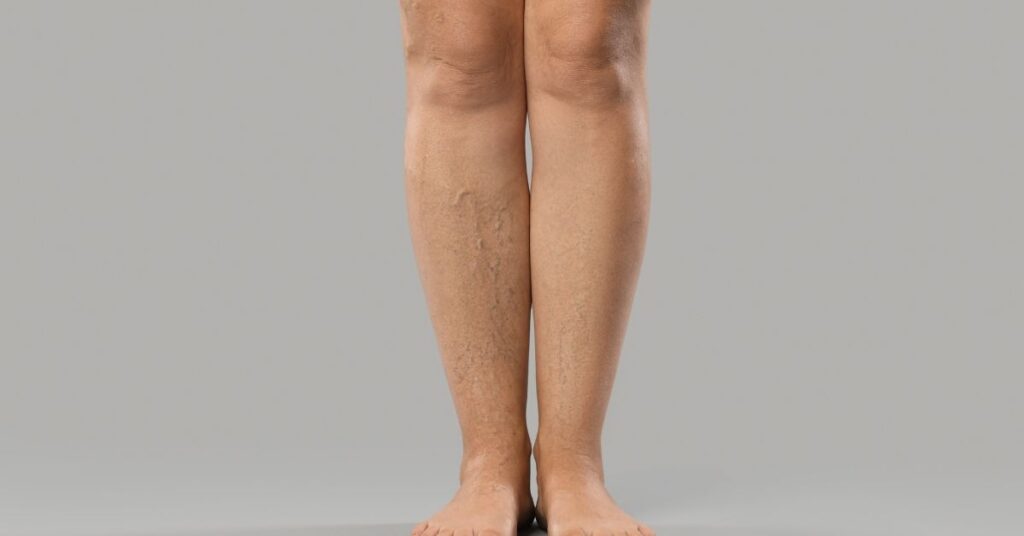
Early symptoms of lymphedema often include a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected arm or leg. Individuals may notice subtle changes, such as a slight swelling in the affected area, which can progressively worsen over time. These initial signs are crucial as they may indicate the onset of lymphedema. If left unmonitored, the swelling can develop into more noticeable symptoms, which may include pain, discomfort, and skin changes. Recognizing these early symptoms is vital for prompt intervention and to prevent further complications.
How does swelling occur in lymphedema?
Swelling in lymphedema occurs due to a buildup of lymph fluid in the tissues, resulting from damage to the lymphatic system. This system is responsible for draining excess fluid, waste, and proteins from the body’s tissues. When lymph vessels are compromised, whether due to surgery, radiation, or other factors, the normal flow of lymph fluid is disrupted. Consequently, this disruption can lead to the accumulation of lymph fluid in the interstitial spaces, causing edema or swelling in the affected arm or leg. Understanding the mechanics behind this swelling can help individuals better track their symptoms and seek appropriate treatment.
What areas of the body are most affected by lymphedema?
Lymphedema typically affects the extremities, most commonly the arms and legs. However, it can also occur in other areas such as the abdomen or genitals. Individuals who have undergone cancer treatment, particularly breast cancer treatment involving lymph node removal or radiation therapy, are at a higher risk of developing lymphedema in the upper limbs. Conversely, those with issues related to the lower extremities may experience lymphedema in their legs or feet. The affected area can vary from person to person, but it is essential to monitor any changes diligently.
How is Lymphedema Diagnosed?
What tests are used to diagnose lymphedema?
Diagnosing lymphedema typically involves a series of clinical evaluations and tests. Healthcare professionals may conduct a physical examination to assess swelling and other symptoms of lymphedema. They may also utilize imaging tests such as lymphoscintigraphy, which involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material to visualize lymphatic flow, or MRI and ultrasound to determine the extent of lymph fluid buildup. These diagnostic tools help healthcare providers formulate an accurate lymphedema diagnosis and tailor an appropriate treatment plan.
How do healthcare professionals diagnose lymphedema symptoms?
Healthcare professionals diagnose lymphedema symptoms by carefully assessing the patient’s medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination. They will look for the characteristic signs of lymphedema, including swelling and any changes in skin texture. Healthcare providers will ask about the patient’s history of cancer treatment, lymph node removal, or any other potential causes of lymphedema. By considering all these factors, professionals can establish a clear diagnosis and determine the most effective management strategies.
What role do lymph nodes play in diagnosing lymphedema?
Lymph nodes play a critical role in diagnosing lymphedema as they are central to the functioning of the lymphatic system. When lymph nodes are removed during cancer surgery or damaged by radiation, the pathway for lymph fluid drainage can be obstructed, leading to swelling. The assessment of lymph node involvement can help healthcare professionals understand the cause of the lymphedema and its severity. In some cases, the presence of swollen lymph nodes may indicate an ongoing issue with lymphatic drainage that requires further investigation and treatment.
What Causes Lymphedema and What Types Exist?
What are the primary causes of lymphedema?
The primary causes of lymphedema include damage to the lymphatic system, which can occur due to various reasons. Cancer treatments, such as surgery and radiation, are significant contributors, as they can disrupt lymph fluid flow. Other causes include infections, trauma, and congenital conditions that affect lymphatic vessel development. Understanding these causes is essential for individuals to recognize their risk of lymphedema and take proactive measures to manage their health.
What is the difference between primary and secondary lymphedema?
Lymphedema is classified into two types: primary and secondary lymphedema. Primary lymphedema is a rare condition that arises from congenital malformations in the lymphatic system, often present at birth or developing during puberty. In contrast, secondary lymphedema is the more common form, resulting from damage to the lymphatic system due to external factors, such as cancer treatment, infections, or injuries. Recognizing the distinction between primary and secondary lymphedema is vital for determining the appropriate treatment and management strategies.
How can cancer treatment contribute to the development of lymphedema?
Cancer treatment can significantly contribute to the development of lymphedema, particularly in patients who undergo surgery to remove lymph nodes or receive radiation therapy. These interventions can lead to damage to the lymphatic system, resulting in impaired lymph fluid drainage. For example, breast cancer treatment often involves the removal of axillary lymph nodes, which can elevate the risk of developing lymphedema in the affected arm. Understanding this relationship can help patients monitor their symptoms and seek timely interventions to mitigate the risk of lymphedema.
What are Effective Treatment Options for Lymphedema?
What are the common lymphedema treatment and management strategies?
Effective treatment options for lymphedema typically encompass a combination of approaches aimed at reducing swelling and managing symptoms of lymphedema. Common strategies include compression therapy, where specialized garments or bandages are used to promote lymph fluid drainage. Manual lymphatic drainage, a technique performed by a certified lymphedema therapist, can also help stimulate lymphatic flow. Other management strategies may include exercise, skin care, and education on self-care practices to empower individuals to take charge of their condition.
How does compression therapy help manage lymphedema symptoms?
Compression therapy is an essential component of lymphedema management. By applying external pressure to the affected arm or leg, compression garments promote the reabsorption of lymph fluid and enhance lymphatic drainage. This therapy helps to reduce swelling and prevent further accumulation of lymph fluid, thereby alleviating discomfort. It is crucial for individuals to work with a healthcare professional to ensure they are using the correct type of compression and wearing it appropriately for maximum effectiveness.
What role does a certified lymphedema therapist play in treatment?
A certified lymphedema therapist plays a pivotal role in the treatment and management of lymphedema. These specialists are trained in various techniques, including manual lymphatic drainage and education on self-management strategies. They conduct thorough assessments to tailor a treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of each individual. By collaborating with a certified lymphedema therapist, patients can receive personalized care that promotes optimal outcomes and helps them effectively manage their condition.
How Can You Prevent Lymphedema Complications?
What are the potential complications of untreated lymphedema?
Untreated lymphedema can lead to several complications, including recurrent infections, skin changes, and mobility issues. The buildup of lymph fluid can create an environment conducive to infections, leading to cellulitis or lymphangitis. Additionally, untreated lymphedema may result in a decrease in range of motion and increased discomfort, impacting daily activities. Recognizing the potential complications associated with untreated lymphedema underscores the importance of early detection and management to maintain overall health and well-being.
How can proper tracking of symptoms help prevent complications?
Proper tracking of lymphedema symptoms can play a crucial role in preventing complications. By maintaining a daily log of swelling, pain levels, and any other noticeable changes, individuals can identify patterns and triggers that exacerbate their condition. This information is valuable when discussing symptoms with healthcare providers, as it can help guide treatment decisions and interventions. Consistent tracking empowers individuals to take an active role in their lymphedema management and can lead to timely interventions that prevent further complications.
What lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing lymphedema?
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing lymphedema or managing existing symptoms. Regular exercise, particularly activities that promote lymphatic flow, can be beneficial. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good skin care, and avoiding infections are essential preventive measures. Staying well-hydrated and managing stress can also support overall lymphatic health. By adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce their risk of lymphedema and improve their quality of life.
FAQS
Q: What is lymphedema and how is it diagnosed?
A: Lymphedema is a condition characterized by swelling, usually in the arms or legs, caused by a blockage in the lymphatic system. A lymphedema diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and may include imaging tests to assess the lymphatic system.
Q: What are the different types of lymphedema?
A: There are primarily two types of lymphedema: primary lymphedema, which is a hereditary condition, and secondary lymphedema, which often develops as a result of cancer or cancer treatment. Each type of lymphedema has its own causes and risk factors.
Q: How can I track my lymphedema symptoms effectively?
A: Keeping a detailed journal can help track lymphedema signs and symptoms. Note any swelling, pain, or changes in skin texture, and record any triggers or treatments used. This information can be valuable for your lymphedema specialist during consultations.
Q: What are common signs and symptoms of lymphedema?
A: Common signs and symptoms of lymphedema include swelling in the affected limb, a feeling of heaviness or tightness, restricted range of motion, and changes in skin texture. If you notice these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.
Q: What are the complications of lymphedema?
A: Complications of lymphedema can include chronic infections, skin changes, and lymphangiosarcoma, a rare type of cancer. Proper management and lymphedema therapy can help mitigate these risks and improve quality of life.
Q: Is there a cure for lymphedema?
A: Currently, there is no cure for lymphedema. However, treatments for lymphedema, such as compression therapy, exercise, and lymphedema surgery, can help manage symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening.
Q: How can lifestyle changes help prevent lymphedema?
A: To help prevent lymphedema, maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and avoid infections. It’s also important to take precautions if you are at risk for lymphedema, especially after surgery or cancer treatment.
Q: What is the role of a lymphedema specialist?
A: A lymphedema specialist is trained to assess and manage lymphedema. They can provide personalized treatment plans that may include lymphedema therapy, education on self-care techniques, and support for patients with lymphedema.
Q: How do I know if my lymphedema is advancing?
A: Monitoring changes in swelling, pain intensity, and any new symptoms can indicate whether lymphedema is advancing. If you notice increased swelling or other complications of lymphedema, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.